Chapter Two INTRODUCTION TO DATA AND INFORMATION Nian
advertisement

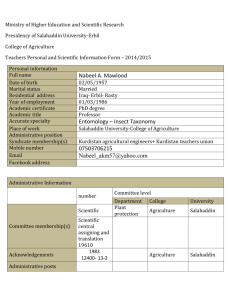
College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Chapter Two INTRODUCTION TO DATA AND INFORMATION Nian Khidr Aziz, MSc. Dept. of Electrical Engineering College of Engineering Salahaddin University-Erbil nian.aziz@su.edu.krd Mobile #: 07504492622 ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 1. Introduction to Computer Systems Computer systems are found everywhere. Computers have become almost as common as televisions. But what is a computer? A computer is a system made of two major components: hardware and software. The computer hardware is the physical equipment. The software is the collection of programs (instructions) that allow the hardware to do its job. ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 2. Computers An electronic device which is capable of receiving information (data) in a particular form and of performing a sequence of operations in accordance with a predetermined set of procedural instructions (program) to produce a result in the form of information or signals ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Computers; More Definitions Computers are devices perform pre-specified mathematical manipulation. or, Computers are millions of electronic switches make ON and OFF according to pre-specified procedures. These procedures are called PROGRAMS. ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 3. Data and Information Data can be defined as a representation of facts (examples: Signs, Sounds, characters, numbers, photos, …etc.), concepts or instructions in a formalized manner which should be suitable for communication, interpretation, or processing by human or electronic machine. Data is represented with the help of characters like alphabets (A-Z,a-z), digits (0-9) or special characters(+,,/,*,<,>,= etc.), or any other symbols. Data is not information. Data requires interpretation to become information. Information is organized or classified data which has some meaningful values for the receiver. ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 4. Analogue and Digital Data Analog and digital signals are used to transmit information. In analog technology, information is translated into electric waves of varying amplitude. In digital technology, information is translated into binary format (zero or one) ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 5. Numbering Systems A number system is a way to represent numbers. We are used to using the base-10 number system, which is also called decimal (1-9). But there are other number systems like: Base-16 (hexadecimal, 0 –F) Base-2 (binary, 0,1). ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 6. Binary Number Digits 1 digits, 21 0 1 2 digits, 22 00 000 01 10 001 010 11 011 100 101 110 3 digits, 23 111 0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 4 digits, 24 ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 7. Binary Coding Binary to Decimal Decimal to Binary Binary to Hexadecimal Digit 8 Digit 4 Digit 2 Digit 1 12 = 1 1 0 0 6= 0 1 1 0 Binary 1111 0001 1100 1001 Hex F 1 C 9 1111000111001001 B= F1C9 H ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 8. Binary, Hex, Decimal ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 9. Data Types Numeric (example: INT, Decimal) Binary (example: bit, BYTE, WORD) Text (String) (example: CHAR, VARCHAR, LONGTEXT) Memo (long text or numbers) Time (example: HH:MM:SS) Date (example: YYYY:MM:DD) Currency (example $, ID) Video Audio ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering 10. File In Computer Literature, file is record of data in a storage medium. Files are created by Software (Applications) , which define the file type. ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Thank You Questions? ©2015 , Nian Khidr Aziz, Salahaddin University-Erbil, www.su.edu.krd