Measuring voltage ratio of a transformer with CRO
advertisement

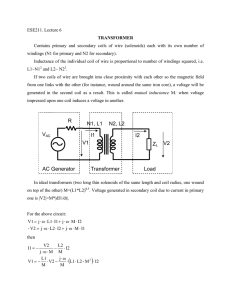
Class: E Name: 18e ( ) Date: 18e Measuring voltage ratio of a transformer with CRO Apparatus You will use the CRO to measure the voltage ratio of a transformer and compare it with the turns ratio. • 1 pair of double C-cores with clip • 1 10-turn coil • 1 25-turn coil • 1 low voltage power supply (d.c./a.c.) • 1 CRO Procedure 1 (a) Make up a transformer consisting of a 10-turn (primary) coil, a 25-turn (secondary) coil, a pair of double C-cores and clip. (b) Connect one lamp each to the primary and secondary coils. (c) Apply 1 V a.c. from a low voltage power supply across the 10-turn coil (Fig 18e-1). power supply secondary coil (25 turns) primary coil (10 turns) time base switched off Fig 18e-1 Compare the brightness of the two lamps. The lamp connected to the secondary coil is brighter than the lamp connected to the primary coil. 2 (a) Connect the CRO across the primary coil (10-turn coil). (b) Switch off the time base. (c) Measure the length of the vertical trace on the screen. © Oxford University Press 2006 New Physics at Work (Second Edition) 45 18e Note: If a dual-trace CRO is used, connect channel 1 across the 10-turn coil and channel 2 across the 25-turn coil to display the primary and secondary waveforms at the same time. The specimen results were obtained with Y-gain setting = 1 V/cm. Class: 3 Name: ( ) Date: (a) Next connect the CRO across the secondary coil (25-turn coil). (b) Measure the length of the vertical trace on the screen. Results: Length of (primary) vertical trace lp = 3.0 cm Length of (secondary) vertical trace ls = 7.0 cm Vp lp = = Vs ls 2.33 Np = Ns 2.50 Voltage ratio of transformer Turns ratio of transformer Discussion If the power supply is switched to 1 V d.c., what would happen to the two lamps? Explain briefly. The lamp connected to the secondary coil is off but the lamp connected to the primary coil is on. It is because no current can be induced in the secondary coil if the current in the primary coil is a smooth d.c. For a.c. operation, compare the voltage ratio with the turns ratio of the transformer. Account for any difference between the two ratios. The voltage ratio is slightly smaller than the turns ratio. It is because the transformer used is not a practical transformer with high efficiency. The voltages in the primary and secondary coils of a transformer depend on turns ratio of the coils. For an ideal transformer: primary voltage = secondary voltage 46 New Physics at Work (Second Edition) number of turns in primary coil number of turns in secondary coil © Oxford University Press 2006