electromagnetic compatibility and cables 1-shielding 2
advertisement
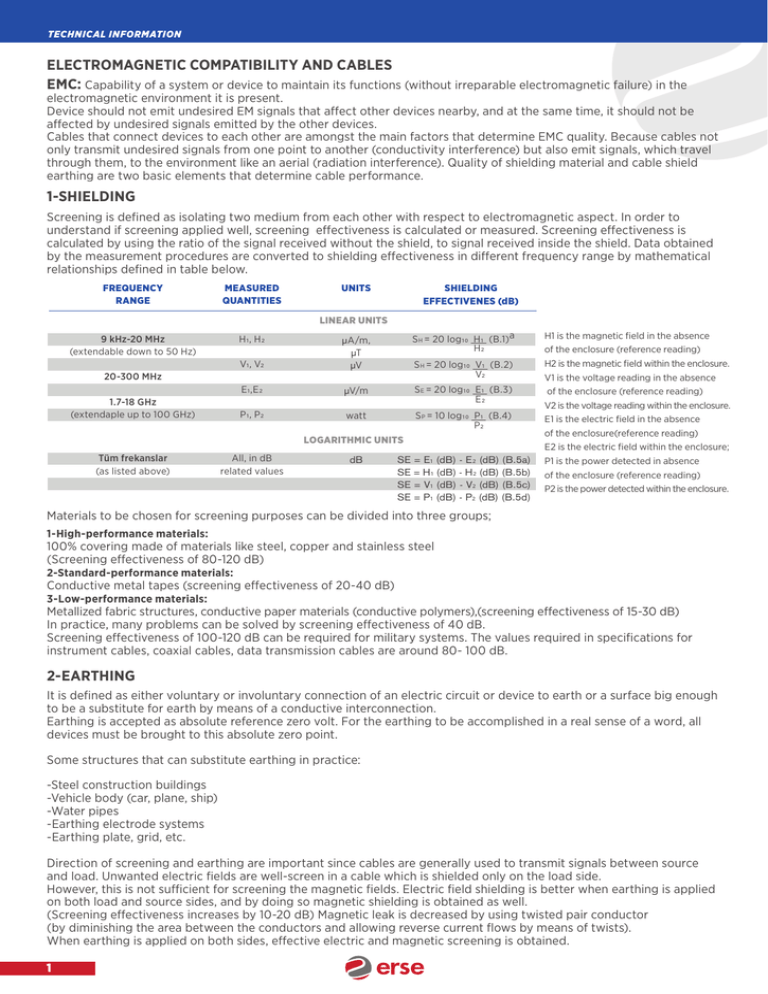
TECHNICAL INFORMATION ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY AND CABLES EMC: Capability of a system or device to maintain its functions (without irreparable electromagnetic failure) in the electromagnetic environment it is present. Device should not emit undesired EM signals that affect other devices nearby, and at the same time, it should not be affected by undesired signals emitted by the other devices. Cables that connect devices to each other are amongst the main factors that determine EMC quality. Because cables not only transmit undesired signals from one point to another (conductivity interference) but also emit signals, which travel through them, to the environment like an aerial (radiation interference). Quality of shielding material and cable shield earthing are two basic elements that determine cable performance. 1-SHIELDING Screening is defined as isolating two medium from each other with respect to electromagnetic aspect. In order to understand if screening applied well, screening effectiveness is calculated or measured. Screening effectiveness is calculated by using the ratio of the signal received without the shield, to signal received inside the shield. Data obtained by the measurement procedures are converted to shielding effectiveness in different frequency range by mathematical relationships defined in table below. FREQUENCY RANGE MEASURED QUANTITIES UNITS SHIELDING EFFECTIVENES (dB) LINEAR UNITS 9 kHz-20 MHz (extendable down to 50 Hz) S H = 20 log10 H1 (B.1)a H2 H1 is the magnetic field in the absence V1, V2 µA/m, µT µV S H = 20 log10 V1 (B.2) V2 H2 is the magnetic field within the enclosure. E1,E2 µV/m S E = 20 log10 E1 (B.3) E2 H1, H2 20-300 MHz 1.7-18 GHz (extendaple up to 100 GHz) P1, P2 S P = 10 log10 P1 (B.4) P2 watt LOGARITHMIC UNITS Tüm frekanslar (as listed above) All, in dB related values dB SE = E1 (dB) - E2 (dB) (B.5a) SE = H1 (dB) - H2 (dB) (B.5b) SE = V1 (dB) - V2 (dB) (B.5c) SE = P1 (dB) - P2 (dB) (B.5d) of the enclosure (reference reading) V1 is the voltage reading in the absence of the enclosure (reference reading) V2 is the voltage reading within the enclosure. E1 is the electric field in the absence of the enclosure(reference reading) E2 is the electric field within the enclosure; P1 is the power detected in absence of the enclosure (reference reading) P2 is the power detected within the enclosure. Materials to be chosen for screening purposes can be divided into three groups; 1-High-performance materials: 100% covering made of materials like steel, copper and stainless steel (Screening effectiveness of 80-120 dB) 2-Standard-performance materials: Conductive metal tapes (screening effectiveness of 20-40 dB) 3-Low-performance materials: Metallized fabric structures, conductive paper materials (conductive polymers),(screening effectiveness of 15-30 dB) In practice, many problems can be solved by screening effectiveness of 40 dB. Screening effectiveness of 100-120 dB can be required for military systems. The values required in specifications for instrument cables, coaxial cables, data transmission cables are around 80- 100 dB. 2-EARTHING It is defined as either voluntary or involuntary connection of an electric circuit or device to earth or a surface big enough to be a substitute for earth by means of a conductive interconnection. Earthing is accepted as absolute reference zero volt. For the earthing to be accomplished in a real sense of a word, all devices must be brought to this absolute zero point. Some structures that can substitute earthing in practice: -Steel construction buildings -Vehicle body (car, plane, ship) -Water pipes -Earthing electrode systems -Earthing plate, grid, etc. Direction of screening and earthing are important since cables are generally used to transmit signals between source and load. Unwanted electric fields are well-screen in a cable which is shielded only on the load side. However, this is not sufficient for screening the magnetic fields. Electric field shielding is better when earthing is applied on both load and source sides, and by doing so magnetic shielding is obtained as well. (Screening effectiveness increases by 10-20 dB) Magnetic leak is decreased by using twisted pair conductor (by diminishing the area between the conductors and allowing reverse current flows by means of twists). When earthing is applied on both sides, effective electric and magnetic screening is obtained. 1 TECHNICAL INFORMATION COAXIAL CABLE ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTIC 1) CHARACTERISTIC IMPEDANCE The most general feature of coaxial cables is impedance. It does not depend on length. It depends on cable size and insulation material. It is expressed in Ohms. Coaxial cables are generally produced as 50 ohm, 75 ohm and 93 ohm cables. A simple formula to determine impedance of a coaxial cable; Z0 = 183 x Vp x log (D/d) ohm Z0 = Characteristic Impedance Vp = Velocity of propagation D = Dielectric (Insulation) Diameter d = Conductor inner diameter 2) CAPACITY (pF/m) It is electric energy accumulated by insulation material, and depends on conductor, insulation and dielectric constant of the insulation material C: 2x x8,85x pF/m ln (D/d) r: Dielectric Constant Dielectric Constant 1 2,3 1,5 1,95 2,15 MATERIAL AIR PE SOLID FOAM PE PTFE FEP d= L (C x VOP) 3) VELOCITY OF PROPAGATION Cable’s velocity of diffussion is equal to the ratio of the velocity of a signal inside the cable to the velocity of light. Example: While the velocity of diffussion in the solid PE insulated cable is 66%, in Foam PE it increases to 87%. This feature can also be shown as delay. Vp: 1 delay: 1,0167164X r r 4) ATTENUATION (dB/100mt) All transmission lines, or coaxial cables, experience loses. In other words, there is the decrease in magnitude of a signal as it travels through any transmitting medium, such as a cable, circuitry or free air. These loses, termed attenuation, will decrease where the efficiency of the line, which in turn limits the power capabilities. They are measured as a ratio or as the logarithm of a ratio (decibel). Those losses, termed attenuation, In order to express cable attenuation performans we need to introduce attenuation consant which is a rating for a cable or other transmitting medium, which is the relative rate of amplitude decrease of voltage or current in the direction of travel. It is measured in decibels per unit length of cable. 5) RETURN LOSS (RL) Cable sizes, quality of insulation material and mistakes made during cable laying influence the characteristic impedance. Any single disorder or mistake results in reflections. Return loss is equal to the ratio of output signal to the reflected signal. 2 TECHNICAL INFORMATION HARMONISED CABLES SYMBOLS HARMONISED CABLES Regulation designation H: A: Harmonised regulation Approved national design Rated Voltage 01 03 05 07 11 100/100 V 300/300 V 300/500 V 450/750 V 600/1000 V Insulation material V V2 V3 B E X R S Polyvinylchloride (PVC) PVC, up to +90°C PVC for low temperatures Ethylenepropylene (EPR) Polyethylene XLPE (cross-linked PE) Rubber Silicone Rubber Sheath or braiding materials V V2 V3 V5 R N Q C4 J T Polyvinylchloride (PVC) PVC, up to +90°C PVC for low temperatures PVC, oil resistance Rubber Cloroprene rubber Polyurethane Screen of copper wire braiding Glass fibre braiding Textile braiding Special construction features H H2 H6 H8 Flat divisible cables Flat non-divisible cables Flat non-divisible cables, for elevators Spiral cables Conductor type U R K F H D E Single-wire round conductor Multiple-wire round conductor Fine stranded (for cables for fixed installations) Fine strands (for flexible cables) Extra fine strands Fine stranded for welding cables Extra fine strands for wilding cables Protective earthing conductor X G 3 Without protective earthing conductor With protective earthing conductor TECHNICAL INFORMATION CABLE SYMBOLS ACCORDING TO VDE STANDARDS TELECOMMUNICATIONS CABLES AND WIRES A G J L S JE Li Outdoor cable Mining cables Installation cables and wires Multicore cables Switchboard cables - Signal cable Installation cables and wire for industrial electronic Stranded wire conductor Insulation material: P Y 2Y 3Y 5Y 6Y 7Y 02Y O2YS Paper insulation Polyvinylchloride PVC Polyethylene (PE) PS, polystrene PTFE FEP ETFE Foam PE, cellular polyethylene Foam-skin PE Structral Features: F Yv 2Yv (C) (L) (St) D (Z) M Mz L LD W (L)2Y b c E (T) STIII STI ST F PİMF TİMF VİMF Bd Lg Cable core essambly with filling PVC reinforced sheath PE reinforced sheath Screen of Copper wire braid Screen of plastic-coated aluminium tape Metal foil screen Concentric layer of copper wires Steel wire braid Lead sheath Lead sheath with added hardener Aluminium sheath, smooth Corrugated Aluminium sheath Corrugated steel sheath Laminated sheath Armouring Protective covering of jute PVC tape Support wire for aerial cable Star quads in local cables Star quads for larger distances Star quads for use of phantom circuits Star quads for railway use Pair in metal foil Triad in metal foil Quad in metal foil Laid up in bundles Laid up in layers 4 TECHNICAL INFORMATION CABLE SYMBOLS ACORDING TO VDE STANDARD POWER CABLES Conductor type: N (N) VDE - standard On the basis of VDE - standard Conductor material: Cu A Copper Aluminium Insulation material: H Y 2Y 2X Halogen Free (HFFR) Polyvinylchloride (PVC) Polyethylene (PE) Cross-linked PE (XLPE) Concentric conductor, screen: C CW CE S SE Concentric copper conductor Consentric copper conductor, in wave conal formation Consentric copper conductor over each core Copper screen Copper screen and conductive layer Armouring: F R B Armour of flat wires Armour of round wires Steel tape armour Sheath material: Y 2Y PVC PE Protective earthing conductor: J O With protective conductor Without protective earthing conductor Conductor type: r... s... o... re Rm V 5 Round conductor Sector-shaped conductor Oval-shaped conductor Single-wire conductor Multiple-wire conductor Compact conductor TECHNICAL INFORMATION COMPARISON OF FIRE TESTS EN, IEC, DIN VDE AND BS FLAME RETARDANCE EN PART CLAUSE TITLE 60332 1 1 1 2 2 2 Test for vertical flame propagation for a single insulated wire or cable - Apparatus Test for vertical flame propagation for a single insulated wire or cable - Procedure for 1 kW pre-mixed flame Test for vertical flame propagation for a single small insulated wire or cable - Procedure for diffusion flame EN PART CLAUSE TITLE 60332 3 10 3 3 3 3 3 21 22 23 24 25 Test for vertical flame spread of vertical mounted bunched wires or cables - Apparatus Category A F/R Category A Category B Category C Category D IEC BS DIN VDE 60332-1-1 EN 60332-1-1 0482-332-1-1 1-2 1-2 332-2-1 2-2 2-2 332-2-2 BS DIN VDE 60332-3-10 EN 60332-3-10 0482-332-3-10 3-21 3-22 3-23 3-24 3-25 3-21 3-22 3-23 3-24 3-25 332-3-21 332-3-22 332-3-23 332-3-24 332-3-25 BS DIN VDE 60754-1 EN 50267-1 0482-267-1 1 2-1 267-2-1 2 2-2 267-2-2 2 2-3 267-2-3 IEC BS DIN VDE 61034-1 EN 61034-1 0482-1034-1 2 2 1034-2 IEC ZERO HALOGEN / CORROSIVINESS OF COMBUSTION GASES EN PART 50267 1 2 CLAUSE 1 2 2 2 3 TITLE Test on gases evolved during combustion of materials from cables - Apparatus Procedures: Determination of the amount of halogen acid gas Procedures: Determination of degree of acidity of gases for materials by measuring pH and conductivitiy Procedures: Determination of degree of acidity of gases for cables by determination of the weighted average of pH and conductivity IEC SMOKE DENSITY EN PART 61034 1 2 CLAUSE TITLE Measurement of smoke density of cables burning under defined conditions - Apparatus Measurement of smoke density of cables burning under defined conditions - Procedure 6 TECHNICAL INFORMATION PERFORMANCE TEST OF USED ON TO ERVİTAL® CABLES 1- IEC 60332-1, VDE 0482-332-1-2, EN 60332-1-2, BS EN 60332-1-2 TEST FOR RESISTANCE TO VERTICAL FLAME DIFFUSION OF A SINGLE INSULATED CONDUCTOR OR CABLE 1 KW PRE-MIXED FLAME A sample cable of 600 mm will be fixed vertically in a metal chamber with exposed front side. A propane gas burner will be mounted in order to obtain a 45° angle with axis of the sample cable. The test time is dependent on the cable diameter. If the sample does not burn, or if the flame extinguishes itself, the test shall be deemed as successful. OUTER DIAMETER (mm) FLAME DURATION SEC D<25 25<D<75 50<D<75 75<D 60 ± 2 120 ± 2 240 ± 2 480 ± 2 2- IEC 60332-3-22, VDE 0482-60332-3-22, EN 60332-3-22, BS EN 60332-3-22 (CAT A) TEST FOR VERTICAL FLAME DIFFUSION ON VERTICALLY FIXED WIRE OR CABLE BUNDLES The test samples are mounted on a steel ladder. The total number of test pieces in the test sample shall be that number required to provide a nominal total volume of non-metallic material of 7 l/m of test sample. The steel ladder is placed on the rear part of a test chamber having a with of 1 m, a depth of 2 m and a height of 4 m. The test chamber should be ventilated by an air vent. The test flame is applied on the sample cable for 40 min. The test is passed if the flames extinguish on their own and no part of the samples is damaged over a length of 2,5 m. 3- IEC 61034-2, VDE 0482-1034-2, EN 61034-2, BS EN 61034-2 MEASUREMENT OF SMOKE DENSITY OF CABLES BURNT UNDER CERTAIN CONDITIONS The volume of test chamber is 3m³ . The measurement system consists of a light source (a standard 100w halogen lamp) and a selenium or silicon photo-electric cell, both installed at a height of 2,15m. A rectangular tray will be filled with alcohol. A ventilator is used to ensure the distribution of smoke. The length of the test samples is 1m. The number of test samples depends on the outer diameter. The samples should be attached horizontally above the tray which is filled with alcohol. The ventilator is started and the alcohol is ignited. Light intensity is recorded by a plotter which is connected to the photocell. The test is passed if the level of light transmission does not exceed the values given in the following table during the test. OUTER DIAMETER (mm) NUMBER OF SAMPLE 1 2 3 N1 N2 7 LIGHT TRANSMISSION >60% >60% >60% >60% >60% N1 = 45 D N2= 45 3D TECHNICAL INFORMATION 4- IEC 60754-1-2, VDE 0482-267-2-1, 2 and 3, EN 50267-2-1,2 and 3, BS EN 50267-2-1,2 and 3 DETERMINATION OF HALOGEN ACID GAS, MEASUREMENT OF PH AND CONDUCTIVITY This test indirectly allows measuring emission of corrosive gas by insulation and sheath compounds. It is possible to measure small quantities of halogens during measurement of the pH-value and the conductivity. In a 500-600 mm long furnace, at least 1g of insulation or sheath compound should be heated up to a temperature of 935 °C. Air flow will ensure that combustion gases pass through a bottle filled with purified water. The test is passed if the pH-values is lower than 4,3 and the electrical conductivity does not exceed 100 S/cm. 5- IEC 60331-21/23 TEST ON INSULATION INTEGRITY This test determines insulation integrity under fire conditions. Cables which are tested according to these standards are marked as FE 180. 1,2 m long sample cable suitable for electrical connection, having outer sheath and other jackets, which are removed at both ends. The prepared sample will be fixed horizontally about 75mm above the burner. The samples will be connected (one 2 A fuse for each conductor) to a voltage source and will be tested with their rated voltage source, is slightly curled in order to prevent electrical contact. The burner is ignited and heated up to a temperature of at least 750°C by means of a thermocouple. The sample will be connected to electrical supply and placed into the flames. The sample will be tested during a period of 180. If none of the 2A fuses has blown during the test period, the test is passed. 6- IEC 60331-1/2, VDE 0482-200, BS EN 50200, BS 8434-1,2 SPECIFICATION FOR PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS FOR CABLES REQUIRED TO MAINTAIN CIRCUIT INTEGRITY UNDER FIRE CONDITIONS This test is applied to cables having resident fire retardant properties used in emergency circuits such as alarm, lighting and communication. A single piece of cable is attached to a special fibre glass wall with cable at the minimum bending radius. It is burned with the 830°C propane burner. The rated tension values of the cable are applied on the conductors during the test. Every five minutes a mechanical shock of 25 kg is applied to the wall the cable is attached to. The tension values must be preserved during the test. 8 TECHNICAL INFORMATION GENERAL FEATURES OF CABLES WITH 450/750/V NOMINAL VOLTAGE AND THERMOPLASTIC INSULATION AND SHEATH TS 9756 HD 21.1 S4 VDE 281/1 INSULATION : Insulation should be made up of the thermoplastic material stated for each type of cable TI 1, TI 2, TI 4, and TI 5 types are suitable for maximum continuous temperature 70 ºC and PVC insulated cables. TI3 type is suitable for maximum continuous conductor temperature 90 ºC and PVC insulated cables. INSULATION FEATURES TEST UNIT TYPE OF COMPOSITION °C °C minute Max. continuous conductor temperature Max. temperature for short circuit conditions Min. thermal stability at 200°C TI 1 TI 2 TI 3 TI 4 TI 5 70 160 - 70 160 - 90 160 240 70 160 - 70 160 - SHEATH: Sheathing should be made up of the thermoplastic material stated for each type of cable. -TM 1 type for PVC sheathed cables in fixed installation. -TM 2 type for PVC sheathed twistable cables. -TM 3 type for PVC sheathed heat resistant cables that conductor temperature does exceed 90 ºC -TM 5 type (H05VV5-F,H05VVC4V5-K) PVC sheathed and oil resistant cables. -TM 6 type for PVC sheathed cables resistant to low temperature. APPLICATION: Sheath is extruded as a homogenous layer; a-Over the core for single core cables. b-Over the core groups ad filler or (if exists) over the inner sheath. FEATURES OF SHEATH TEST Plunge into mineral oil Temperature of oil Plunge time Min. thermal stability at 200°C UNITE °C hours minute TYPE OF COMPOSITION TM 1 TM 2 TM 3 TM 4 TM 5 TM 6 - - 240 - 90±2 70x24 - - ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES TEST Voltage applied on semi-finished cables (aa) Voltage applied on cores (aa) Wall thickness up to 0,60mm Wall thickness above 0,60mm Long term resistance of insulation to direct current Temperature of water Voltage applied 9 UNITE RATED VOLTAGE OF CABLES 300/300V 300/500V 450/750V V V V V 2000 2000 2500 1500 2000 1500 2000 2000 °C V 60±5 220 60±5 220 60±5 220 TECHNICAL INFORMATION CABLE CORE COLOURS ACCORDING VDE 0293, TS HD 308 S2 Cables and cordons with green-yellow core CORES COLOURSb CORE NUMBER Protector 3 4 4a 5 Green-Yellow Green-Yellow Green-Yellow Green-Yellow Energy Blue Blue Blue Brown Brown Brown Brown Black Black Black Grey Grey a: Only for determined applications b: Common center conductor that not insulated like metallic sheath, armour or screen wires did not take attention as a core in this table. Common center conductor is described with self position, because of this it is not required to describe with a colour Cables and cordons are without green-yellow core CORES COLOURSb CORE NUMBER Protector 2 3 a 3 4 5 Blue Blue Blue Blue Energy Brown Brown Brown Brown Brown Black Black Black Black Grey Grey Grey Black a: Only for determined applications b: Common center conductor that not insulated like metallic sheath, armour or screen wires did not take attention as a core in this table. Common center conductor is described with self position, because of this it is not required to describe with a colour Single core cables: Following colours should be used for insulation of sheathed single core cables and insulated conductors: -Two colours from green-yellow compound for protective conductor. -Blue is for neutral conductor black, brown or grey are recommended for phase conductors. Other colour can use for determined applications. 10 TECHNICAL INFORMATION PAS 5308 PART-1 MULTIPAIR COLOUR CODE 1- Identification of not individually pairs -Two pair collectively screened cables are in quad formation colour coded in rotation black, blue,green, brown -Single triple will be blue , black, green All other cables up to 50 pairs conform to the coding of following table: PAIR NO A WIRE B WIRE PAIR NO 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 BLACK BLACK BLUE BLACK BLUE GREEN BLACK BLUE GREEN BROWN BLACK BLUE GREEN BROWN WHITE BLACK BLUE GREEN BROWN WHITE RED BLACK BLUE GREEN BROWN BLUE GREEN GREEN BROWN BROWN BROWN WHITE WHITE WHITE WHITE RED RED RED RED RED ORANGE ORANGE ORANGE ORANGE ORANGE ORANGE YELLOW YELLOW YELLOW YELLOW 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 2- Individually screened pairs - Screened pairs are identified by a numbered tape under the separator tapes of the pair screens - Each pair has one black and one blue core 11 A WIRE WHITE RED ORANGE BLACK BLUE GREEN BROWN WHITE RED ORANGE YELLOW BLACK BLUE GREEN BROWN WHITE RED ORANGE YELLOW GREY BLACK BLUE GREEN BROWN WHITE B WIRE YELLOW YELLOW YELLOW GREY GREY GREY GREY GREY GREY GREY GREY VIOLET VIOLET VIOLET VIOLET VIOLET VIOLET VIOLET VIOLET VIOLET TURQUOISE TURQUOISE TURQUOISE TURQUOISE TURQUOISE TECHNICAL INFORMATION PAS 5308 PART-2 MULTIPAIR COLOUR CODE 1- Identification of not individually screened pairs -Two pair collectively screened cables are in quad formation colour coded in rotation: Black, blue, green, brown -Single triple will be blue, white, orange All other cables up to 50 pairs conform to the coding of following table: PAIR NO A WIRE B WIRE PAIR NO 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 WHITE WHITE WHITE WHITE WHITE RED RED RED RED RED BLACK BLACK BLACK BLACK BLACK YELLOW YELLOW YELLOW YELLOW YELLOW WHITE/BLUE WHITE/BLUE WHITE/BLUE WHITE/BLUE WHITE/BLUE BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 A WIRE RED/BLUE RED/BLUE RED/BLUE RED/BLUE RED/BLUE BLUE/BLACK BLUE/BLACK BLUE/BLACK BLUE/BLACK BLUE/BLACK YELLOW/BLUE YELLOW/BLUE YELLOW/BLUE YELLOW/BLUE YELLOW/BLUE WHITE/ORANGE WHITE/ORANGE WHITE/ORANGE WHITE/ORANGE WHITE/ORANGE ORANGE/RED ORANGE/RED ORANGE/RED ORANGE/RED ORANGE/RED B WIRE BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY 2- Individually screened pairs - Screened pairs are identified by a numbered tape under the separator tapes of the pair screens - Each pair has one black and one blue core 3-Identification of cores Core 1 to 40: Yellow with black printed number core 41 to 80: Black with white printed number 12 TECHNICAL INFORMATION COLOUR CODE BASED ON DIN 47100 (Without colour repetition) 13 CORE NO COLOURS FOR THE CORES CORE NO COLOURS FOR THE CORES 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 WHITE BROWN GREEN YELLOW GREY PINK BLUE RED BLACK VIOLET GREY-PINK RED-BLUE WHITE-GREEN BROWN-GREEN WHITE-YELLOW YELLOW-BROWN WHITE-GREY GREY-BROWN WHITE-PINK PINK-BROWN WHITE-BLUE BROWN-BLUE WHITE-RED BROWN-RED WHITE-BLACK BROWN-BLACK GREY-GREEN YELLOW-GREY PINK-GREEN YELLOW-PINK GREEN-BLUE 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 YELLOW-BLUE GREEN-RED YELLOW-RED GREEN-BLACK YELLOW-BLACK GREY-BLUE PINK-BLUE GREY-RED PINK-RED GREY-BLACK PINK-BLACK BLUE-BLACK RED-BLACK WHITE-BROWN-BLACK YELLOW-GREEN-BLACK GREY-PINK-BLACK RED-BLUE-BLACK WHITE-GREEN-BLACK BROWN-GREEN-BLACK WHITE-YELLOW-BLACK YELLOW-BROWN-BLACK WHITE-GREY-BLACK GREY-BROWN-BLACK WHITE-PINK-BLACK PINK-BROWN-BLACK WHITE-BLUE-BLACK BROWN-BLUE-BLACK WHITE-RED-BLACK BROWN-RED-BLACK BLACK-WHITE TECHNICAL INFORMATION COLOUR CODE ACCORDING TO 47100 (With colour repetition from core no 45 and above ) CORE NO COLOURS FOR THE CORES CORE NO COLOUR FOR THE CORES 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 WHITE BROWN GREEN YELLOW GREY PINK BLUE RED BLACK VIOLET GREY-PINK RED-BLUE WHITE-GREEN BROWN-GREEN WHITE-YELLOW YELLOW-BROWN WHITE-GREY GREY-BROWN WHITE-PINK PINK-BROWN WHITE-BLUE BROWN-BLUE WHITE-RED BROWN-RED WHITE-BLACK BROWN-BLACK GREY-GREEN YELLOW-GREEN PINK-GREEN YELLOW-PINK GREEN-BLUE 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 YELLOW-BLUE GREEN-RED YELLOW-RED GREEN-BLACK YELLOW-BLACK GREY-BLUE PINK-BLUE GREY-RED PINK-RED GREY-BLACK PINK-BLACK BLUE-BLACK RED-BLACK WHITE BROWN GREEN YELLOW GREY PINK BLUE RED BLACK VIOLET GREY-PINK RED-BLUE WHITE-GREEN BROWN-GREEN WHITE-YELLOW YELLOW-BROWN WHITE-GREY 14 TECHNICAL INFORMATION COLOUR CODE ACCORDING TO DIN 47100 (Twisted pairs) COLOUR OF THE PAIRS PAIR NUMBER 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 15 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 a-Core b-Core WHITE GREEN GREY BLUE BLACK GREY-PINK WHITE-GREEN WHITE-YELLOW WHITE-GREY WHITE-PINK WHITE-BLUE WHITE-RED WHITE-BLACK GREY-GREEN PINK-GREEN GREEN-BLUE GREEN-RED GREEN-BLACK GREY-BLUE GREY-RED GREY-BLACK BLUE-BLACK BROWN YELLOW PINK RED VIOLET RED-BLUE BROWN-GREEN YELLOW-BROWN GREY-BROWN PINK-BROWN BROWN-BLUE BROWN-RED BROWN-BLACK YELLOW-GREY YELLOW-PINK YELLOW-BLUE YELLOW-RED YELLOW-BLACK PINK-BLUE PINK-RED PINK-BLACK RED-BLACK TECHNICAL INFORMATION J-Y(St)Y…Lg FIRE ALARM AND COMMUNICATION CABLES Colour Code According To DIN VDE 0815 2 paired installation cables are stranded as star guad 1. Pair: a-core Red b-core Black 2. Pair: a-core White b-core Yellow 4 and multi-paired installation cables: a-core of first pair in each layer is Red, other pairs are White b-core: Blue, Yellow, Green, Brown, Black in continuous repetation In order: From outside to inside b-wire Blue Yellow Green Brown Black Pair Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 J-H(St)H…Bd FEATURES BASIC COLOURS OF PAIRS Pair Number a-core b-core 1 Blue Red 2 Grey Yellow 3 Green Brown Pair Number Sub-group 1. Layer 2 4 8 12 16 20 32 40 52 Star guad Pair 4 Pairs Sub-unit 4 Pairs Sub-unit 4 Pairs Sub-unit 4 Pairs Sub-unit 4 Pairs Sub-unit 4 Pairs Sub-unit 4 Pairs Sub-unit 1 4 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 White Black 2. Layer 7 8 10 16 TECHNICAL INFORMATION INDOOR TYPE TELEPHONE CABLES (VBV & VBV-K / HBH & HBH-K / VBAPV & VBAPV-K / HBAPH & HBAPH-K / PDV & PDV-K) INSULATION COLOURS OF GROUP WITH TEN PAIRS COLOURS OF INSULATION GROUP NR. A-WIRE B-WIRE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 WHITE WHITE WHITE WHITE WHITE RED RED RED RED RED BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY GROUP NR. COLOURS OF IDENTIFICATION TABE BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY WHITE-BLUE WHITE-ORANGE WHITE-GREEN WHITE-BROWN WHITE-GREY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 CORE ARRANGEMENT 17 GROUP NR. CORE ARRANGEMENT 1. Layer 2. Layer 2. Layer 1 2 3 4 6 10 20 30 50 100 200 PAIR PAIR PAIR PAIR PAIR PAIR 10 PAIR Sub-group 10 PAIR Sub-group 10 PAIR Sub-group 10 PAIR Sub-group 50 PAIR Sub-group 7 7 - 7 7 - - TECHNICAL INFORMATION GENERAL STRUCTURE OF PD-PAP TELEPHONE CABLES (STAR QUAD) WHITE BLACK WHITE RED BLACK RED BLUE BLUE QUAD (1) ORANGE ORANGE QUAD (2) WHITE WHITE BLACK RED BLACK GREEN GREEN QUAD (3) RED BROWN BROWN QUAD (4) 1 WHITE 2 5 BLACK RED GREY GREY QUAD (5) 4 3 18 TECHNICAL INFORMATION INDENTIFICATION TABE OF GROUP AND SUB GROUP GROUP NO COLOURS OF IDENTIFICATION TABE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN GREY WHITE-BLUE WHITE-ORANGE WHITE-GREEN WHITE-BROWN WHITE-GREY 20 Pair core (2 Sub-group) 30 Pair core (3 Sub-group) 50 Pair core (5 Sub-group) 100 Pair core (10 Sub-group) 50 PAIRS IDENTIFICATION TABE OF UNIT AND SUBGROUP GROUP NO 1 2 3 4 19 COLOURS OF IDENTIFICATION TABE BLUE ORANGE GREEN BROWN 200 Pair core (20 Sub-group) (4x50 Pair group) TECHNICAL INFORMATION METRIC SIZES STANDARD FLEXIBLE CONDUCTORS VDE 0295; IEC 60228; EN 60228 CLASS OF CONDUCTOR 5 6 5 6 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 CROSS-SECTIONAL AREA mm 2 STRANDING NO.WIRES-SIZE WIRES mm NOMINAL DIAMETER OF CONDUCTOR mm NOMINAL WEIGHT kg/km 0,05 0,22 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,65 0,75 0,75 1,0 1,25 1,35 1,5 2,0 2,5 3,0 4,0 4,5 6 8 10 16 25 35 50 70 95 120 150 185 240 300 400 500 7X0,10 7X0,20 7X0,30 16X0,20 28X0,15 151X0,065 14X0,25 24X0,20 42X0,15 32X0,20 40X0,20 19X0,30 30X0,25 28X0,30 50X0,25 44X0,30 56X0,30 65X0,30 84X0,30 120X0,30 80X0,40 128X0,40 200X0,40 280X0,40 400X0,40 356X0,50 485X0,50 120X0,30 765X0,50 944X0,50 1225X0,50 1530X0,50 2034X0,50 1768X0,60 0,3 0,6 0,9 0,93 0,94 0,98 1,1 1,14 1,12 1,34 1,47 1,5 1,6 1,87 2,09 2,4 2,61 2,8 3,21 3,75 4,2 5,3 7,1 8,5 10,3 12,4 14,5 16,0 18,0 20,0 23,0 26,0 30,0 33,5 0,5 2,0 4,5 4,5 4,5 4,5 5,8 6,7 6,7 8,9 11,1 12,0 13,4 17,8 22,3 27 36 40 53 71 89 142 223 312 445 623 846 1068 1335 1647 2136 2670 3560 4450 20 TECHNICAL INFORMATION CONSTRUCTION OF THE CU WIRE CONDUCTOR VDE 0295; IEC 60228; EN 60228 Cross Section 0,035 0,05 0,08 0,09 0,14 0,25 0,34 0,38 0,5 0,75 1,0 1,5 2,5 4 6 10 16 25 35 50 70 95 120 150 185 240 300 400 500 630 21 Multiple Wire Round Conductor Vde 0295 Class 2 Column1 Multi Stranded Wires Standard Construction 7x0,30 7x0,37 7x0,43 7x0,52 7x0,67 7x0,85 7x1,05 7x1,35 7x1,70 7x2,13 7x2,52 19x1,83 19x2,17 19x2,52 37x2,03 37x2,27 37x2,52 61x2,24 61x2,50 61x2,89 61x3,23 91x2,97 Column 2 Finely Stranded Wires VDE 0295 Class5 Column 3 VDE 0295 Class56 Column4 Column 5 Column 6 Column 6 7x0,08 7x0,25 7x0,27 7x0,30 7x0,37 7x0,43 7x0,52 19x0,41 19x0,52 19x0,64 49x0,51 49x0,65 84x0,62 133x0,58 113x0,69 189x0,69 259x0,69 336x0,67 392x0,69 494x0,69 627x0,70 790x0,70 2228x0,60 18x0,10 14x0,15 19x0,15 12x0,20 16x0,20 24x0,20 32x0,20 30x0,25 50x0,25 56x0,30 84x0,30 80x0,40 128x0,40 200x0,40 280x0,40 400x0,40 356x0,50 485x0,50 614x0,50 765x0,50 944x0,50 1225x0,50 1530x0,70 2034x0,50 1768x0,60 18x0,10 32x0,10 42x0,10 21x0,15 28x0,15 42x0,15 56x0,15 84x0,15 140x0,15 224x0,15 192x0,20 320x0,20 512x0,20 800x0,20 1120x0,40 705x0,30 990x0,30 1340x0,30 1690x0,30 2123x0,30 1470x0,40 1905x0,40 2385x0,40 - 7x0,124 18x0,10 32x0,10 42x0,10 48x0,10 64x0,10 96x0,10 128x0,10 192x0,10 320x0,10 512x0,10 768x0,10 128x0,10 2048x0,10 3200x0,10 4410x0,10 - 14x0,07 24x0,07 36x0,07 65x0,07 88x0,07 100x0,07 131x0,07 195x0,07 260x0,07 392x0,07 615x0,07 1040x0,07 1560x0,07 2600x0,07 4116x0,07 6370x0,07 9100x0,07 - 26x0,05 72x0,05 128x0,05 174x0,05 194x0,05 256x0,05 384x0,05 512x0,05 768x0,05 128x0,05 - Extra fine stranded wires Standard construction TECHNICAL INFORMATION CLASS 2 STRANDED CONDUCTORS FOR SINGLE AND MULTI-CORE CABLES Nominal cross-sectional area mm2 Circular The number of conductor wires Circular compressed Formatted Cu Al Cu 1 2 3 4 0,5 0,75 1 1,5 2,5 4 6 10 16 25 35 50 70 95 120 150 185 240 300 400 500 630 800 1200 1400a 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 19 19 19 37 37 37 37 61 61 61 91 91 b b b b b b 7 7 7 7 19 19 19 37 37 37 37 61 61 61 91 91 b b b b b b 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 12 15 18 18 30 34 34 53 53 53 53 b b b b b b 1600 1800a 2000 2500 Al Cu Al 5 6 7 6 6 6 6 6 6 12 15 15 15 30 30 30 53 53 53 53 b b b b b b 6 6 6 6 12 15 18 18 30 34 34 53 53 53 b b b b b b b 6 6 6 6 12 15 15 15 30 30 30 53 53 53 b b b b b b b Conductor resistance at 20 ° C Bare copper Tinned copper Aluminum and Ω / km Ω / km aluminum alloy conductorsΩ / km 8 36 24,5 18,1 12,1 7,41 4,61 3,08 1,83 1,15 0,727 0,524 0,387 0,268 0,193 0,153 0,124 0,0991 0,0754 0,0601 0,047 0,0366 0,0283 0,0221 0,0151 0,0129 0,0113 0,0101 0,009 0,0072 9 10 36,7 24,8 18,2 12,2 7,56 4,7 3,11 1,84 1,16 0,754 0,529 0,391 0,27 0,195 0,154 0,126 0,1 0,0762 0,0607 0,0475 0,0369 0,0286 0,0224 0,0151 0,0129 0,0113 0,0101 0,009 0,0072 3,08 1,91 1,2 0,868 0,641 0,443 0,32 0,253 0,206 0,164 0,125 0,1 0,0778 0,0605 0,0469 0,0367 0,0291 0,0247 0,0212 0,0186 0,0165 00149 0,0127 a) These sizes are non-preferred. Other non-preferred sizes are recognized for some specialized applications but are not within the scope of this TS EN 60228 standard. b) The minimum number of wires for these sizes is not specified. These sizes may be constructed from 4, 5 or 6 equal segments (Milliken). c) For stranded aluminium alloy conductors having the same nominal cross-sectional area as an aluminium conductor the resistance value should be agreed between the manufacturer and the purchaser. 22 TECHNICAL INFORMATION CONDUCTOR RESISTANCE VALUES ACCORDING TO VDE 0295 EN 60228/IEC 60228 Conductor Dimension Nominal cross-sectional area mm2 0,05 0,08 0,09 0,14 0,20 0,25 0,34 0,50 0,75 1 1,50 2,50 4 6 10 16 25 35 50 70 95 120 150 185 240 300 400 500 630 23 Power cables and wires Copper Conductors Tinned wires Class1 Class2 Welding cables Aluminium Conductors Bare wires Bare wires Class5 Class6 Class1 Class2 Class5 Class6 Class1 Ω/km Ω/km Ω/km Ω/km Ω/km 36,70 24,80 18,20 12,20 7,56 4,70 3,11 1,84 1,16 0,734 0,529 0,391 0,270 0,195 0,154 0,126 0,1260 0,0762 0,0607 0,0475 0,0369 0,0286 ~380 ~240 ~230 ~140 ~96,8 ~79,3 ~57,1 40,10 26,70 20,00 13,70 8,21 5,09 3,39 1,50 1,24 0,795 0,565 0,393 0,277 0,210 0,164 0,132 0,108 0,0817 0,0654 0,0495 0,0391 0,0292 36,00 24,50 18,10 12,10 7,41 4,61 3,08 1,83 1,15 0,727 0,524 0,387 0,268 0,193 0,153 0,124 0,0991 0,0754 0,0601 0,0470 0,0366 0,0283 ~360 ~230 ~215 ~138 ~95 ~78 ~56 39,00 26,00 19,50 13,30 7,98 4,95 3,33 1,91 1,21 0,780 0,554 0,386 0,272 0,206 0,161 0,129 0,106 0,0801 0,0641 0,0486 0,0384 0,0287 1,200 0,868 0,641 0,443 0,320 0,253 0,206 0,164 0,125 0,100 - Copper Conductors Bare Wires Tinned Wires Ω/km Ω/km Ω/km 1,910 1,200 0,868 0,641 0,443 0,320 0,253 0,206 0,164 0,125 0,100 0,0778 0,0605 0,0469 1,160 0,758 0,536 0,379 0,268 0,198 0,155 0,125 0,102 - 1,190 0,780 0,552 0,391 0,276 0,204 0,159 0,129 0,105 - Class2 TECHNICAL INFORMATION AWG AMERICAN WIRE GAUGE (SOLID COPPER WIRES) CLASS CONDUCTOR (AWG) CROSS SECTIONAL mm2 NOMINAL DIAMETER OF CONDUCTOR mm NOMINAL WEIGHT kg/km WIRE RESISTANCE (Ω/km) 20 ° C 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 18 17 16 16 14 14 12 12 12 10 0,0049 0,0062 0,0081 0,0103 0,0127 0,0159 0,0201 0,0255 0,0324 0,0401 0,0507 0,0649 0,0806 0,102 0,128 0,162 0,205 0,259 0,324 0,411 0,519 0,653 0,823 0,897 1,04 1,31 1,31 2,08 2,08 3,31 3,3 3,08 5,26 0,079 0,089 0,102 0,114 0,127 0,142 0,16 0,18 0,203 0,226 0,254 0,287 0,32 0,361 0,404 0,455 0,511 0,574 0,643 0,724 0,813 0,912 1,02 1,22 1,15 1,29 1,47 1,63 1,85 2,052 2,052 1,99 2,59 0,0433 0,0552 0,0720 0,0912 0,113 0,141 0,179 0,228 0,289 0,357 0,451 0,576 0,716 0,908 1,14 1,44 1,82 2,31 2,89 3,66 4,61 5,8 7,32 8,26 9,24 11,6 11,8 18,5 18,9 29,5 30,1 28,9 46,8 3540 2780 2130 1680 1360 1080 857 675 532 430 340 266 214 169 135 106 84,2 66,6 53,2 41,9 33,2 26,4 21 21,2 16,6 13,6 13,6 8,28 8,56 5,21 5,38 5,59 3,28 24 TECHNICAL INFORMATION AMERICAN WIRE GAUGE (STRANDED COPPER WIRE) 25 GAUGE (AWG) STRANDING (NOM. AWG) INCHES APPROX OD. mm CROSS-SECTION mm2 WEIGHT kg/km WIRE RESISTANCE (Ω/km) 20 ° C 36 34 32 32 30 30 28 28 27 26 26 26 24 24 24 22 22 22 20 20 20 20 20 18 18 18 18 18 16 16 16 16 16 14 14 14 14 12 12 12 12 10 10 10 10 7 x 44 7 x 42 7 x 40 19 x 44 7 x 38 19 x 42 7 x 36 19 x 40 7 x 35 7 x 34 10 x 36 19 x 38 7 x 32 10 x 34 19 x 36 42 x 40 7 x 30 19 x 34 26 x 36 7 x 28 10 x 30 19 x 32 26 x 34 42 x 36 7 x 26 16 x 30 19 x 30 42 x 34 65 x 36 7 x 24 19 x 29 26 x 30 65 x 34 105 x 36 7 x 22 19 x 26 42 x 30 105 x 34 7 x 20 19 x 25 65 x 30 165 x 34 37 x 26 65 x 28 105 x 30 0,006 0,075 0,0093 0,010 0,012 0,012 0,015 0,016 0,017 0,019 0,021 0,020 0,024 0,024 0,024 0,023 0,030 0,031 0,030 0,038 0,037 0,037 0,036 0,038 0,048 0,047 0,049 0,047 0,047 0,060 0,058 0,059 0,059 0,059 0,076 0,071 0,075 0,075 0,096 0,093 0,095 0,095 0,115 0,120 0,118 0,152 0,191 0,236 0,254 0,305 0,305 0,381 0,406 0,432 0,483 0,533 0,508 0,610 0,610 0,610 0,584 0,762 0,787 0,762 0,965 0,940 0,940 0,914 1,965 1,220 1,190 1,240 1,190 1,190 1,520 1,470 1,500 1,500 1,500 1,930 1,800 1,910 1,910 2,440 2,360 2,410 2,410 2,920 3,050 3,000 0,014 0,022 0,034 0,035 0,057 0,059 0,089 0,090 0,110 0,141 0,126 0,155 0,227 0,200 0,240 0,205 0,355 0,382 0,330 0,563 0,506 0,614 0,522 0,531 0,897 0,810 0,963 0,844 0,822 1,430 1,228 1,316 1,306 1,329 2,271 2,434 2,127 2,110 3,360 3,087 3,291 3,315 4,740 5,224 5,317 0,249 0,397 0,639 0,639 0,997 0,997 1,588 1,588 2,014 2,526 2,526 2,526 4,032 4,032 4,032 4,032 6,388 6,388 6,388 10,191 10,181 10,181 10,181 10,181 16,175 16,175 16,175 16,175 16,175 25,756 25,756 25,756 25,756 25,756 41,012 41,012 41,012 61,160 61,160 61,160 103,613 103,613 103,613 103,613 103,613 1360,6 856,0 538,4 538,4 367,4 367,4 232,0 232,0 182,4 145,6 145,6 145,6 90,8 90,8 90,8 90,8 57,4 57,4 57,4 35,7 35,7 35,7 35,7 35,7 22,7 22,7 22,7 22,7 22,7 14,2 14,2 14,2 14,2 14,2 8,95 8,95 8,95 8,95 5,61 5,61 5,61 3,54 3,54 3,54 3,54 TECHNICAL INFORMATION CURRENT CARRYING CAPACITY OF FLEXIBLE CABLES Nominal Cross Section MEASURE mm2 0,08 0,14 0,25 0,34 0,5 0,75 1 1,5 2,5 4 6 10 16 25 35 50 70 95 120 150 185 240 300 400 500 GROUP 1 One or more single-core cables installed in conduit GROUP 2 Multi-core cables e.g. plastic sheathed cables, Building cable, mobile cables CURRENT CARRYING CAPACITY A FUSE FUSE A CURRENT CARRYING CAPACITY A 2,5 6 8,5 9 10 11 12 16 21 27 35 48 65 88 110 140 175 210 250 - 10 16 20 25 35 50 63 80 100 125 160 200 250 - 0,5 1,5 2,5 3,5 5 13 16 20 27 36 47 65 87 115 143 178 220 265 310 355 405 480 555 - 10 16 20 25 35 50 63 80 100 125 160 224 250 300 355 355 425 500 - A GROUP 3 Single-core cables freely installed in air, hereby the cables are installed with in termediate spaces of the cable diameter as a minimum, as well as single-core wiring in switching and distribution systems CURRENT CARRYING FUSE CAPACITY A A 6 8,5 10 12 16 20 25 34 45 57 78 104 137 168 210 260 310 365 415 475 560 645 770 890 16 20 25 35 50 63 80 100 125 160 200 250 310 355 425 425 500 600 630 850 26 TECHNICAL INFORMATION LOGISTICS Erse serves with the latest technology packaging, wrapping and cutting machines in its separate logistics warehouse with 2800 m2 storing capacity so can make more effective logistic activities. Erse aims to make protective packaging for the cables that facilitates and accelerates the logistics activities of the business partners. The cables in accordance with international standards of production and transport are packaged and shipped pursuant to customer needs. Upon request from the customers, technical knowhow and support on the most suitable package types and cable lengths are provided. Erse does not require an additional fee from its customers for the standard packaging within its framework of logistics. OUR PACKAGE TYPES Wooden drums Cardboard box Plastic drums Plywood drums Pallet Coils with shrink Euro Pallet Heat Treatment Assurance: Only heat treated drums and pallets are used in our export products. Incoterms: The shipping is made in accordance with Incoterms rules within the framework of mutual understanding with our cust omers. 27 TECHNICAL INFORMATION WOODEN DRUMS (STANDARD) DRUM CODE NUMBER Fd mm Bd mm Ad mm L1 mm L2 mm MAXIMUM CARRYING CAPACITY kg MD-40 MD-50 MD-60 60 70 80 90 100 120 140 160 180 200 400 500 600 630 710 800 900 1000 1250 1400 1600 1800 2000 200 250 300 315 355 400 450 500 630 710 800 1000 1250 40 45 50 56 80 80 80 80 80 80 80 100 100 310 350 350 415 520 520 690 710 890 890 1100 1100 1350 250 290 300 315 400 400 560 560 670 670 850 840 1045 100 150 200 250 250 400 750 900 1700 2000 3000 4000 5000 DRUM WEIGHT kg 3 4 5 17 25 31 47 71 144 175 280 380 550 Fd:Flange Diameter Ad:Arbor Hole Diameter Bd:Barrel Diameter L1:OverallWindingWidth L2:Inner Winding Width 28 TECHNICAL INFORMATION MAX. CARRYING CAPACITANCE OF DRUMS DEPEND ON OUTER DIAMETER OF CABLES CABLE D mm 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 29 MD 40 MD 50 MD 60 420 310 235 185 150 14 735 540 430 335 270 230 195 165 140 1070 780 590 465 385 330 270 235 210 185 160 145 100 130 115 130 120 60 70 80 1110 840 640 470 388 315 254 238 190 180 140 134 102 96 92 90 65 62 60 58 56 2024 1480 1064 890 680 564 470 385 360 300 239 228 218 172 165 159 122 117 113 110 80 78 76 73 2755 2340 1463 1152 980 760 643 542 454 430 358 294 280 228 220 210 167 160 156 150 116 113 109 106 103 76 74 70 72 90 100 120 140 2727 2265 2967 160 180 2227 2435 2830 200 2730 2202 1768 1404 1206 1032 880 749 632 603 505 485 402 387 315 304 294 285 226 220 215 209 162 157 153 150 146 108 105 103 2866 2349 1910 1540 1339 1159 1000 860 736 705 599 576 485 468 389 377 365 299 290 282 226 220 214 209 204 158 154 150 148 144 110 105 102 10 1990 1756 1545 1355 1184 1139 990 856 827 709 688 668 567 550 462 450 438 428 352 344 336 329 265 259 254 249 244 190 187 183 180 177 174 130 127 125 123 120 2480 2205 1960 1737 1535 1352 1304 1145 999 967 839 814 700 680 663 564 550 537 450 440 430 422 348 340 334 327 264 259 254 249 254 240 187 184 180 178 175 172 170 126 124 122 121 119 117 2172 1930 1870 1657 1608 1420 1244 1210 1180 1028 1003 866 846 828 710 692 678 664 560 549 539 529 437 430 422 415 408 330 325 139 314 310 305 230 235 232 228 225 222 220 216 160 158 156 154 152 150 2527 2248 2172 1927 1867 1650 1450 1410 1370 1200 1166 1009 985 962 824 806 788 722 653 640 627 615 510 502 492 484 475 386 380 373 367 360 356 280 276 270 267 263 260 256 252 190 187 184 182 180 178 174 2954 2608 2522 2218 2150 1880 1826 1583 1540 1500 1289 1257 1227 1040 1017 994 972 812 795 779 763 750 610 600 589 578 568 558 442 435 428 420 414 408 400 304 300 295 290 287 282 280 275 270 266 264 TECHNICAL INFORMATION D.C VOLTAGE DROPS V drop = 2 x l x L x R l = Face Current (A) L = Length (km) R = Maximum conductor temperature, the resistance value of the expected (Ω/km) X = Reactance (Ω/km) Cos Ø = Power Factor f = Frequency(Hz) Z = Impedance (Ω/km) A.C SINGLE PHASE VOLTAGE V drop = 2 x l x L (RCos Ø + X Sin Ø) d = Conductor Diameter (mm) l = Conductor Length (m) A.C THREE PHASE VOLTAGE V drop = 3x l x L x (RCos Ø + X Sin Ø) REACTANCE: INDUCTANCE: IMPEDANCE: x=2x L=0,2 x [In(2a) + 0,25 ] 106 d Z= xfxLxl R2+X2 POWER CONVERSION FACTOR Sin Ø= 1 - Cos2 Ø NOTE: Calculations Power Factor (Cos Ø) 0.8 Surface Current (I) 1 A and Length (L) is taken as 1 km. ELECTRICAL CALCULATIONS AND FORMULAS SHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT 0,6 / 1 kV + 90 ºC ship type cables short-circuit current formula. GENERAL FORMULA: IK= 226 S t In 234+Tk 234+Tb lk = Short-circuit current (kA) S = Cross section (mm2) T = Short circuit time (sec) Tk= The expected maximum conductor temperature (short time)(ºC) Tb= Maximum conductor temperature is expected (normal conditions) (ºC) FORMULA 1 : XLPE and the HF90 standards for materials temperature Tk = & Tb = 90 º C to 250 º C, respectively. These values are placed instead of the formula, the general formula for XLPE and HF90 materials; lk = 146 S t FORMULA 2 : tThe standards for PVC materials temperature Tk = & Tb = 70 º C to 150 º C, respectively. PVC materials of general formula wherein the values for the orthogonality; lk = 31,66 S 30 TECHNICAL INFORMATION MAX. CARRYING DISTANCE OF VARIOUS POWER IN DETERMINED VOLTAGE DROP ACCORDING TO CABLE CROSS SECTION (3-380 V THREE PHASES) Power Current Power kW A Cos Ø 2,5 3 3,5 4 4,5 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 14 16 18 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 130 150 180 200 250 300 31 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 14 16 18 19 23 27 31 35 37 46 55 65 72 83 93 107 125 143 160 180 197 232 268 320 350 405 500 0.82 0.85 CROSS SECTION mm 2 1,5 2,5 4 240 200 170 150 135 120 100 85 75 66 400 330 285 250 223 200 166 142 125 110 100 82 75 640 535 455 400 353 320 265 225 200 175 160 133 113 100 88 6 800 685 600 530 480 400 340 300 265 240 200 170 150 130 120 95 10 1000 890 800 670 570 500 445 400 335 285 250 220 200 160 130 115 100 16 1070 920 800 725 640 535 460 400 355 320 255 215 189 160 140 25 35 1120 1000 835 720 630 560 500 400 335 285 250 220 200 160 1170 1050 880 780 700 560 470 400 350 310 280 220 50 1000 800 670 570 500 445 400 335 285 250 220 200 70 805 705 625 560 470 400 350 310 280 255 228 95 850 770 635 550 480 425 380 340 290 250 120 800 690 600 535 480 440 370 320 265 150 755 670 600 550 465 400 335 300 185 740 675 570 495 410 370 295 240 640 535 480 385 310 TECHNICAL INFORMATION MAX. CARRYING DISTANCE OF VARIOUS POWER IN DETERMINED VOLTAGE DROP ACCORDING TO CABLE CROSS SECTION (U-220 V SINGLE PHASE) Power kW Current Power A 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 14 16 18 20 25 30 40 9 11 14 16 18 21 23 27 32 36 41 46 55 64 72 82 91 114 136 180 Cross Section mm 2 1,5 2,5 30 24 20 17 15 13 12 50 40 33 29 25 22 20 16 15 13 4 54 49 40 35 32 26 23 20 17 16 6 69 60 53 48 40 34 30 26 24 20 17 10 80 67 57 50 45 40 38 28 25 23 16 92 80 72 64 54 46 40 35 32 26 25 100 83 71 62 55 50 40 33 35 100 88 78 70 56 47 36 VOLTAGE DROP: %AU = 3 32 TECHNICAL INFORMATION CONVERSION TABLES Length cm. m. Km. Inch (In) Foot (ft) Yard (yd) State Mile Naut Mile 1 centimeter (cm) 1 meter (m) 1 kilometer (km) 1 Inch (in) 1 foot 1 yard 1 state mile 1 naut mile 1 100 105 2,540 30,48 91,44 - 0,01 1 1000 0,254 0,3048 0,9144 1069 1852 0,001 1 1,609 1,852 0,3937 39,37 39370 1 12 36 63346 72913 0,0328 3,281 3281 0,833 1 3 5280 6080 1,094 1094 0,0278 0,3333 1 1760 2027 0,6214 1 1152 0,5396 0,8684 - AREA cm2 1 square centimeter (cm²) 1 1 square meter (m²) 1000 1 Ar (a) 1 hectare (ha) 1 square kilometer (km²) 1 square inch 6,452 1 square foot (ft²) 929 8361 1 squre yard 1 square mile 1 acre WEIGHT 1 gram (gr) 1 kilogram (kg) 1 tone (metric) 1 ounce (oz) 1 libre (lb.) 1 stone 1 small tone 1 big tone VOLUME 1 cubic centimeter (cm³) 1 cubic decimeter (dm³) 1 cubic inch (in³) 1 cubic foot ft³ 1 cubic yard 1 ounce (USA) 1 ounce (UK) 1 galon (USA) 1 galon (UK) 1 pint (UK) 33 m2 a (Ar) ha km2 in2 ft2 Yard2 mil2 Acre 0,0001 1 100 1000 0,0929 0,8361 4050 0,01 1 100 1000 40,5 0,01 1 100 259 0,405 0,01 1 2,59 - 0,155 1550 1 144 1296 - 10,76 1076 1 9 43640 1,196 119,6 0,0039 0,111 1 4850 2,47 0,3861 0,0016 0,0247 247,1 640 1 gr. kg. Metric ton ounce Libre pound stone Short ton Big ton 1 1000 28,35 453,6 6530 907,190 1106050 0.001 1 1000 0,028 0,454 6,35 907,2 1016 0,001 1 0,0064 0,907 1,016 0,0332 35,27 35274 1 16 224 32000 35,840 2,205 2204,6 0,0625 1 14 2000 2240 0,157 157,47 0,004 0,071 1 142,9 160 0,0011 1,1023 0,007 1 1,120 0,00098 0,9842 0,0063 0,8929 1 cm3 1 1000 16,39 29,57 28,41 3785 4546 568,2 dm3 liter 0,001 1 0,0164 28,32 764,6 0,02296 0,0284 3,785 4,546 0,5682 in3 ft3 Yard3 0,061 61,02 1 1728 46656 1,805 1,734 231 277,4 34,68 0,035 1 27 0,1337 0,1603 0,02 0,0370 1 - UK ounce 0,038 33,81 0,5541 957,5 25853 1 0,9607 128 153,7 19,21 USA ounce 0,353 35,3 0,5768 966,6 26,909 1,041 1 133,2 160 20 USA gallon 0,2462 7,481 202 1 1,201 0,1501 UK gallon 0,22 6,232 168,2 0,8327 1 0,125 UK pint 1,76 0,0288 49,83 1345 0,0520 0,05 6,662 8 1 TECHNICAL INFORMATION ABBREVATIONS OF STANDARDS ASSOCIATED ACCORDING TO COUNTRIES SHORT NAME EXPANSION COUNTRY SHORT NAME EXPANSION COUNTRY AFNOR ANSI ASTM BASEC BSI(BS) BV CATV CEBEC CEE CEI CEN CENELEC CNET CNOMO CMA CSA CSTB DEMKO DIN DKE ECMC ELOT EIC EN ERA ESI FAR FTZ GOST HD HN ICEA IEC IEE Association Française De Normalisation American National Standarsd Instutie American Standard of Testing Materials British Approvals Service For Electric Cables British Standard Institution Bureau Veritas Community Antenna Television Comite Electrotechinique Belge Commission on Rules for the aproval Electrical Equipment Comitato Electotechnico Belge Italiano European Committ ee For Strdardisation Comite Europeen De Normalisation Electrotechn guess Cntre National d’’etude de Telecommuication Comite de Normalisation des Moyens de Production Cable Makers Association Canadian Standars Approval Centre Scientifique et Technique du Batiment Denmarks Eletrische Materiel Control Deutches Institute Für Normung Deutsche Elekrotechische Kommission imDIN undVDE Electric Cable Makers Confderation Hellenic Organisat on For Standardisation Energy Industries Council European Standards Electrical Research Association Electrocal Supply Industry Federal Air Regulation Fernmedetechnisches Zentralamt USRR-Standards Harmonisierrugs-Dokumate Harmonization des Normes Insulated Cable Engineers Assocation International Electrotechnical Commission Institue Of Electrical Engineers France Usa Usa Uk Uk France Int. Belgium Int. Italy Ecc Ecc France France Uk Canada France Den. Den. Ger. Uk Uk Greece Ger. Ger. Uk Usa Ger. Ussr Int. France Usa Europe Uk IEEE IMQ ISDN ISO KEMA LCIE LLOYDS LPC MESC MIL NEC NEN NF NFC NEMA NEMKO NP NSAI OCMA ÖVE SEMKO SETI SEV SNV TSE UKOOA UL UNEL UNI USE VDE VDEW ZVEH ZVEI Institue Of Electrical And Electronic Engineers Instituto Italiano Del Macho D Qualita Integraded Services Digital Network International Standard Organisation Keuring van Electrotechnische Materialen Laboratorie Central des Industries Electriques Lloyds Register Of Shiping Loss Prevention Council Material And Equipment Standardsand Code United States Millitary Specification National Electrical Code Nederlands Normalisatie-Instituut Normes Françaises Normes Françaises Class C National Electrical Manufacturer Association Norks Electrisk Materiell Controll Portuguese Da Qualidade National Standards Authorty of Irland Oil Companies Meterials Association Österreichischer Vrband für Electrotechnik Sveska Electr ska Materiel Kontrollanstalten Elektriska Inspektoratet Schweizerischer Electontechnicher Verein Schweizerischer Normenverband Turkish Standard Institue Uk Offshore Operators Association Underwiters Laboratories Unifiazione Electretechnia Unifiazione Nationale Italiano Union Techniqe del”electr te(Ute) Verband Deustcher Elktrotechniker Vereiningung Deuscher Elektrizitatswerke e.V Zentralverband der Deutschen Elektrohandwerke Zentralverband der Electrotechnic-und Electonic Uk Italy Int. Global Netherlands France Uk Uk Netherlands Usa Usa Netherlands France France Usa Norway Portugal Ireland Uk Austria Sweeden Finland Switzerland Switzerland Turkey Uk Usa Italy Italy France Ger. Ger. Ger. Ger. 34