Wireless Wire—60 GHz Ultra
advertisement

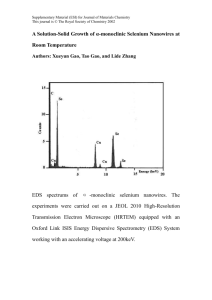
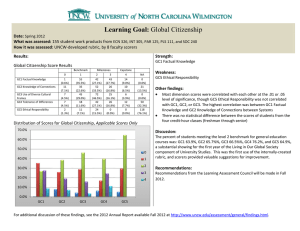
Small Temperature Sensor Using mm-wave data and power transfer Presenter : ir. Hao Gao Promotor : Prof. dr. ir Peter Baltus dr. Marion Matters-Kammerer dr. Dusan Milosevic Outline Sensors with Wireless Power Transfer Mm-wave RF Wireless Power Receiver Mm-wave RF Tag 60 GHz Ultra Low Power Radio Conclusion 1 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl Sensors with Wireless Power Transfer Medical and Health monitoring Structure Health monitoring Body Area Network Wireless Sensor Networks Smart building Low data rate / low duty cycle / ultra-low power 2 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl Sensor Evolution Bottom Buttom (With Solar Cell) 38mm Top Cons.: 8cm × 4cm 32cm2 Antenna Integration Assembly Components Battery Size Hight Cost (Y.H. Chee, Ali Niknejad, University of California at Berkeley, 2006) Cons.: 3.8cm × 2.5cm 9.5cm2 PCB Based Harvesting Method not easy to integrate (2.4 GHz) (1.8 GHz) ( © BWRC,UCB, US, 2006) 3 25mm © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl 0.2cm × 0.1cm 0.02cm2 Solution: mm-Wave On-chip antenna (60 GHz) Why mm-Wave ? Small wavelength enables: Integrate antenna on-chip Develop antenna arrays to Provide high antenna gain Provide highly directional pencil beams Wide bandwidth available at 60 GHz enables High data rate in the order of Gbits/s Short transmission burst 4 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl mm-wave Problem Rectifier performance conflicts with antenna size. mm-Wave enables antenna on-chip. Wide bandwidth available at 60 GHz. High data rate in the order of Gbits/s. Short transmission burst. Rectifier performance at mm-Wave : Efficiency is low. 5 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl Benchmarking Frequency ( GHz ) 6 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl 60 GHz mm-wave Inductor-Peaked Rectifier Problems: Low input voltage High threshold voltage Signal feed through GND RFIN DCOUT GND GND 520 µm 7 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl 350 µm GND Mm-wave Wireless Temperature Sensor Base Station with Phase Array Base Station Wireless Temperature Sensor Nodes Vdd Cstorage RFin 8 RF-DC Converter Ultra Low Power End of Enable Transmitter Burst Temperature RFout Monitor Correlated Sensor © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl L6 M3 L7 M6 ULP Tx 0.94mm Three Stage Inductor Peaked Rectifier 9 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl M9 Rfout- M14 L11 M8 M10 M11 M12 ULP Temperature Correlated Tx λ/4 monopole antenna Storage Capacitor Array 1.16mm L9 L8 L10 End of Burst Monitor M13 R1 C5 M4 RF-DC Converter Rfout+ L3 M7 M1 C2 L2 M5 L4 C3 C1 L1 C4 L5 Storage Capacitor Array M2 RFIN Mm-wave Wireless Temperature Sensor 0.75mm 71 GHz Tags : Block Diagram On-Chip Antenna: Small size Advantage: Monolithic, fully integration Small size, 2mm ×1mm 10 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl Rectifier: Used as the supply voltage generator End-of-Burst: Used as the input power monitor 71 GHz Tags : Measurement 11 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl Future : 60GHz Radio-Triggered Monolithic Wireless Sensor Node 12 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl 60GHz data transfer: Ultra Low Power Radio • Average power consumption optimization Cause High stand-by power High Power consumption of the mmW front-end Circuitry complexity Modulation complexity System architecture 13 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl Minimize power floor Remove the high-power PLL Relax Linearity Eliminate the square-law Solutions! Duty-cycled wakeup receiver (WuRx) Injection-locked oscillator (IJLO) OOK based selfdemodulation IJLO used in the envelop detection 60GHz Injection-locked Oscillator 14 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl Wireless Sensor System Evaluation TX Ant Ant Modulation Power Gain TX Gain Rx 10 dBm 30 dBi 0 dBi OOK Pac. BW Tscav Rx % Len 2 GHz 10ms 20 bits 50 System parameters Gain NF IIP3 Pdc (dB) (dB) (dBm) (mW) LNA 16.2 4.8 -18 5 Mixer -15 15 -22.4 Pout Sensitivity Pdc frf (GHz) (dBm) (dBm) (mW) IJLO 61.6 -22.5 -60 3 60 GHz RF Front-End Parameters 15 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl Conclusion Battery-less sensor nodes enable many applications Mm-wave wireless power transfer with integrated on chip antenna is an elegant way for low cost solution Key Circuit Blocks: High efficiency rectifier System Level : 60 GHz ultra low power radio 16 © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl Acknowledgment © Hao Gao, MsM group, TU/e, h.gao@tue.nl