Equivalent Resistance
advertisement
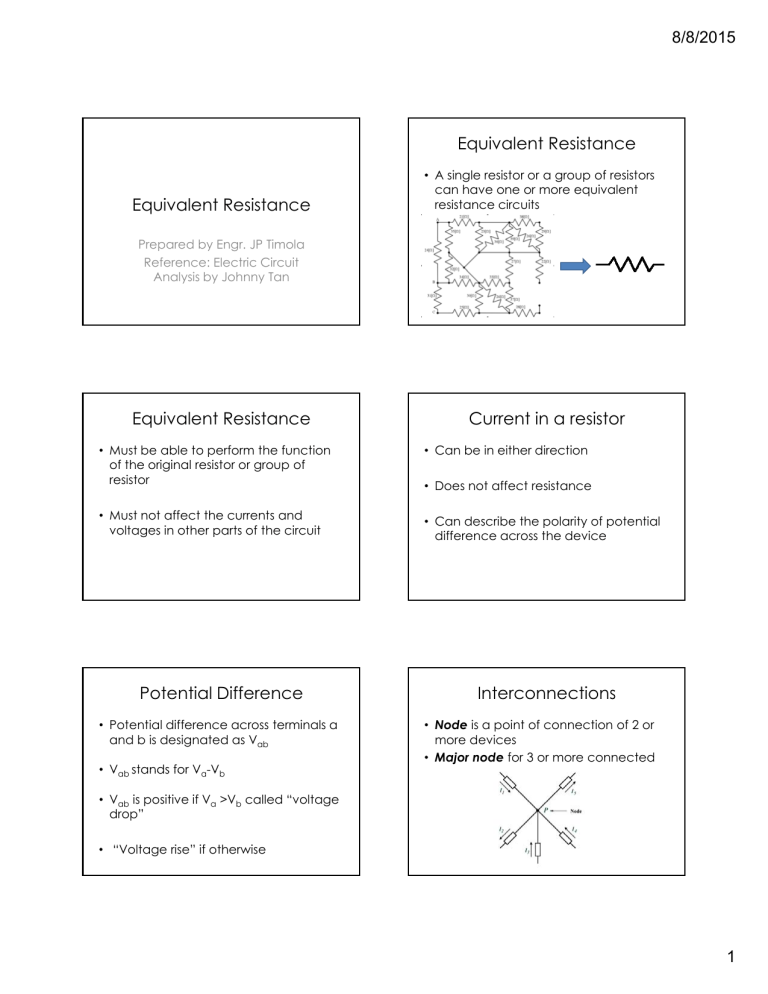
8/8/2015 Equivalent Resistance Equivalent Resistance • A single resistor or a group of resistors can have one or more equivalent resistance circuits Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electric Circuit Analysis by Johnny Tan Equivalent Resistance Current in a resistor • Must be able to perform the function of the original resistor or group of resistor • Can be in either direction • Must not affect the currents and voltages in other parts of the circuit • Can describe the polarity of potential difference across the device Potential Difference • Potential difference across terminals a and b is designated as Vab • Vabb stands for Va-V Vb • Does not affect resistance Interconnections • Node is a point of connection of 2 or more devices • Major node for 3 or more connected • Vab is positive if Va >Vb called “voltage drop” • “Voltage rise” if otherwise 1 8/8/2015 Interconnections • Electric network is the interconnection of 2 or more devices • Electric circuit is formed if the network contains at least one closed path Resistors in Series • RT = R1+ R2 + R3… • I T = I 1 = I 2 = I 3… • VT = V1 + V2 + V3… Resistors in Parallel IT = I1 + I2 + I3… VT = V1 = V2 =V3 … 1 1 1 1 ... RT R1 R2 R3 Resistors in Series • Resistors are in series if they are connected end-to-end • Each carry the same current • No N more than th 2 resistor i t connected t d to t same node Resistors in Parallel • In parallel if constant potential difference is applied across them • End terminals are connected to same node or conductor Two Resistors in Parallel RR 1 1 2 RT R1 R2 I 2 IT I1 IT R2 R1 R2 R1 R1 R2 2 8/8/2015 PROBLEM 1 • Determine the equivalent resistance with respect to terminals a and b PROBLEM 3 • Determine the equivalent resistance with respect to terminals a and b PROBLEM 5 • Determine the equivalent resistance with respect to terminals a and b PROBLEM 2 • Determine the equivalent resistance with respect to terminals a and b PROBLEM 4 • Determine the equivalent resistance with respect to terminals a and b PROBLEM 6 • Determine the unknown currents 3 8/8/2015 PROBLEM 7 EQUIVALENT THREE TERMINAL NETWORKS • Determine the unknown currents • when electric circuit contain networks neither in series or in parallel, we can replace some parts of the circuit by their three-terminal equivalents EQUIVALENT THREE TERMINAL NETWORKS • Any passive three-terminal network may be reduced to any one of the networks: • Delta (∆) or Pi (π) Wye(Y) or tee (T) PROBLEM • Determine the equivalent resistance between a and b DELTA NETWORK AND ITS WYE EQUIVALENT R12 R1 R2 R2 R3 R3 R1 R3 R1 R12 R31 R12 R23 R31 R23 R1 R2 R2 R3 R3 R1 R1 R2 R12 R23 R12 R23 R31 R31 R1 R2 R2 R3 R3 R1 R2 R3 R31 R23 R12 R23 R31 PROBLEM • Determine the currents indicated 4 8/8/2015 PROBLEM • Determine the equivalent resistance between a and i 5