Decision Tree
advertisement
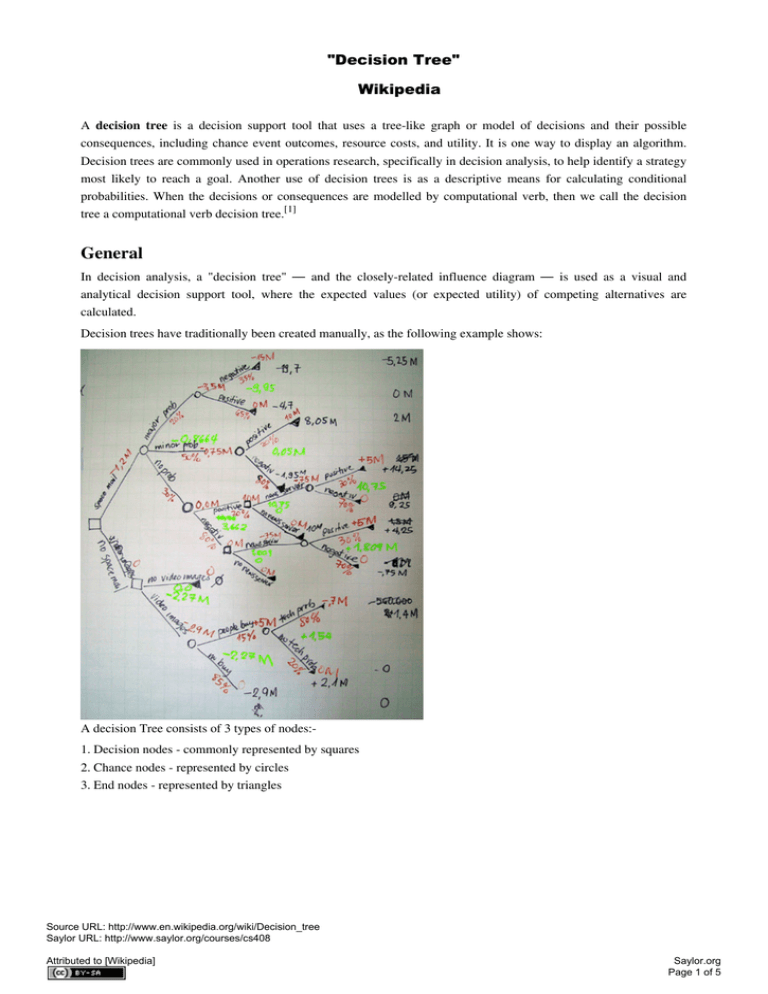
"Decision Tree" Wikipedia A decision tree is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like graph or model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. It is one way to display an algorithm. Decision trees are commonly used in operations research, specifically in decision analysis, to help identify a strategy most likely to reach a goal. Another use of decision trees is as a descriptive means for calculating conditional probabilities. When the decisions or consequences are modelled by computational verb, then we call the decision tree a computational verb decision tree.[1] General In decision analysis, a "decision tree" — and the closely-related influence diagram — is used as a visual and analytical decision support tool, where the expected values (or expected utility) of competing alternatives are calculated. Decision trees have traditionally been created manually, as the following example shows: A decision Tree consists of 3 types of nodes:1. Decision nodes - commonly represented by squares 2. Chance nodes - represented by circles 3. End nodes - represented by triangles Source URL: http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/courses/cs408 Attributed to [Wikipedia] Saylor.org Page 1 of 5 Drawn from left to right, a decision tree has only burst nodes (splitting paths) but no sink nodes (converging paths). Therefore, used manually, they can grow very big and are then often hard to draw fully by hand. Analysis can take into account the decision maker's (e.g., the company's) preference or utility function, for example: The basic interpretation in this situation is that the company prefers B's risk and payoffs under realistic risk preference coefficients (greater than $400K—in that range of risk aversion, the company would need to model a third strategy, "Neither A nor B"). Source URL: http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/courses/cs408 Attributed to [Wikipedia] Saylor.org Page 2 of 5 Influence diagram A decision tree can be represented more compactly as an influence diagram, focusing attention on the issues and relationships between events. Uses in teaching Decision trees, influence diagrams, utility functions, and other decision analysis tools and methods are taught to undergraduate students in schools of business, health economics, and public health, and are examples of operations research or management science methods. Advantages Amongst decision support tools, decision trees (and influence diagrams) have several advantages: Decision trees: • Are simple to understand and interpret. People are able to understand decision tree models after a brief explanation. • Have value even with little hard data. Important insights can be generated based on experts describing a situation (its alternatives, probabilities, and costs) and their preferences for outcomes. • Use a white box model. If a given result is provided by a model, the explanation for the result is easily replicated by simple math. • Can be combined with other decision techniques. The following example uses Net Present Value calculations, PERT 3-point estimations (decision #1) and a linear distribution of expected outcomes (decision #2): Source URL: http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/courses/cs408 Attributed to [Wikipedia] Saylor.org Page 3 of 5 Example Decision trees can be used to optimize an investment portfolio. The following example shows a portfolio of 7 investment options (projects). The organization has $10,000,000 available for the total investment. Bold lines mark the best selection 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7, which will cost $9,750,000 and create a payoff of 16,175,000. All other combinations would either exceed the budget or yield a lower payoff.[2] Example In the game of "20 Questions", the querent tries to construct a short binary decision tree that isolates a specific item. The item's identity question is asked when the current decision tree node is considered reliable by the querent. References [1] Yang, T. (Dec. 2006). "Computational Verb Decision Trees". International Journal of Computational Cognition (Yang's Scientific Press) 4 (4): 34–46. [2] Y. Yuan and M.J. Shaw, Induction of fuzzy decision trees (http:/ / www. sciencedirect. com/ science?_ob=ArticleURL& _udi=B6V05-4007D5X-C& _user=793840& _coverDate=01/ 27/ 1995& _fmt=summary& _orig=search& _cdi=5637& view=c& _acct=C000043460& _version=1& _urlVersion=0& _userid=793840& md5=b66b56153f6780c30e07201eadd454cf& ref=full). Fuzzy Sets and Systems 69 (1995), pp. 125–139 External links • 5 Myths About Decision Tree Analysis in Litigation (https://paperchace.com/decision-trees/?p=6) • Decision Tree Analysis (http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTED_04.htm) mindtools.com • Decision Analysis open course at George Mason University (http://gunston.gmu.edu/healthscience/730/ default.asp) • Extensive Decision Tree tutorials and examples (http://www.public.asu.edu/~kirkwood/DAStuff/ decisiontrees/index.html) • Cha, Sung-Hyuk; Tappert, Charles C (2009). " A Genetic Algorithm for Constructing Compact Binary Decision Trees (http://www.jprr.org/index.php/jprr/article/view/44/25)". Journal of Pattern Recognition Research (http://www.jprr.org/index.php/jprr) 4 (1): 1–13. • Decision Trees in PMML (http://www.dmg.org/v4-0/TreeModel.html) Source URL: http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/courses/cs408 Attributed to [Wikipedia] Saylor.org Page 4 of 5 Article Sources and Contributors Decision tree Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?oldid=415279979 Contributors: A m sheldon, AaronS, Aaronbrick, Airsplit, Ajo Mama, AlexHorovitz, Alexlinsker@gmail.com, Altenmann, Anders gorm, Andreas Kaufmann, Anna512, Antonielly, Arthuralbano, BMF81, Barnwellr, Beetstra, Bethjaneway, Bobo192, Boxplot, Bumbulski, C45207, C777, Can't sleep, clown will eat me, Capricorn42, Changes84, Charles Matthews, CharlieVNL, Chendy, Cntras, Computationalverb, Coppertwig, Damicatz, Daniel Quinlan, Dawei san, Dcoetzee, Ddxc, Delaszk, Dmccreary, DouglasGreen, Dstouwdam, DundeeD, Dyoung418, Dysprosia, EightiesRocker, Ejjazaccountant, Eph1090, Estard, Evandrojr, Fijal, Fintor, Fox, Franz D'Amato, Friend of facts, Frodet, Fæ, Giftlite, Hamaryns, Hike395, Ichbinder, Informavores, Insight55, Janez Demsar, Jeff3000, Jetski217, Jheald, JonHarder, Juan Daniel López, Justjennifer, Karl-Henner, Kevinwenke, Kuru, Louharris, MacGyverMagic, Mdd, Memming, Mennan, Michael Hardy, Michal.burda, Mitar, MrOllie, Mydogategodshat, Neilc, Nerd, Nrobbins, Object01, Ogai, Pce3@ij.net, Pearle, Peruvianllama, Pgan002, Philip Trueman, Philly jawn, Pintaio, Polyextremophile, Quentar, Quiark, RJASE1, Raand, Raul654, Retardo, RexNL, Rich Farmbrough, Rlsheehan, Ronz, Salix alba, Sbisolo, Sdrtirs, Sesu Prime, Shinyplastic, Sioraf, SkyWalker, Skyy Train, Stephen Milborrow, Stopitallready, StradivariusTV, Strenshon, Sunsetsky, The Rambling Man, TheEternalVortex, Thopper, Tobias Bergemann, Tom@thomasbcox.com, Verne Equinox, Waveguy, Whayes, Wtmitchell, Xs2me, Yaniv.bl, Yrithinnd, 196 anonymous edits Image Sources, Licenses and Contributors Image:Manual decision tree.jpg Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Manual_decision_tree.jpg License: Public Domain Contributors: User:Polyextremophile Image:Decision-Tree-Elements.png Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Decision-Tree-Elements.png License: Public Domain Contributors: User:Polyextremophile Image:RiskPrefSensitivity2Threshold.png Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:RiskPrefSensitivity2Threshold.png License: GNU Free Documentation License Contributors: A m sheldon Image:Factory2 InfluenceDiagram.png Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Factory2_InfluenceDiagram.png License: GNU Free Documentation License Contributors: A m sheldon Image:Investment decision Insight.png Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Investment_decision_Insight.png License: Public Domain Contributors: User:Polyextremophile License Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported http:/ / creativecommons. org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3. 0/ Source URL: http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/courses/cs408 Attributed to [Wikipedia] Saylor.org Page 5 of 5