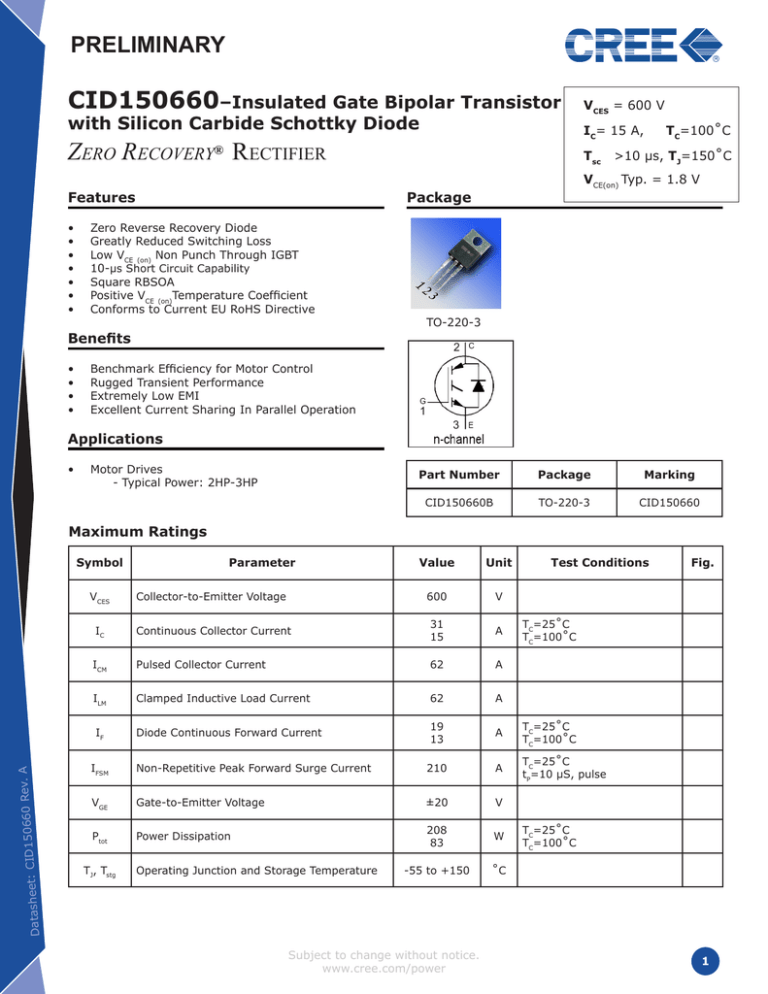
PRELIMINARY
CID150660–Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
with Silicon Carbide Schottky Diode
IC= 15 A,
Zero Recovery® Rectifier
Features
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Tsc
TO-220-3
2
Benchmark Efficiency for Motor Control
Rugged Transient Performance
Extremely Low EMI
Excellent Current Sharing In Parallel Operation
1
3
Applications
•
>10 µs, TJ=150˚C
Benefits
•
•
•
•
TC=100˚C
VCE(on) Typ. = 1.8 V
Package
Zero Reverse Recovery Diode
Greatly Reduced Switching Loss
Low VCE (on) Non Punch Through IGBT
10-µs Short Circuit Capability
Square RBSOA
Positive VCE (on)Temperature Coefficient
Conforms to Current EU RoHS Directive
VCES = 600 V
Motor Drives
- Typical Power: 2HP-3HP
Part Number
Package
Marking
CID150660B
TO-220-3
CID150660
Maximum Ratings
A
D150660 Rev.
Datasheet: CI
Symbol
Parameter
Value
Unit
Test Conditions
VCES
Collector-to-Emitter Voltage
600
V
IC
Continuous Collector Current
31
15
A
ICM
Pulsed Collector Current
62
A
ILM
Clamped Inductive Load Current
62
A
IF
Diode Continuous Forward Current
19
13
A
TC=25˚C
TC=100˚C
TC=25˚C
tP=10 µS, pulse
IFSM
Non-Repetitive Peak Forward Surge Current
210
A
VGE
Gate-to-Emitter Voltage
±20
V
Ptot
Power Dissipation
208
83
W
-55 to +150
˚C
TJ, Tstg
Operating Junction and Storage Temperature
Subject to change without notice.
www.cree.com/power
Fig.
TC=25˚C
TC=100˚C
TC=25˚C
TC=100˚C
PRELIMINARY
Electrical Characteristics @ TJ =25°C (unless otherwise specified)
Symbol
Parameter
V(BR)CES
∆V(BR)CES/∆TJ
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Collector-to-Emitter Breakdown Voltage
600
V
Temperature Coeff. of Breakdown Voltage
0.3
V/°C
Test Conditions
VGE = 0 V, IC=500 µA
VGE = 0 V, IC= 1.0 mA, (25°C150°C)
1.80
2.05
2.10
2.20
2.50
2.60
V
IC = 15 A, VGE =15 V
IC = 15 A, VGE =15 V
IC = 15 A, VGE =15 V
Gate Threshold Voltage
4.5
5.5
V
VCE = VGE, IC = 250 µA
Temperature Coeff. of Threshold Voltage
-10
mV/°C
gfe
Forward Transconductance
10.6
S
ICES
Zero Gate Voltage Collector Current
5.0
500
VFM
Diode Forward Voltage Drop
2.5
3.25
IGES
Gate-to-Emitter Leakage Current
VCE(on)
Collector-to-Emitter Saturation Voltage
VGE(th)
∆VGE(th)/∆TJ
150
1000
µA
V
Fig.
TJ = 125°C
TJ = 150°C
5,6,7
10,11
12
10,11
12,13
VCE = VGE, IC = 1.0 mA, (25°C150°C)
VCE = 50 V, IC, = 20 A, PW=80 µs
VGE = 0 V, VCE = 600 V
VGE = 0 V, VCE = 600 V, TJ = 150°C
IC = 15 A
IC = 15 A, TJ = 150°C
±100
nA
Typ.
Max.
Unit
0.6
°C/W
8
VGE = ±20 V
Thermal Characteristics
Symbol
Parameter
RθJC
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Case-IGBT
RθJC
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Case-Diode
1.8
°C/W
RθCS
Case-to-Sink, Flat, Greased Surface
0.5
°C/W
RθJA
Junction-to-Ambient, Typical Socket Mount
62
°C/W
RθJA
Junction-to-Ambient (PCB Mount, Steady State)
40
°C/W
Wt
Weight
1.44
g
Test Conditions
Fig.
Test Conditions
Fig.
Switching Characteristics @ TJ =25°C (unless otherwise specified)
Symbol
Parameter
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Qg
Total Gate Charge (Turn-On)
56
84
nC
Qge
Gate - Emitter Charge (Turn-On)
7.0
10
nC
Qgc
Gate - Collector Charge (Turn-On)
26
39
nC
Eon
Turn-On Switching Loss
85
µJ
Eoff
Turn-Off Switching Loss
420
µJ
Etot
Total Switching Loss
505
µJ
CID150660 Rev. A
IC = 15 A
Vcc = 400 V
VGE = 15 V
CT1
IC = 15 A, VCC =400 V
VGE = 15 V, RG = 22 Ω
L = 200 µH, Ls = 150 nH
TJ = 25°C
CT4
PRELIMINARY
Switching Characteristics @ TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise specified) continued . . .
Symbol
td(on)
tr
td(off)
tf
Eon
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Turn-On Delay Time
34
ns
Rise Time
22
ns
Turn-Off Delay Time
160
ns
Fall Time
122
ns
90
µJ
Turn-On Switching Loss
Eoff
Turn-Off Switching Loss
570
µJ
Etot
Total Switching Loss
660
µJ
td(on)
Turn-On Delay Time
34
ns
Rise Time
28
ns
Turn-Off Delay Time
165
ns
Fall Time
232
ns
Cies
Input Capacitance
850
pF
Coes
Output Capacitance
75
pF
Cres
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
35
pF
tr
td(off)
tf
RBSOA
Reverse Bias Safe Operating Area
SCSOA
Short Circuit Safe Operating Area
10
µs
Reverse Recovery Energy of the Diode
20
µJ
trr
Diode Reverse Recovery Time
30
ns
Irr
Diode Peak Reverse Recovery Current
1
A
Erec
Parameter
CID150660 Rev. A
FULL SQUARE
Test Conditions
Fig.
IC = 15 A, VCC =400 V
VGE = 15 V, RG = 22 Ω
CT4
L = 200 µH, Ls = 150 nH
TJ = 25°C
IC = 15 A, VCC =400 V
VGE = 15 V, RG = 22 Ω
L = 200 µH, Ls = 150 nH
TJ = 150°C
IC = 15 A, VCC =400 V
VGE = 15 V, RG = 22 Ω
L = 200 µH, Ls = 150 nH
TJ = 150°C
CT4
14,16
WF1
WF2
CT4
15,17
WF1
WF2
VGE = 0 V
VCC =30 V
f = 1.0 MHz
TJ = 150°C, IC = 62 A, Vp = 600 V
VCC = 500 V, VGE = +15 to 0 V
RG = 22 Ω
4
CT2
TJ = 150°C, Vp = 600 V, RG = 22 Ω
VCC = 360 V, VGE = +15 to 0 V
CT3
WF4
TJ = 150°C
IF = 15 A, VCC =400 V
VGE = 15 V, RG = 22 Ω
L = 200 µH, Ls = 150 nH
CT4
WF3
PRELIMINARY
Typical Performance
IRGB/S/SL15B60KDPbF
35
240
30
200
25
160
Ptot (W)
IC (A)
20
15
80
10
�
40
5
0
120
0
20
40
60
80
0
100 120 140 160
0
T C (°C)
20
40
60
80
100 120 140 160
T C (°C)
Fig. 1 - Maximum DC Collector Current
Fig. 2 - Power Dissipation vs. Case
DCTemperature
Collector Current vs.
Fig. 2 - Power Dissipation
vs. Case
Fig. 1 - Maximum
vs. Case
Temperature
Case Temperature
Temperature
100
100
10 µs
100 µs
1
DC
0.1
10
IC A)
IC (A)
10
1
10
100
1
1ms
1000
0
10000
10
VCE (V)
Fig. 3 - Forward SOA
Fig.TC3=25
- Forward
°C; TJ ≤SOA
150°C
TC = 25°C; TJ d 150°C
www.irf.com
CID150660 Rev. A
100
1000
VCE (V)
Fig. 4 - Reverse Bias SOA
Fig. 4TJ-=150
Reverse
Bias
°C; VGE
=15 SOA
V
TJ = 150°C; VGE =15V
3
PRELIMINARY
Typical Performance
IRGB/S/SL15B60KDPbF
100
100
90
VGE
VGE
VGE
VGE
VGE
80
60
90
70
50
40
60
40
30
20
20
10
10
0
1
2
3
4
5
0
6
= 18V
= 15V
= 12V
= 10V
= 8.0V
50
30
0
VGE
VGE
VGE
VGE
VGE
80
ICE (A)
ICE (A)
70
= 18V
= 15V
= 12V
= 10V
= 8.0V
0
1
2
VCE (V)
Fig. 5 - Typ. IGBT Output Characteristics
TJ=-40
°C;Output
tp=300Characteristics
μs
Fig. 5 - Typ.
IGBT
3
4
5
6
VCE (V)
TJ = -40°C; tp = 300µs
Fig. 6 - Typ. IGBT Output Characteristics
TJ=25
°C; tp=300
μs
Fig. 6 - Typ. IGBT
Output
Characteristics
12
11
TJ = 25°C; tp = 300µs
10
9
8
12
60
100
90
VGE
VGE
VGE
VGE
VGE
80
60
50
10
= 15V
= 12V
= 10V
= 8.0V
9
50
40
125°C
175°C
7
1
306 0
5
102
10
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
VCE (V)
Fig. 7 - Typ. IGBT Output Characteristics
Fig. 7 - Typ. T
=150Output
°C; tp=300
μs
IGBT
Characteristics
J
4
3
3
20
4
-40°C
25°C
25°C
150°C
75°C
204
30
0
6
5
408 2
IF (A)
ICE (A)
70
11
= 18V
7
TJ = 150°C; tp = 300µs
CID150660 Rev. A
00
0.0
0.0
0.5
0.5
1.01.0 1.5 1.5 2.0 2.0
2.5
2.5
3.0
3.0
3.5
VF (V)
Fig. 8 - Typ. Diode Forward Characteristics
Fig.
8 - Typ. Diode Forward Characteristics
tp = 80µs
www.irf.com
PRELIMINARY
Typical Performance
IF(AVG) Forward Current (A)
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
Tc Case Temperature (°C)
IRGB/S/SL15B60KDPbF
Fig. 9 - Diode Current Derating
20
20
18
18
16
16
14
12
ICE = 5.0A
VCE (V)
VCE (V)
14
ICE = 15A
10
ICE = 30A
8
12
6
4
4
2
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
0
20
ICE = 15A
ICE = 30A
8
6
0
ICE = 5.0A
10
4
6
8
VGE (V)
Fig. 10 - Typical V vs. V
160
140
16
ICE (A)
VCE (V)
ICE = 30A
T J = 150°C
20
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
VGE (V)
Fig. 12 - Typical VCE vs. VGE
Fig.
11 - Typical
VCE
TJ=150
°Cvs.
VGE
Fig.12
TJ = 150°C
www.irf.com
80
40
2
T J = 150°C
60
4
4
CID150660 Rev. A
20
100
ICE = 5.0A
ICE = 15A
6
0
18
T J = 25°C
120
14
8
16
Fig. 11 - Typical V vs. VGE
18
10
14
Fig. 11
10 - Typical VCE vs.CEVGE
TJ=25°C
TJ = 25°C
20
12
12
VGE (V)
CE
GE
Fig. 9 - Typical
VCE
Fig.10
TJ=-40
°Cvs.
VGE
TJ = -40°C
10
20
0
T J = 25°C
0
5
10
15
20
VGE (V)
Fig. 13 - Typ. Transfer Characteristics
Fig. 12 - Typ.
Characteristics
Fig.13
VCETransfer
=50V; tp=
10 μs
VCE = 50V; tp = 10µs
5
PRELIMINARY
Typical Performance
IRGB/S/SL15B60KDPbF
IRGB/S/SL15B60KDPbF
1800
2200
1600
1800
2000
2000
1400
1600
1800
1800
Energy (µJ)
Energy (µJ)
1200
1000
1000
800
800
600
800
1000
600
800
400
0
10
15
20
3010
30
40
IC (A)
30
35 20 40
IC (A)
40
ttd
FON
tRtF
10
50
10
50
0
400
700
800
300
600
700
700
600
200
500
100
400
0
10
22
EOFF
EON
EOFF
39
62
300
400
Rg (Ohms)
200
300
100
100
200
390
62
0Rg (Ohms)
0
40
50
EON
100
EON
82
tdOFF
tdOFF
100
8250
50
100
R G (:)
R G (:)
tdON
100
tR
tdON
tFt
R
10
100
100
15 -Loss
Typ. vs.
Energy
Fig. 16 - Typ.Fig.
Energy
RG Loss vs. RG
TJ = 150°C;
L=200µH;
TJ = 150°C; L=200
CE= 400V
µH;
V
=
400
V VLoss
CE
Fig. 15 - Typ. Energy
vs. RG
ICE==15
15A;
VGE= 15V
ICE= 15TA;=V150°C;
V
GE
L=200µH; VCE= 400V
J
6
ICE= 15A; VGE= 15V
CID150660 Rev. A
50
tF
0
100
6
30
1000
EON
400
500
22
10
40
Fig. 14 - Typ. Switching Time vs. IC
TJ = 150°C; L=200µH; VCE= 400V
Fig.
14
Fig.
15- -Typ.
Typ.Switching
SwitchingTime
Timevs.
vs.ICIC
Fig.15
RG= 22:; VGE= 15V
TTJJ==150°C;
VCE
= 400V
150°C;L=200µH;
L=200 µH;
VCE
= 400 V
RRGG==22:;
= =15V
22 ΩV; GE
VGE
15 V
EOFF
500
600
200
10
30
I (A)
20C
1000
800
900
500
800
20
IC (A)
900
600
900
tR10
0
OFF
0
tdON
20
Energy (µJ)
Energy (µJ)
Energy (uJ)
0
25
20
100
Fig.
- Typ.35Energy
25 13 30
40 Loss vs. I C
TJIc =(A)150°C; L=200µH; VCE= 400V
Fig. 13
- Typ.
Loss vs. IC
Fig. 14 - Typ. Energy
vs.Energy
IC
RLoss
G= 22:; VGE= 15V
TJ =µH;
150°C;
TJ = 150°C; L=200
VCE=L=200µH;
400 V VCE= 400V
22:; VGE= 15V
RG= 22 Ω; VGE=R15
G=
EV
15
1000
700
Energy (uJ)
10
Ic (A)
10
300
EON
0
200
0
0
200
800
EON
400
600
tdOFF
100
EON
200
400
400
600
EON
EOFF
tdOFF
Swiching Time (ns)
Swiching Time (ns)
Energy (uJ)
Energy (uJ)
1400
1200
900
EOFF
1000
1200
1400
1000
EEOFF
OFF
1200
1400
1600
1600
0
1000
Swiching Time (ns)
Swiching Time (ns)
2200
200
1000
150
150
10
0
50
0
50
100
R G (:)
150
100
150
R G (:)
Fig.
16-17Typ.
Switching
Time
vs.vs.
RGRG
Fig.
- Typ.
Switching
Time
TJT=J =
150°C;
L=200µH;
VCE
==
600V
150°C;
L=200
µH;
V
600
CE
Fig. 16- Typ. Switching Time vs. RV
G
ICEI=
15A;
15 V
AGE
; V=GE15V
=V15
V
CE= L=200µH;
TJ = 150°C;
CE = 600V
www.irf.com
ICE= 15A; VGE= 15V
www.irf.com
0
0
10
20
30
40
IF (A)
PRELIMINARY
Fig. 21 - Typical Diode ERR vs. IF
TJ = 150°C
Typical Performance
16
10000
14
300V
Cies
1000
VGE (V)
Capacitance (pF)
12
100
10
8
6
Coes
4
Cres
2
0
10
0
20
40
60
80
400V
100
0
20
VCE (V)
Fig.Typ.
18 - Capacitance
Typ. Capacitance
Fig. 22vs. vs.
V VCE
VGE=0 V; f= 1 MHz CE
VGE= 0V; f = 1MHz
8
40
60
Q G , Total Gate Charge (nC)
19 - Typ.
Gate
Charge
vs.VVGE
Fig.19
Fig.
23 Fig.
- Typical
Gate
Charge
vs.
GE
ICE=15 A; L= 600 μH
ICE = 15A; L = 600µH
www.irf.com
IRGB/S/SL15B60KDPbF
Thermal Response ( Z thJC )
1
D = 0.50
0.20
0.1
0.10
0.05
WJ
0.01
0.02
0.01
R1
R1
WJ
W1
W1
R2
R2
W2
W2
Ci= WiRi
Ci iRi
R3
R3
W3
W3
WC
W
Ri (°C/W) Wi (sec)
0.231
0.000157
0.175
0.000849
0.201
0.011943
Notes:
1. Duty Factor D = t1/t2
2. Peak Tj = P dm x Zthjc + Tc
SINGLE PULSE
( THERMAL RESPONSE )
0.001
1E-6
1E-5
1E-4
1E-3
1E-2
1E-1
t1 , Rectangular Pulse Duration (sec)
20 - Maximum Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction-to-Case (IGBT)
Fig 24. Fig.
Maximum
Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction-to-Case (IGBT)
Z thJC )
10
D = 0.50
1
CID150660
Rev. A
0.20
1E+0
PRELIMINARY
Typical Performance
IRGB/S/SL15B60KDPbF
L
L
VCC
DUT
0
+
-
80 V
1K
DUT
Fig.C.T.2 - RBSOA Circuit
Fig.C.T.1 - Gate Charge Circuit (turn-off)
diode clamp /
DUT
Driver
L
- 5V
360V
DC
480V
Rg
DUT
Rg
Fig.C.T.3 - S.C.SOA Circuit
DUT /
DRIVER
VCC
Fig.C.T.4 - Switching Loss Circuit
R=
DUT
VCC
ICM
VCC
Rg
10
CID150660 Rev. A
Fig.C.T.5 - Resistive Load Circuit
www.irf.com
PRELIMINARY
IRGB/S/SL15B60KDPbF
30
tF
500
tF
25
400
20
300
300
10
5% V CE
5% VCE
100
0
-1 0 0
0 .0
0.5
1 .5
1530
90% ICE
90% tes
t current
1020
tes t current
10% tes t current
5%
5%VCEV C E
t RI
10%
CE
5 10
00
00
0
1.0
2040
200
200
100
100
5
E o ff L o s s
E off Loss
-0 .5
V CE (V)
200
ICE (A)
V CE (V)
15
5 % 10%
IC E ICE
tR
400
400
9 0 I% IC E
90%
CE
300
2550
500
500
ICE (A)
600
Eon
Los s
E on
Loss
-100
-100
-0.2
-5
-0.1
-5-10
0.0
0.1
t (µS )
t (µ S )
WF.1- Typ. Turn-off Loss
@ TJ = 150°C using CT.4
WF.2- Typ. Turn-on Loss
@ TJ = 150°C using Fig. CT.4
500
10
0
25
20
500
20
10
400
15
0
300
250
QRR
200
-2 0
0
100
-3 0
0
Pe a k
IR R
-4 0 00
-5-100
00
-00.00
.06
tRR
0.05
0 .0 4
0.100 . 1 4
t (µ S )
WF.3- Typ. Reverse Recovery
@ TJ = 150°C using CT.4
www.irf.com
10
CID150660 Rev. A
0.15
200
150
IC E
200
100
5-2 0
100
50
0-3 0
0
-5
-4 0
-1 0 0
10
-1 0
Peak IRR
Peak IRR
VCE (V)
VCE (V)
10 %
Pe a k
IR R
ICE (A)
tR R
300
-1 0
0
V CE
ICE (A)
0
400
0
-1 0
0
10
20
30
-5 0
t (µ S )
WF.4- Typ. Short Circuit
@ TJ = 150°C using CT.3
11
PRELIMINARY
Package Dimensions
PACKAGE TO-220-3
POS
J
N
K
D
Min
Max
A
.170
.180
4.32
4.57
B
.028
.036
.71
.91
C
.014
.021
.36
.53
D
.59
.61
14.99
15.49
E
.395
.410
10.04
10.41
F
Q
G
S
R
P
B
C
.100 TYP
.200 BSC
F
G
11
CID150660 Rev. A
2.54 TYP
5.08 BSC
J
.048
.054
1.22
1.37
K
.235
.255
5.97
6.47
L
.100
.110
2.54
2.79
M
.149
.153
3.79
3.88
N
.102
.112
2.60
2.84
P
.530
.550
13.47
13.97
Q
L
Millimeters
Max
A
E
M
Inches
Min
45˚
45˚
R
.045
.055
1.15
1.39
S
.130
.150
3.31
3.81
Recommended solder pad layout.
PRELIMINARY
Recommended Solder Pad Layout
TO-263-2
TO-220-2
TO-220-3
Part Number
Package
Marking
CID150660B
TO-220-3
CID150660
This product has not been designed or tested for
use in, and is not intended for use in, applications
implanted into the human body nor in applications
in which failure of the product could lead to death,
personal injury or property damage, including but
not limited to equipment used in the operation of
nuclear facilities, life-support machines, cardiac
defibrillators or similar emergency medical
equipment, aircraft navigation or communication or
control systems, air traffic control systems, or
weapons systems.
Copyright © 2001-2005 Cree, Inc. All rights
reserved. Permission is given to reproduce this
document provided the entire document (including
this copyright notice) is duplicated.
The information in this document is subject to
change without notice.
Cree and the Cree logo are trademarks of Cree,
Inc.
Cree, Inc.
Power Products
4600 Silicon Drive • Durham, NC 27703 • USA
Tel: 919-313-5300 • Fax: 919-313-5451
www.creepower.com
The levels of environmentally sensitive, persistent biologically toxic (PBT), persistent organic pollutants (POP), or otherwise restricted materials in this product are below the
maximum concentration values (also referred to as the threshold limits) permitted for such substances, or are used in an exempted application, in accordance with EU Directive
2002/95/EC on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (RoHS), as amended through April 21, 2006.
Page 6 • CSD06060, Rev H
This product has not been designed or tested for use in, and is not intended for use in, applications implanted into the human body nor in
applications in which failure of the product could lead to death, personal injury or property damage, including but not limited to equipment used
in the operation of nuclear facilities, life-support machines, cardiac defibrillators or similar emergency medical equipment, aircraft navigation or
communication or control systems, air traffic control systems, or weapons systems.
Copyright © 2006 Cree, Inc. All rights reserved. The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Cree, the Cree logo, and Zero
Recovery are registered trademarks of Cree, Inc.
12
CID150660 Rev. A
Cree, Inc.
4600 Silicon Drive
Durham, NC 27703
USA Tel: +1.919.313.5300
Fax: +1.919.313.5451
www.cree.com/power