Field Effect Transistors (FET)
advertisement
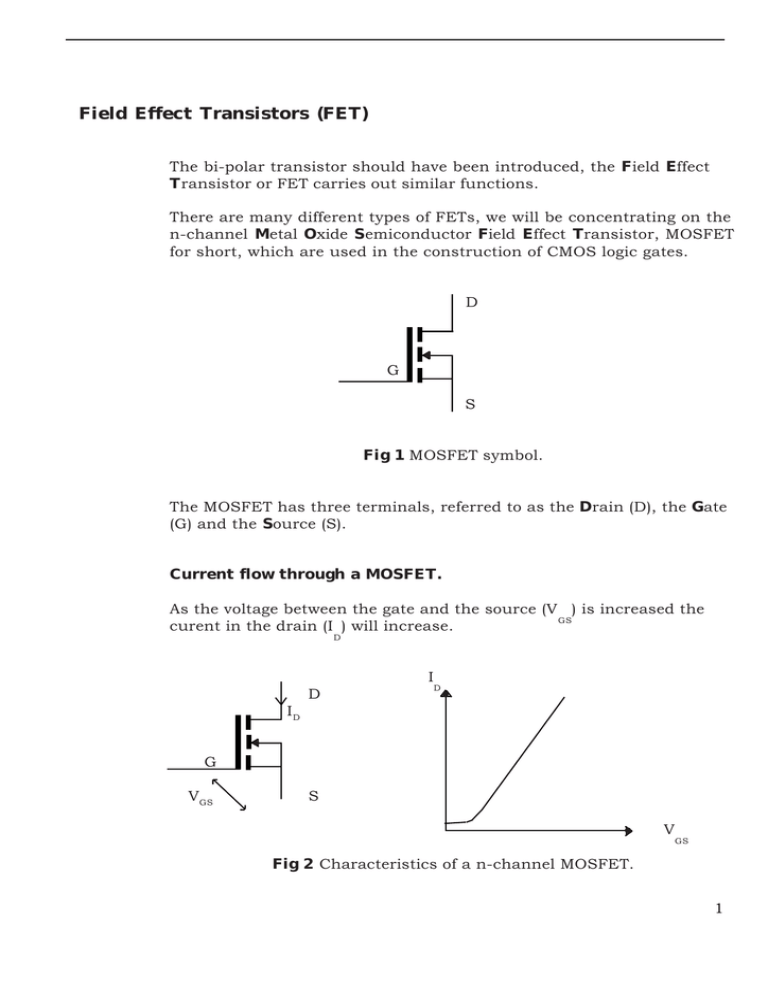
Field Effect Transistors (FET) The bi-polar transistor should have been introduced, the Field Effect Transistor or FET carries out similar functions. There are many different types of FETs, we will be concentrating on the n-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor, MOSFET for short, which are used in the construction of CMOS logic gates. D G S Fig 1 MOSFET symbol. The MOSFET has three terminals, referred to as the Drain (D), the Gate (G) and the Source (S). Current flow through a MOSFET. As the voltage between the gate and the source (V ) is increased the GS curent in the drain (I ) will increase. D I D D ID G VGS S V GS Fig 2 Characteristics of a n-channel MOSFET. 1 Unlike the bipolar transistor the current in the drain I D does not depend upon an input current, but upon a voltage difference between the gate and source V . GS It can be assumed that the gate does not draw any current as the resistance between the gate and source is greater than10 9 Ω. Switching Action of a MOSFET. +Vs Lamp (load) ID Input 0V Output Voltage V V in GS Fig 9.3 The MOSFET switch. When the input voltage (V in) is increased the drain current ID will increase. The increase in current will increase the voltage across the load, thus decreasing V . out The relationship between the voltage V GS and the drain current ID is called the transconductance (g m) and has units of AV-1 or S. gm = ID / VGS Therefore I D = g m x VGS This can be comparable with the DC current gain (h FE) of the bi-polar transistor. 2 Circuit Analysis. Example: The MOSFET shown in Fig 4 has a transconductance (g ) of 0.25S (250mS). M Calculate the minimum input voltage needed to make the bulb operate at the correct current rating. 6V 6V, 0.55A ID V IN 0V Fig 4 ID = 0.55A VGS = ID / g M VGS = 0.55 / 0.25 = 2.2 volts 3 Student example The characteristics of the MOSFET are: PTot Max W VDS Max VGS Max V V 70 100 20 g S ID Max A r DS On Ω 1.75 10 0.5 m 12 V Relay 12v, 4A Logic Systems Vin 0V What is the minimum value of Vin to operate the relay at the correct rating ? A.0.44 V C. 0.7 V B.2.3 V D. 3.0 V The function of the diode placed reverse bias across the relay is to : A protect the MOSFET when the relay energizes. B protect the MOSFET when the relay de-energizes. C protect the relay when it energizes. D protect the relay when it de-energizes. 4