Lab 1: Fabricating and Testing a Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
advertisement

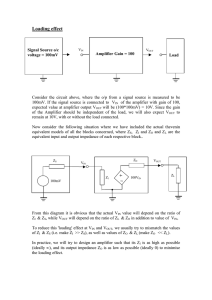
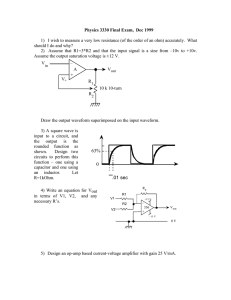
Lab 1: Fabricating and Testing a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) May 11, 2008 Department of Computer Science & Electrical Engineering CMPE 450: Capstone I University of Maryland Baltimore County Assigned : Due (Fabrication): Due (Soldering): 1 Overview This lab involves fabricating a PCB, purchasing the necessary components, soldering the parts on the board and conducting a series of tests. The lab is spread over a period of two weeks, during which the student will fabricate the board and purchase the components over the first week. In the second week, the student will complete soldering and the functional testing. This knowledge will be very useful when the student have to build and test small circuits for the Capstone project later in the course. Prerequisite “PCB Prototyping Guide” provides a detailed tutorial of the PCB fabrication design cycle from the schematic capture to fabrication1 . It is highly recommended that you familiarize with the step-by-step instructions provided for the fabrication in the guide. Part A: PCB Fabrication You will fabricate an op-amp based design. The circuit design and board layout is already completed, and the layout file will be provided to you for fabrication. This circuit is already tested hence validation is not an issue. Thus, during the debugging you can focus completely on the fabrication validation without worrying about the design and the layout validation. The design includes an op-amp-based non-inverting amplifier and square wave generator. As the name suggests, non-inverting amplifiers rectify the signal. Figure 1: Non Inverting Amplifier Square wave generators are used to generate square waves of different frequencies and duty cycle. 1 This document is available... 2 Figure 2: Square Wave Generator Fabricate the PCB Conduct the fabrication by following step-by-step instruction listed in the PCB Prototyping Guide. Compile the Bill of Materials 1. Select resistor and capacitor values for a square wave with 50% duty cycle and frequency of 1 KHz (http: //hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/electronic/etroncon.html provides a good overview of opamps) 2. Select R1 and R2 values for the non inverting amplifier to achieve a gain of 2. 3. Op-amps will be provided but you are responsible for the resistors. You can either buy them at radio shack or place the order with the TA. These components are absolute pre-requisite for the next lab session. Part B: Solder Components and Conduct Validation Instruments • DC Power Supplies (+Vcc, -Vcc and Vin) • Function Generator (Vin) • Oscilloscope (Vin and Vout) Materials • Fabricated PCB • Components listed in Bill of Materials Soldering By now you should already have the fabricated board and components ready. Solder each component into place. Once soldering is completed, conduct the following experiments listed below. Non-Inverting Amplifier 1. For Vin = 1 V, 2 V and -1 V, measure the Vout and the gain (Vout / Vin). Vin Vout Gain -1 1 2 3 2. Generate a sine wave using a function generator with frequency 1 kHz over a range of different amplitudes from 0.5V to 5V (try increments of 1 Volt). (a) Plot Vout and Vin (use a scope for measurements) over time. Square wave Generator 1. Connect Vcc and −Vcc so that the system oscillates. 2. Use the scope to capture Vout . 4