Name
Class
Date
Quick Lab
CONSUMER
Interpreting Information in a Pedigree
Organizing information is often the key to solving a problem. Tracing the hereditary
characteristics over many generations can be confusing unless the information is
well organized. In this lab, you will learn how to organize hereditary information,
making it much easier to analyze.
OBJECTIVES
Analyze a pedigree.
Construct a pedigree.
MATERIALS
• paper
• pencil
Procedure
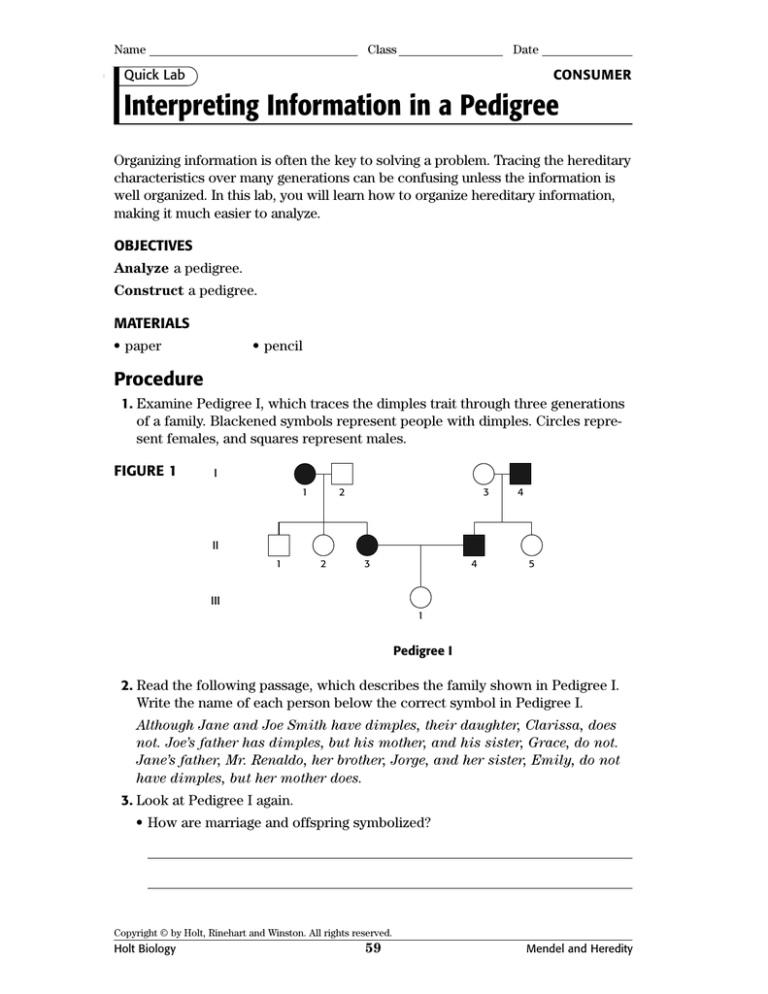
1. Examine Pedigree I, which traces the dimples trait through three generations
of a family. Blackened symbols represent people with dimples. Circles represent females, and squares represent males.
FIGURE 1
I
1
2
3
4
II
1
2
3
4
5
III
1
Pedigree I
2. Read the following passage, which describes the family shown in Pedigree I.
Write the name of each person below the correct symbol in Pedigree I.
Although Jane and Joe Smith have dimples, their daughter, Clarissa, does
not. Joe’s father has dimples, but his mother, and his sister, Grace, do not.
Jane’s father, Mr. Renaldo, her brother, Jorge, and her sister, Emily, do not
have dimples, but her mother does.
3. Look at Pedigree I again.
• How are marriage and offspring symbolized?
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Biology
Program Title
59
Mendel and
Chapter
Heredity
Title
Name
Class
Date
Interpreting Information in a Pedigree continued
• What do the Roman numerals symbolize?
4. Construct a pedigree based on the following passage about curly hair.
Andy, Penny, and Delbert have curly hair, but their mother, Mrs. Cummins,
does not. Mrs. Giordano, Mrs. Cummin’s sister, has curly hair, but her parents, Mr. & Mrs. Lutz, do not. Deidra and Darlene Giordano have curly
hair, but their sister, Katie, like her father, has straight hair.
Analysis and Conclusions
1. Summarizing Observations What type of information does a pedigree
contain?
2. Evaluating Models What advantages does a pedigree have over a written
passage?
3. Interpreting Information Take another look at Pedigree I. A genetic counselor analyzing Pedigree I suggests that a person only needs to have one
dominant allele for dimples (D) in order to have dimples. If this is true, what
is the genotype of person 1 in the third generation of Pedigree I?
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Biology
Program Title
60
Mendel and
Chapter
Heredity
Title
TEACHER RESOURCE PAGE
Name
Class
Date
Quick Lab
CONSUMER
Interpreting Information in a Pedigree
Organizing information is often the key to solving a problem. Tracing the hereditary
characteristics over many generations can be confusing unless the information is
well organized. In this lab, you will learn how to organize hereditary information,
making it much easier to analyze.
OBJECTIVES
Analyze a pedigree.
Construct a pedigree.
MATERIALS
• paper
• pencil
Procedure
1. Examine Pedigree I, which traces the dimples trait through three generations
of a family. Blackened symbols represent people with dimples. Circles represent females, and squares represent males.
FIGURE 1
I
1
2
3
Mrs. Renaldo Mr. Renaldo
Mrs. Smith
4
Mr. Smith
II
1
2
3
Jorge Emily Jane
4
5
Joe
Grace
III
1
Clarissa
Pedigree I
2. Read the following passage, which describes the family shown in Pedigree I.
Write the name of each person below the correct symbol in Pedigree I.
Although Jane and Joe Smith have dimples, their daughter, Clarissa, does
not. Joe’s father has dimples, but his mother, and his sister, Grace, do not.
Jane’s father, Mr. Renaldo, her brother, Jorge, and her sister, Emily, do not
have dimples, but her mother does.
3. Look at Pedigree I again.
• How are marriage and offspring symbolized?
A straight line connecting a circle and square indicates a marriage, with a
descending line leading to any offspring.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Biology
Program Title
77
Mendel and
Chapter
Heredity
Title
TEACHER RESOURCE PAGE
Name
Class
Date
Interpreting Information in a Pedigree continued
• What do the Roman numerals symbolize?
Roman numerals identify each generation.
4. Construct a pedigree based on the following passage about curly hair.
Andy, Penny, and Delbert have curly hair, but their mother, Mrs. Cummins,
does not. Mrs. Giordano, Mrs. Cummin’s sister, has curly hair, but her parents, Mr. & Mrs. Lutz, do not. Deidra and Darlene Giordano have curly
hair, but their sister, Katie, like her father, has straight hair.
I
Mr. Lutz
Mrs. Lutz
II
Mr. Cummins
Mrs. Cummins
Mrs. Giordano
Mr. Giordano
III
Andy
Penny Delbert
Diedra Darlene Katie
Analysis and Conclusions
1. Summarizing Observations What type of information does a pedigree
contain?
A pedigree contains hereditary information, which is genetic information
about what traits are passed from one generation to the next.
2. Evaluating Models What advantages does a pedigree have over a written
passage?
Answers will vary, but should indicate that a pedigree organizes hereditary
information visually, making it easier to interpret than information in a
written passage.
3. Interpreting Information Take another look at Pedigree I. A genetic counselor analyzing Pedigree I suggests that a person only needs to have one
dominant allele for dimples (D) in order to have dimples. If this is true, what
is the genotype of person 1 in the third generation of Pedigree I?
The genotype of person 1 in the third generation is dd. If dimples are a
dominant trait, the person would have to have two recessive alleles to not
have dimples.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Biology
Program Title
78
Mendel and
Chapter
Heredity
Title