TECH
BRIEF
ESD Protection
Video Input and Output Lines
Background
Electronic systems are sensitive to
both external and internal sources
of overvoltage transients. This can
be in the form of external ElectroStatic Discharge (ESD) or internally
generated Electrical Fast Transients
(EFT). The purpose of this application brief is to detail Video port
protection.
current loads, (such as the flyback
transformer) pump lasers or other
harsh environments. The EFT can be
introduced via the power supply or
inductively coupled onto a signal
line. Regardless of the method of
introduction, the results may be soft
or hard failures similar to ESD failures.
Circuit Examples
The Solution
The Problem
Externally generated ESD pulses
are introduced into the Video port
and travel through the connector
onto the system board. Once on
the board, they will propagate down
the signal lines toward the integrated
circuits(IC). Most ICs are designed
with 2000 volts of internal ESD
protection.
However it is not
uncommon to measure over 8000
volt ESD transients in consumer
environments. Without sufficient
protection, the Video system can
experience visual distortion or
corrupted data. In addition, the IC
could be permanently damaged
rendering the whole system inoperable.
protection:
• Computer (laptop / desk top)
• Graphic card
• Set-top box
• Video game console (Xbox,
Playstation 2)
In order to provide the IC with
protection against ESD and EFT
transients, the use of suppression
products is recommended. The
suppressors are installed between
the signal line and the power supply
or shield ground (parallel connection) to shunt the transient from the
signal line to AC ground.
Examples of products which can
benefit from Video port transient
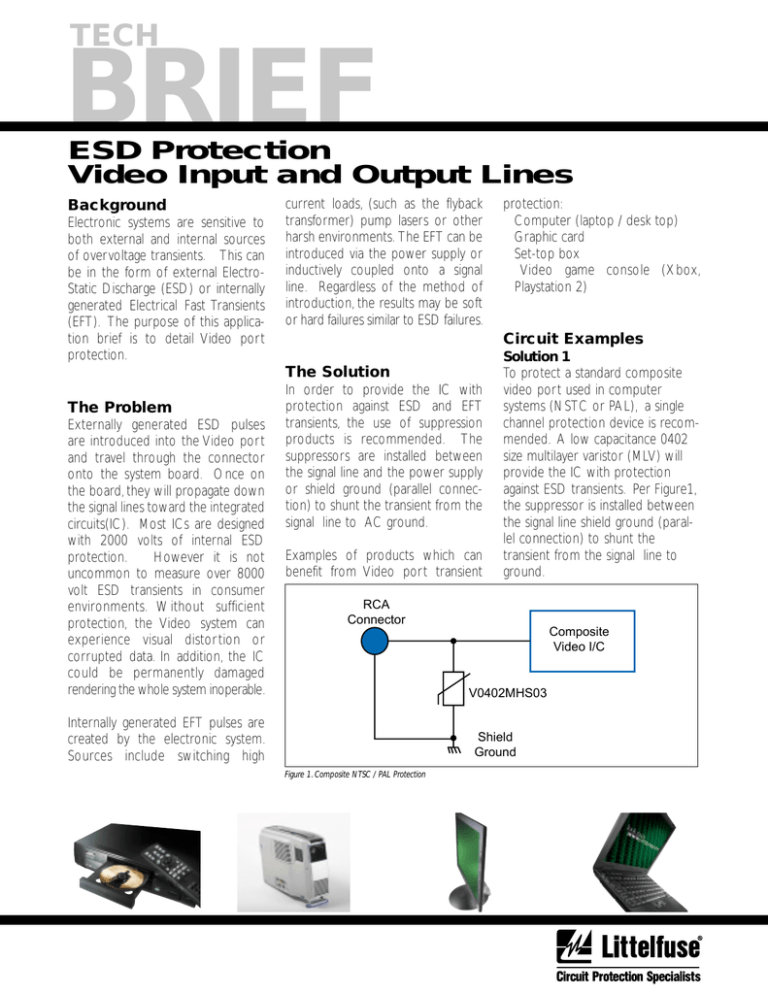
Solution 1
To protect a standard composite
video port used in computer
systems (NSTC or PAL), a single
channel protection device is recommended. A low capacitance 0402
size multilayer varistor (MLV) will
provide the IC with protection
against ESD transients. Per Figure1,
the suppressor is installed between
the signal line shield ground (parallel connection) to shunt the
transient from the signal line to
ground.
RCA
Connector
Composite
Video I/C
V0402MHS03
Internally generated EFT pulses are
created by the electronic system.
Sources include switching high
Shield
Ground
Figure 1. Composite NTSC / PAL Protection
Solution 2
Figure 2 shows the SP0502AAHT
providing ESD protection of a SVideo port. The integrated single
chip solution consists of low capacitance (3pF) steering diodes to direct
the overvoltage transient into either
the power supply (Vcc) or ground.
S-Video
Connector
S-Video
Controller
SP0502AAHT
VCC
Y (Intensity)
C (Color)
GND (Y/C)
Figure 2. S-Video Protection
Solution 3
Figure 3 shows the integrated
SP724AHT providing ESD and EFT
protection of a Component Video
port. The low capacitance (3pF)
steering diodes direct the overvoltage transient into either the power
supply (Vcc) or ground. An alternative solution is to replace the
SP724AHT integrated device with
three MLVs as show in figure 1.
Component
Video RCA
Connectors
VCC
Y (Intensity)
Pb (Color Difference)
Pb (Color Difference)
Shield
Ground
GND (Y/C)
Shield
Ground
Figure 3. Component Video Protection
SP721
Graphics
Controller
Outside World
Video
Port
Solution 4
Figure 4 shows the SP721 providing
ESD and EFT protection of a standard VGA port for analog RGB
video. As in figures 2 and 3, the low
capacitance (3pF) steering diodes
direct the overvoltage transient into
either the power supply (Vcc) or
ground.
S-Video
Controller
SP724AHT
Figure 4. VGA Port Protection
Littelfuse, Inc.
800 E. Northwest Highway
Des Plaines, IL 60016
(847) 824-1188
www.littelfuse.com/esd
Specifications, descriptions and illustrative material in this literature are as accurate as known at time of publication, but are
subject to change without notice. Littelfuse is a registered trademark of Littelfuse Incorporated.
EC632
Copyright © 2001 Littelfuse, Inc., All Rights Reserved. Printed in U.S.A. JANUARY 2002




