Distributed and Cloud Computing
K. Hwang, G. Fox and J. Dongarra
Chapter 9: Ubiquitous Clouds and
The Internet of Things
(suggested for use in 5 lectures in 250 minutes)
Prepared by Kai Hwang
University of Southern California
April 5, 2012
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9-1
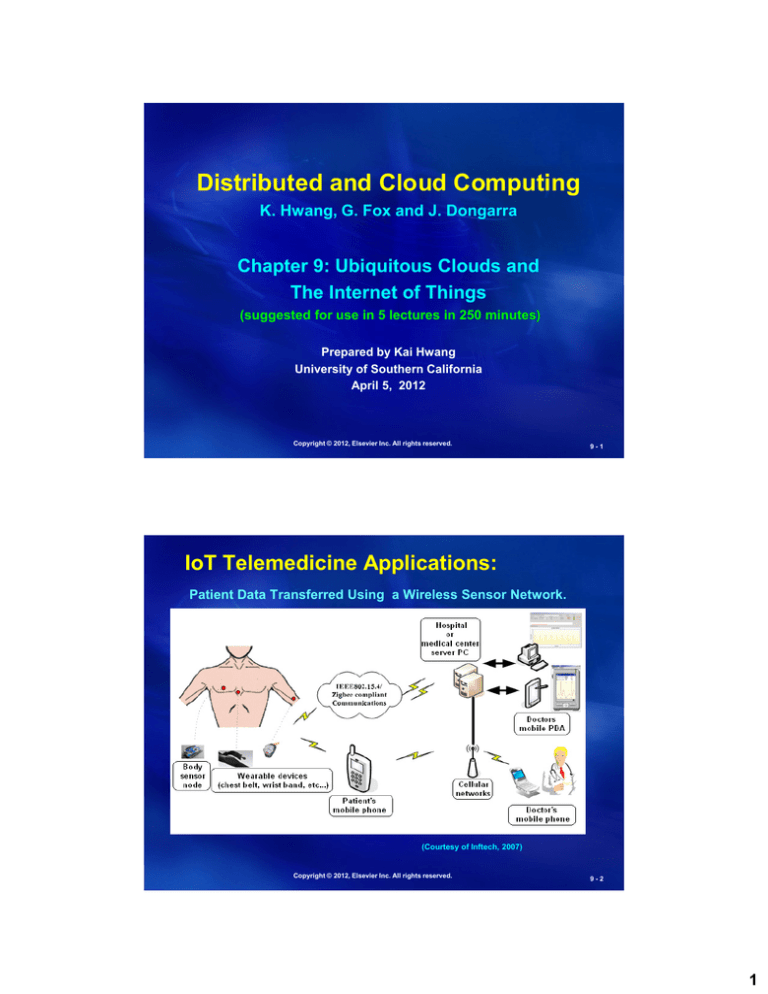
IoT Telemedicine Applications:
Patient Data Transferred Using a Wireless Sensor Network.
(Courtesy of Inftech, 2007)
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9-2
1
ZigBee Applications (Wireless
Home-Area Networks, WHAN)
security
security
HVAC
HVAC
AMR
AMR
lighting
lightingcontrol
control
access
accesscontrol
control
patient
monitoring
fitness
monitoring
TV
VCR
DVD/CD
remote
BUILDING
AUTOMATION
CONSUMER
ELECTRONICS
ZigBee
PERSONAL
HEALTH CARE
asset mgt
process control
environmental
energy mgt
Wireless Control that
Simply Works
INDUSTRIAL
CONTROL
RESIDENTIAL/
LIGHT
COMMERCIAL
CONTROL
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
PC &
PERIPHERALS
mouse
keyboard
joystick
security
security
HVAC
HVAC
lighting
control
lighting
control
access
control
access
control
lawn
& garden
lawn
& garden
irrigation
irrigation
9-3
Slide 3
Retail and logistics : How RFID Works in Business Sales ?
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9-4
2
Smart Building Using IOT Technology
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9-5
Smart Power Grid
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9-6
3
Current Research Challenges:
Multi-core-CPU and many-core GPU and beyond :
Heterogeneous (asymmetric) chip multiprocssors
Virtualization support for cloud computing over
distributed and automated datacenters
Cloud security, data integrity, privacy and
copyright protection, and trust management
in clouds and future Internet
Advances in RFID tracking, sensor networks, and
GPS technologies to build the Internet of things
Ubiquitous cloud computing and social networking
using the clouds in the age of Internet of things
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9-7
Example 1:
Game Cloud
built at USC
GamePipe Lab,
No.1 Game program
among 10 in the USA
(Courtesy of Zhao, Hwang, and Villeta, Feb. 2012 [7])
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9-8
4
Reduction of Gaming Latency and
Improvement of the QoS and QoE (Frame Rate)
on The Game Cloud at USC GamePipe Lab. 2012
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9-9
Example 2: MapReduce Skyline
Composition of Web Services
in Inter-Cloud Applications
(Courtesy of L. Chen, K. Hwang, and J. Wu, Jan. 2011 [6])
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9 - 10
5
Reduction of Web Service Composition Time
from 929 ms to 220 ms using fewer Skyline representatives
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9 - 11
Example 3: Internet of Things: Sensor Grids
A pleasingly parallel example on Clouds
A sensor (“Thing”) is any source or sink of time series
In the thin client era, smart phones, Kindles, tablets, Kinects,
web-cams are sensors
Robots, distributed instruments such as environmental
measures are sensors
Web pages, Googledocs, Office 365, WebEx are sensors
Ubiquitous Cities/Homes are full of sensors
They have IP address on Internet
Sensors – being intrinsically distributed are Grids
However natural implementation uses clouds to consolidate and
control and collaborate with sensors
Sensors are typically “small” and have pleasingly parallel cloud
implementations
(Courtesy of Geoffrey Fox, 2012)
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
12
9 - 12
6
Sensors as a Service (SaaS)
Output
Sensor
Sensors as a Service
A larger sensor ………
Sensor
Processing as
a Service
(MapReduce)
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
(Courtesy of Geoffrey Fox, 2012)
9 - 13
Mobility Support and Security Measures
for Mobile Cloud Computing
Cloud
Service
Models
Infrastructure
Cloud
(The IaaS
Model)
Mobility Support and
Data Protection Methods
Platform Cloud
(The PaaS
Model)
Hardware and Software
Measures for Cloud Security
Special air interfaces
Mobile API design
File/Log access control
Data coloring
Hardware/software root of trust,
Provisioning of virtual machines,
Software watermarking
Host-based firewalls and IDS
Wireless PKI ,
User authentication,
Copyright protection
Disaster recovery
Network-based firewalls
and IDS
Trust overlay network
Reputation system
OS patch management
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9 - 14
7
Cloudlets- A trusted, VM-based, and Resource-Rich Portal for Upgrading
Mobile Devices with Cognitive Abilities for Mobile access of the cloud to explore LocationAware Cloud Applications such as : Opportunity Discovery, Fast Information Processing,
and Intelligent Decision Making on The Road, etc.
(Courtesy of SAtyanarayanan, et al. “The Case of VM-based Cloudlets in Mobile Computing”,
IEEE Pervasive Computing, Vol.8, No. 4, April 2009)
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9 - 15
Cloudlet Makes It Possible for Mobile Devices to
Access the internet Easily for Obtaining Mobile and
Cost-Effective Computing Services
Both mobile devices and centralized clouds or datacenters are limited in their own ways.
Handsets are limited by resource proverty, etc while the distance cloud has the WAN
latency and collision issues with too many clients login, simulteneously.
Widely deployed Cloudlets enable distributed cloud computing
and handling at convenient stores, class rooms, or anyone while on the move.
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9 - 16
8
Fast VM synthesis
(in less than 100 sec on
the Kimberlaey
prototype at CMU)
makes it possible to
build VM overlay in
transient cloudlets, that
is customized to bind
cloud resources in
distance to satisfy the
user need.
Trust and security
issues are major factors
in Cloudlet deployment.
(Courtesy of SAtyanarayanan, et al. 2009)
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
9 - 17
9


