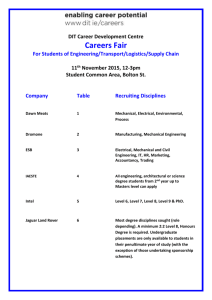
Tutorial OpAmps

OpAmps Circuits
Tutorial
www.electronics.dit.ie
Question 1
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q1- Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q1 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Question 2
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q2 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q2 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q2 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q2 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Question 3
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q3 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q3 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q3 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q3 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q3 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Question 4
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q4 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q4 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q4 - Solution
www.electronics.dit.ie
Q4 - Solution
Question 5
An op-amp-based inverting integrator is measured at 100Hz to have an voltage gain of -100V/V. At what frequency is its gain reduced to
-1V/V? What is the integrator time constant?
Solution:
The gain is given by: G (
ω
)
=
1
ω
RC that is
G ( 200
π
)
=
1
200
π
RC
=
100 therefore
G (
ω
)
=
1
ω
RC
=
20000
π
2
π f
=
1 V / V
τ =
RC
= f
1
20000
π
=
10000 Hz www.electronics.dit.ie
www.electronics.dit.ie
Question 5A
An op-amp-based inverting integrator is measured at 100Hz to have an voltage gain of -100V/V. At what frequency is its gain reduced to
-1V/V? What is the integrator time constant?
Solution:
For integrator, the gain decays 20dB/decades. That is, when frequency increase by a factor, the gain decreases by the same factor. Therefore, when the gain decrease from 100V/V by factor of 1/100 to -1V/V, the frequency should increase by 100 times. That is, at 10000Hz the gain will reduced to -1V/V.
Question 6
A differentiator uses an ideal op-amp, a 10K resistor, and a 0.01uf capacitor. What is the frequency f o at which its input and output sine wave signals have equal magnitude? What is the output signal for for a 1-V p-p sine wave input with frequency equal to 10f o
?
Solution:
The transmission function of differentiator is given by:
G (
ω
)
= −
R
1 j
ω
C
= − j
ω
RC
= − j
ω ×
10000
×
0 .
01
×
10
−
6 = − j 0 .
0001
ω for G (
ω
0
)
=
0 .
0001
ω
0
=
1
ω
0
=
10000 f
0
=
10000 / 2
π when f=10f o G ( 10
×
10000 )
=
0 .
0001
×
100000
=
10 www.electronics.dit.ie
Question 7
7.
A weighted summer circuit using an ideal op-amp has three inputs using 100K resistors and a feedback resistor of 50K. A signal v1 is connected to two of the inputs, while a signal v2 is connected to the third. Express v0 in terms of v1 and v2. If v1=3V, v2=-3V, what is v0?
Solution: v
0
= −
R
R f
1 v
1
+
R
R f
2 v
2
+
R
R f
3 v
3
= −
50
100 v
1
+
50
100 v
2
+
50
100 v
1
= −
v
1
+
1
2 v
2
= −
( 3
−
1 .
5 )
= −
1 .
5 V www.electronics.dit.ie
Question 8
Design an op-amp circuit to provide an output v
0
= −
3 v
1
+
1
2 v
2
Choose relatively low values of resistors but ones for which the input current (for each source) does not exceed 0.1mA for 2-V input signals.
Solution:
The input resistors can be determined as:
R
R
1 f =
3 and
R f
R
2
=
1
2
⇒
R
2
=
6 R
1
R
1
= v
1 i
1
≥
2 V
0 .
1 mA
=
20 K
Ω
R
2
≥
2 V
0 .
1 mA
=
120 K
Ω
, R f
=
60 K
Ω www.electronics.dit.ie
Question 9
9
For the difference amplifier use superposition to find v0 in terms of the input voltages v1 and v2: v
1
=
10 sin( 2
π ×
60 t )
−
0 .
1 sin( 2
π ×
1000 t ), Volts v
2
=
10 sin( 2
π ×
60 t )
+
0 .
1 sin( 2
π ×
1000 t ), Volts
Solution:
Disabling v1, the circuit is a non-inverting amplifier, therefore v
02
=
( 1
+
10 R
) v
2
R
=
11 v
2 www.electronics.dit.ie
Question 9 (cont.)
9
Solution:
Disabling v2, the circuit is an inverting amplifier, therefore v
01
= −
10 R
R v
1
= −
10 v
2
Therefore the total output should be: v
0
= v
01
+ v
02
=
11 v
1
−
10 v
2 v
0
= sin( 2
π ×
60 t )
−
2 .
1 sin( 2
π ×
1000 t ), Volts www.electronics.dit.ie