Electronics - David Hartkop
advertisement

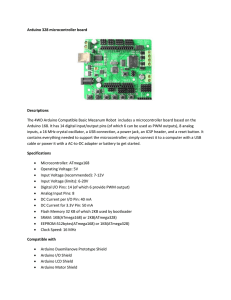
PCCLD Electronics Workshop introducing microcontrollers Document released as Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 3.0 Online Resources Basic Electronics Resources A fun basic electronics tutorial on Instructables: http://www.instructables.com/id/Basic-Electronics/?ALLSTEPS “Basic Electronics” published online by NYU School of Engineering: http://engineering.nyu.edu/gk12/amps-cbri/pdf/Basic%20Electronics.pdf Some more advanced electronics tutorials and info: http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/ Arduino Microcontroller Resources Tutorials from the Arduino Home Page http://arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/HomePage Electronics and Arduino tutorials on Sparkfun https://www.sparkfun.com/tutorials Arduino and peripherals tutorials on Adafruit https://learn.adafruit.com/search?q=tutorials Video tutorial series on YouTube by Open Source Hardware Group https://youtu.be/09zfRaLEasY 1 What are Microcontrollers? “A microcontroller (sometimes abbreviated µC, uC or MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit containing a processor core, memory, and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of Ferroelectric RAM, NOR f lash or OTP ROM is also often included on chip, as well as a typically small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to themicroprocessors used in personal computers or other general purpose applications.” From Wikipediia at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microcontroller A small computer that can be built into other electronic things! A microcontroller built into a device for a specif ic purpose is called an embedded system. Some example devices that have embedded systems include the following: Microwave oven DVD Player Musical gift card Digital camera Car (if it has a computer) Wristwatch 3D printer 2D printer Cash register Vending machine Heart pacemaker Lithium rechargeable battery A self contained robot 2 A microcontroller in a system Driver Circuits Sensors Turn small signals into bigger signals for some action in the real world. Create an electrical signal from something in the real world. Software Output pins Input pins Microcontroller Examples of embedded systems: Buttons -> microwave’s controller -> display & radar unit Buttons -> vending machine’s controller -> dispenser motors RPM sensor -> car’s fuel injection controller -> fuel injectors Video camera -> robot’s controller -> robot hand motors 3 A general setup Laptop Computer Has the ‘development environment’ for programming the Arduino. USB Cable Lets us download software into the Arduino. Arduino Microcontroller Runs the program it is given. Can receive I/O from its pins and communicate back to the laptop. Can also run without the laptop on batteries. Hookup Wires Connect pins of the Arduino to components on a breadboard. Breadboard Makes it easy to connect together different components. Electronic Components Various electronic parts with specif ic functions. Can be sensors or output devices or some intermediary part. They can be connected to a breadboard. 4 The Arduino UNO microcontroller USB Connector Power Input 9-12v DC Reset button Computer-to-Arduino Communication pins Powered pins Digital I/O & Pulse width modulation (PWM marked with ~ ) Analog inputs (or digital outputs) ATmega328 Microprocessor chip Arduino-to-Arduino Communication pins 5 Components in the kit 1 Small Breadboard 2 Large Breadboard 3 8x8 LED matrix 4 4-character LED display 5 10 conductor female pin ribbon cable 6 Hook up wires 7 7 segment LED display x 2 8 strip of straight header pins 9 strip of 90 degree header pins 11 variable reisistor 50Kohm 12 Ultrasonic Molule 13 USB Cable 14 LM 35 temperature sensor x 1 15 Phototransistor x 1 16 dynamic microphone/speaker 17 piezo buzzer 18 LED, Rec x 4 19 LED, Green x 4 20 LED, Blue x 4 21 Photo resistor x 3 22 Tactile surface mount pushbutton x 8 23 Key Pad 24 Arduino Uno 25 tilt switch x 2 26 Joystick 27 Arduino Uno development shield 28 remote cotnrol transmitter 29 IR remote cotnrol receiver 29 3-Color LED module 30 SPDT relay module 31 9v battery pack 32 Display Module 33 resistors, assorted resistances 34 Micro Servo Chip 74HC595N 8-bit shift register (not pictured) 6 1 2 5 3 4 6 7 8 10 9 11 12 13 15 16 14 17 18 24 22 21 23 19 25 26 20 27 28 29 31 30 32 33 34 7 The breadboard is your friend! What it looks like: How it is wired: busses Terminal strips (or rows) 8 The Arduino development environment The development environment is a program that runs on a desktop computer and helps in the process of writing computer code for the Arduino. The Arduino development environment is called Arduino. It appears as the following window: Individual software programs that you write for the Arduino are called ‘sketches.’ The Arduino development environment makes it easy to f n i d and save sketches by organizing them into a ‘Sketchbook’ on your computer. For a complete explanation of the Arduino development environment, visit the Arduino site here: http://arduino.cc/en/Guide/Environment 9 Electronic components & symbols 10 11 Some fun ideas! 3D Printers Creative modif ied products Drones LED signs Robot projects 12 Video game consoles