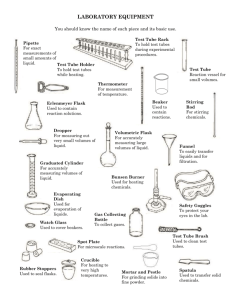
Triple Beam Balance Graduated Cylinder Test Tube Beaker Petri
advertisement

Triple Beam Balance Graduated Cylinder Test Tube Beaker used to measure the mass of solid objects. It has three beams that each measure mass to a different unit place (ones, tens, hundreds). Units of mass include milligrams, grams, and kilograms. used to measure the volume of liquids in milliliters (mL) or liters (L). It is read by looking at the very bottom of the curve of liquid in the cylinder. This curve of liquid is called a meniscus. a long, narrow type of glassware in which liquids can be stored and heated. These have round bases and are stored in test tube racks or mounted on test tube stands. a type of glassware. It can be used to store liquids, heat liquids, and measure the volumes of liquids. They have broad, flat bases. These usually measure liquid volumes in milliliters (mL). Petri Dish most often used for growing cultures of microorganisms, such as bacteria or mold. They may also be used as containers in the lab. Hot Plate a type of lab equipment used to heat substances (usually liquids). It has a flat platform where a beaker containing a liquid can be placed. Ruler, Meter Stick, and Tape Measure Spring Scale Compass are used to measure length. These tools usually have two edges—one that measures in metric units (millimeters, centimeters, and meters), and one that measures in U.S. system units (inches and feet). used to measure the weight, or gravitational force, of an object. It is used by attaching an object to the hook at the end of the scale, then the weight is displayed on the tube of the scale in Newtons (N) or pounds (lb). a tool that detects magnetic fields. When no local fields are present, this will detect Earth's magnetic field. The arrow this tool generally points North, so a person using it can tell which direction (North, South, East, or West) he or she is facing. Microscope used to view objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, such as cells. Binoculars are used for seeing objects that are distant, but not as far away as space. Hand Lens Telescope used to look at objects up close. It makes objects appear larger. is used to view objects that are very far away, such as planets and moons. Stopwatch is used to measure time in seconds and minutes. Thermometer used to measure temperature in either °C or °F. This tool is read by looking at the number that is displayed at the top of the red line inside the tool. anemometer used to measure wind speed wind vane used to measure wind direction. barometer used to measure air pressure. rain gauge Spectroscopes Erlenmeyer Flask a tool used for measuring the amount of rain that falls in a given period of time. devices that separate electromagnetic radiation into different wavelengths. a type of laboratory flask with a flat bottom, a conical body, and a cylindrical neck. Triple Beam Balance Graduated Cylinder Test Tube Beaker Petri Dish Hot Plate Ruler, Meter Stick, and Tape Measure used to measure the mass of solid objects. It has three beams that each measure mass to a different unit place (ones, tens, hundreds). Units of mass include milligrams, grams, and kilograms. used to measure the volume of liquids in milliliters (mL) or liters (L). It is read by looking at the very bottom of the curve of liquid in the cylinder. This curve of liquid is called a meniscus. a long, narrow type of glassware in which liquids can be stored and heated. These have round bases and are stored in test tube racks or mounted on test tube stands. a type of glassware. It can be used to store liquids, heat liquids, and measure the volumes of liquids. They have broad, flat bases. These usually measure liquid volumes in milliliters (mL). most often used for growing cultures of microorganisms, such as bacteria or mold. They may also be used as containers in the lab. a type of lab equipment used to heat substances (usually liquids). It has a flat platform where a beaker containing a liquid can be placed. are used to measure length. These tools usually have two edges—one that measures in metric units (millimeters, centimeters, and meters), and one that measures in U.S. system units (inches and feet). Spring Scale Compass Microscope Binoculars Hand Lens Telescope Stopwatch used to measure the weight, or gravitational force, of an object. It is used by attaching an object to the hook at the end of the scale, then the weight is displayed on the tube of the scale in Newtons (N) or pounds (lb). a tool that detects magnetic fields. When no local fields are present, this will detect Earth's magnetic field. The arrow this tool generally points North, so a person using it can tell which direction (North, South, East, or West) he or she is facing. used to view objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, such as cells. are used for seeing objects that are distant, but not as far away as space. used to look at objects up close. It makes objects appear larger. is used to view objects that are very far away, such as planets and moons. is used to measure time in seconds and minutes. Thermometer used to measure temperature in either °C or °F. This tool is read by looking at the number that is displayed at the top of the red line inside the tool. anemometer used to measure wind speed wind vane used to measure wind direction. barometer used to measure air pressure. rain gauge Spectroscopes Erlenmeyer Flask a tool used for measuring the amount of rain that falls in a given period of time. devices that separate electromagnetic radiation into different wavelengths. a type of laboratory flask with a flat bottom, a conical body, and a cylindrical neck.