Stress Force per unit cross-sectional area, unit = Nm
advertisement
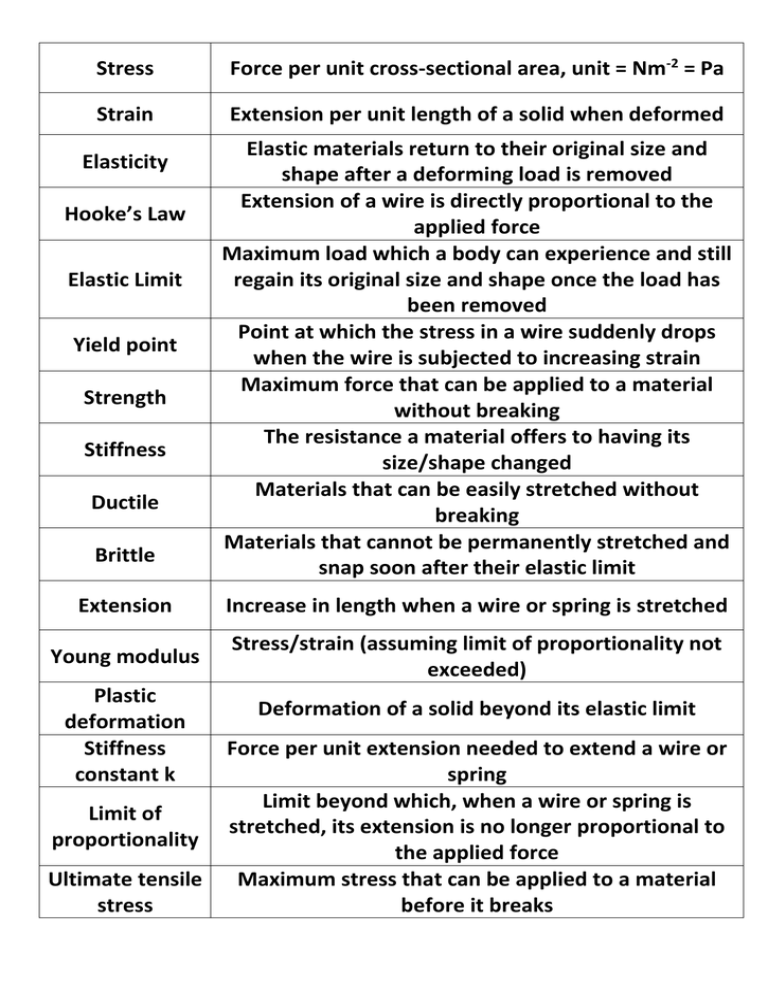
Stress Force per unit cross-sectional area, unit = Nm-2 = Pa Strain Extension per unit length of a solid when deformed Elasticity Hooke’s Law Elastic Limit Yield point Strength Stiffness Ductile Brittle Elastic materials return to their original size and shape after a deforming load is removed Extension of a wire is directly proportional to the applied force Maximum load which a body can experience and still regain its original size and shape once the load has been removed Point at which the stress in a wire suddenly drops when the wire is subjected to increasing strain Maximum force that can be applied to a material without breaking The resistance a material offers to having its size/shape changed Materials that can be easily stretched without breaking Materials that cannot be permanently stretched and snap soon after their elastic limit Extension Increase in length when a wire or spring is stretched Young modulus Stress/strain (assuming limit of proportionality not exceeded) Plastic deformation Stiffness constant k Limit of proportionality Ultimate tensile stress Deformation of a solid beyond its elastic limit Force per unit extension needed to extend a wire or spring Limit beyond which, when a wire or spring is stretched, its extension is no longer proportional to the applied force Maximum stress that can be applied to a material before it breaks