Lecture 6
advertisement

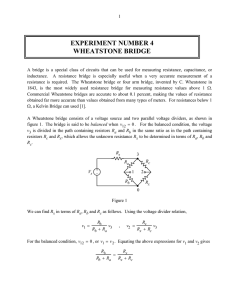
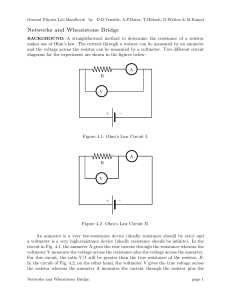
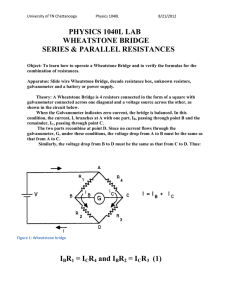
Lecture 6: Chapter 2, Part 4 Matthew Shuman 1 1.1 Measuring Voltage and Current — Not in Text Ammeter An ammeter is used to measure current. If the gauge is 50mV at 1mA, what is the value of R necessary to measure 2A? Figure 1: This is how an analog ammeter is constructed 1.2 Voltmeter A voltmeter is used to measure voltage. If the gauge is 50mV at 1mA, what is the value of R necessary to measure 20V? Figure 2: This is how an analog voltmeter is constructed 1.3 Digital Multimeter Dissection of a DMM during lecture. 1 2 Measuring Resistance - The Wheatstone Bridge — Not in Text A Wheatstone Bridge is useful for measuring variable resistances. There are three types of variable resistors. 1. Thermistor 2. Photoresistor 3. Strain Gauge Figure 3: A Wheatstone Bridge is just two voltage dividers ENGR 201 3 Delta-to-Wye (Pi-to-Tee) Equivalent Circuits — Section 2.7 in Text Combining the resistors in a Wheatstone Bridge does not work, because there are no resistors in simple parallel or series combinations. A Wye-to-Delta or Delta-to-Wye conversion is necessary for this simplification. Figure 4: This shows the labeling of resistors in a wye-delta transformation. Use these equations to convert Y to ∆. Ra = R1 R2 + R2 R3 + R3 R1 R1 (1) Rb = R1 R2 + R2 R3 + R3 R1 R2 (2) Rc = R1 R2 + R2 R3 + R3 R1 R3 (3) R1 = Rb Rc Ra + Rb + Rc (4) R2 = Ra Rc Ra + Rb + Rc (5) R3 = Ra Rb Ra + Rb + Rc (6) Use these equations to convert ∆ to Y. ENGR 201