Blooms Taxonomy in P2 - James Gillespie`s Primary School
advertisement

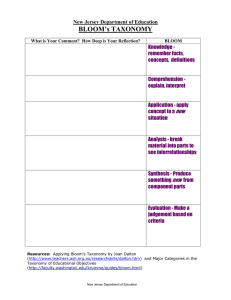
Blooms Questioning Cards based on the Taxonomy Chart Remembering Questions: Who were the characters? When & where did the story take place? List the main events in the correct sequence What happened after…? How many…? Who was it that…? When did…..? Which is true or false…? Make a facts chart using information about a character/s or the setting Understanding Questions: Can you summarize the chapter / story in your own words? Who do you think…? Can you explain why…? What words in the chapter suggest…? Can you find a word which means…? What events in the story show / suggest…? How might you describe…? Can you predict what might happen after …? Make a story board showing the sequence of main events. Applying Questions: What examples can you find from the text to explain…? Which words/phrases would you select from the text to explain…? What do you think might have happened if…? What 3 questions would you ask in an interview with….? What important messages do you think the author has given? Have you, or someone you know, had the same kind of experience/s as the characters in the story? Explain... Make up a puzzle or game using information from the story. Analysing Questions: How were the events in this story similar to …? What was the problem with…? What is the theme of the story? What evidence can you find in the text to suggest…? How is … similar to …? What is the relationship between…? Make a flow chart to showing the main events What conclusions might you make about …? What do you see as other possible outcomes / endings ? What was the turning point in this story? Evaluating Questions: Was the main character good or bad? Explain List 5 strengths & 5 weaknesses of the main character or plot Can you think of a better solution to…? How might you have dealt with …? What change/s to………. would you recommend? Do you agree with… / the way in which…… ? Do you see any qualities in……..that you can identify with? What have you learned from reading this story…? Creating Questions Can you make up your own short story including the same characters ? Can you create a new character for the story? Can you think of a new title for the book? Can you design a new cover for the book? Rewrite the ending of the story changing it from happy to sad or vice versa. Compose a song or rhyme relating to part of the story. James Gillespie’s Primary School “The purpose of education is to change the thoughts, feelings and actions of pupils” Benjamin Bloom Creating Evaluating Analysing Applying Understanding Robyn Rutherford & Alison Carson Class Teachers James Gillespie’s Primary School Whitehouse Loan Edinburgh Remembering In Primary 2, we are working hard to develop good comprehension and thinking skills in our pupils. We encourage the children to think for themselves, listen, analyse and interpret information independently. One tool which we will be using to promote and develop these skills is Bloom’s Taxonomy. This booklet aims to provide you with useful suggestions as to how you might support and enhance the development of your child’s thinking skills at home. What is Bloom’s Taxonomy? Bloom’s Taxonomy was originally created by a psychologist, Benjamin Bloom in the 1950s. Bloom identified different intellectual levels of thinking that are vital for learning. In order to facilitate development and progression, and to support the acquisition of thinking skills, Bloom devised a questioning taxonomy (model). This model is frequently displayed as a pyramid and was updated in the 1990s to reflect modern educational needs. The pyramid is as follows: The Big Six Explained Bloom’s Taxonomy in School As the pyramid illustrates, there are six levels of thinking: the simplest forms at the base progressing to the more complex at the top. During Terms 3 and 4 we aim to develop thinking skills across the curriculum. Remembering: Remembering questions are the most frequently asked questions and require children to think about the who, what, where, when and why of a subject. These questions only require children to recall information directly from the text. Understanding: When children move on from remembering questions, they are required to explain ideas and concepts in their own words. Applying: When asked to apply, children are Creating Evaluating Analysing encouraged to think and use what they have learned to resolve a situation or solve a new problem. A good example of this would be to ask your child ‘What might have happened if?’ Applying Understanding Remembering Analysing: Children should be encouraged to break down information into parts to support their understanding and be encouraged to talk about the reasons and motives behind the actions of the characters. Evaluating: Children are required to think By basing our questioning techniques on this model, we can encourage our children to analyse information and create new ideas. These thinking skills are built up through active lessons and activities that extend beyond basic rote memorization of facts. and make judgements and decisions of their own. A good example of this is asking your child to justify an opinion. Creating: Presenting children with creating questions will require them to use the information and ideas from texts together to create a new idea. Initially we will use Bloom’s Taxonomy during reading activities. Reading comprehension activities will be focused around the different types of questioning outlined on the pyramid. Our classroom displays will support pupils to become familiar with the different levels of questioning and their corresponding colours. Once the children understand the types of questions we will extend Bloom’s Taxonomy into other areas of the curriculum. Bloom’s Taxonomy at Home Bloom’s Taxonomy activities will feature in homework tasks. Clear instructions on how you might support these tasks will be provided on the weekly homework sheet. We have included in this booklet appropriate questions starters linked to each of the taxonomy levels. These will help you to compile a range of different types of questions to support your child’s reading comprehension and development of thinking skills at home. .