Response of First Order Transfer Functions First Order Functions
advertisement
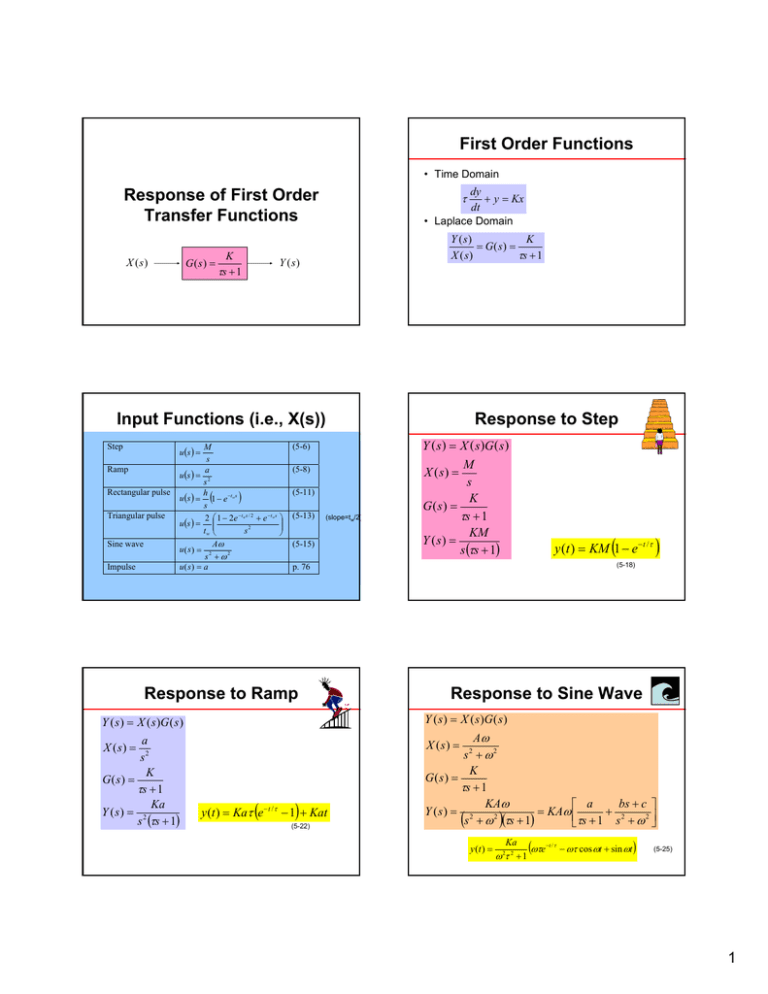
First Order Functions • Time Domain dy + y = Kx dt • Laplace Domain Response of First Order Transfer Functions K G( s) = τs + 1 X (s ) τ K Y ( s) = G( s) = τs + 1 X ( s) Y (s ) Input Functions (i.e., X(s)) Step u (s ) = Ramp Rectangular pulse Triangular pulse Sine wave Impulse M s a u (s ) = 2 s h u (s ) = 1 − e −tw s s 2 ⎛ 1 − 2e − t w s / 2 + e − t w s ⎞ ⎟⎟ u (s ) = ⎜⎜ tw ⎝ s2 ⎠ ( Aω s2 + ω2 u( s ) = a u( s) = ) (5-6) (5-8) (5-11) (5-13) (slope=tw/2) (5-15) Y ( s ) = X ( s )G ( s ) M X ( s) = s K G( s) = τs + 1 KM Y ( s) = s (τs + 1) y (t ) = KM (1 − e − t /τ ) (5-18) p. 76 Response to Ramp Y ( s ) = X ( s )G ( s ) a X ( s) = 2 s K G( s) = τs + 1 Ka Y ( s) = 2 s (τs + 1) Response to Step Response to Sine Wave Y ( s ) = X ( s )G ( s ) Aω s + ω2 K G( s) = τs + 1 bs + c ⎤ KAω ⎡ a = KAω ⎢ + 2 Y ( s) = 2 2 2 (s + ω )(τs + 1) ⎣τs + 1 s + ω ⎥⎦ X ( s) = y (t ) = Kaτ (e − t /τ − 1) + Kat (5-22) 2 y (t ) = Ka ω 2τ 2 + 1 (ωτe −t / τ − ωτ cos ωt + sin ωt ) (5-25) 1 Example: FOPDT Time Delays (θ) In time domain: • Replace t with (t-θ) and multiply by S(t-θ) • This is a response of a first order model to a step function M • First order with a step function is: KM y (t ) = KM 1 − e − t /τ Y ( s) = f (t − θ ) ⋅ S (t − θ ) ( In Laplace domain • Multiply by e-θs ) s (τs + 1) • Now add time delay y (t ) = KM (1 − e − ( t −θ ) /τ )⋅ S (t − θ ) e −θs F (s ) Y ( s) = Integrating Process KM ⋅ e −θs s (τs + 1) Pumped Tank Example • Pumped Tank dh = qi − q dt sAH ′( s ) = Qi′( s ) − Q ′( s ) H ′( s ) 1 = Qi′( s ) sA A H ′( s ) 1 1 =− [Qi′( s ) − Q′( s )] Q′ ( s) sA sA • This is not a first order model • Called an integrating process (no steady-state gain) • Step function in q or qi results in ramp in h!! H ′( s ) = Qi′( s ) = M s H ′( s ) = M s2 A Problem 4.7 Assumptions H, L, and V are molar flow rates y’s and x’s are mole fractions in vapor and liquid • Wanted: X 1′(s ) X 0′ (s ) X 1′(s ) Y1′(s ) Y2′(s ) X 0′ (s ) Y1′(s ) Y2′(s ) • Molar holdup H is constant dH =0 dt • Given: Stirred tank blending system (or stage on distillation column) dH = L0 + V2 − (L1 + V1 ) dt dx1H = x0 L0 + y2V2 − ( x1L1 + y1V1 ) dt y1 = a0 + a1 x1 + a2 x12 + a3 x13 Vapor pressure correlation • Constant molal overflow L0 = L1 V1 = V2 • Simplification: only use L and V (no subscripts) 2





