Networking - IS120 Course Website

Networking
Objectives
• Explain networking terminology
• View TCP/IP settings
• Access network resources
• View folder and file sharing permissions
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 2
Networking Terminology
• Client/Server Networks
– Client/server model:
• Central idea of networking
• Relationship between two computers
– Desktop computer (the client) makes service request of another computer (the server)
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 3
Figure 11-1 Client/server relationship
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 4
Peer-to-Peer Networks
• Employ desktop computers that are equally capable of being both clients and servers
• Example: small office/home office network
• Fedora 13:
– Provides peer-to-peer networking with Samba
– Samba:
• Based on Server Message Block (SMB)
• Identical to protocols provided by Windows 7
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 5
Figure 11-2 Peer-to-peer network
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 6
Networking Terminology (continued)
• LANs (local area networks)
– Usually confined to a geographic area
– Can be small, linking two or three computers
– Often link hundreds of computers used by many people
• WANs (wide area networks)
– Connects different LANs using services such as:
• Dedicated, leased data lines, satellite links, and data packet carrier services
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 7
Figure 11-3 Local area network
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 8
Figure 11-4 Wide area network
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 9
Networking Terminology (continued)
• Internet
– System of linked networks
– Communications highway for millions of users
• Intranet
– Private network that uses Internet-type applications
– Available only within a single organization
– For large organizations:
• Allows easy access to Web-based applications
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 10
Networking Terminology (continued)
• VPN (virtual private network)
– Uses tunneling to transfer data securely
– Helps to save money by using:
• Public Internet to connect securely with private network
• Internet Protocol
– Main networking protocol
– Allows communication of data across a network
– Computers can deliver packets based on unique IP addresses
– Foundation of the Internet Protocol Suite
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 11
Networking Terminology (continued)
• Protocols
– Set of rules that enables two computers to talk to each other
– Computing standard that defines the syntax and regulations of a connection across a network
• Internet Protocol addresses
– Identify two computers or devices in a network
– IPv4 (IP Address Version 4):
• 32 bits divided into four octets between 0 – 255
– IPv6: consists of 128 bits
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 12
The Internet Protocol Suite
• Set of protocols used in combination for different networking tasks
• IP and TCP:
– Underlying standards that all other protocols use
– Commonly referred to as TCP/IP
• TCP:
– Organizes data into packets and sends them to IP
– Rebuilds files from individual packets IP sent
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 13
The Internet Protocol Suite (continued)
• Layers of the Internet Protocol Suite
– Network (or Network Access) layer: links computers
– Internet layer: allows IP to transfer packets across the link
– Transport layer: uses TCP to organize packets
– Application layer: consists of protocols for specific types of transfer
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 14
The Internet Protocol Suite (continued)
Figure 11-5 Internet Protocol Suite
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 15
The Internet Protocol Suite (continued)
• Application layer protocols
– HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): allows Web users to request Web sites from remote servers
– FTP (File Transfer Protocol): allows for the rapid transfer of files across the Web
– POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3): sends and receives e-mail
– SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): sends and receives e-mail
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 16
Viewing TCP/IP Settings
• IP address:
– Numerical label assigned to devices participating in a computer network
• The subnetwork, or subnet:
– Logically visible, distinctly addressed part of a single
IP network
• The gateway IP address: node on a TCP/IP network
• DNS IP address of server providing domain name resolution:
– Translates domain names into numerical (binary) identifiers
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 17
Viewing TCP/IP Settings (continued)
• Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP):
– Used by hosts (DHCP clients) to retrieve IP address assignments and other configuration information
– Uses a client/server architecture
• In the absence of DHCP:
– All hosts on a network must be manually configured with static IP addresses
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 18
Viewing TCP/IP Settings in Windows 7
• Use Windows 7 GUI tools or command line
• To display the Network Connection Details window:
– Click Start
– Right-click Network
– Click Properties
– Click the Local Area Connection link
– Click Details
• No value for the DHCP enabled property indicates:
– An administrator assigned a static configuration
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 19
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux
Figure 11-6 Network
Connection Details window
Courtesy Course
Technology/Cengage Learning
20
Viewing TCP/IP Settings in Windows 7
(continued)
• IPCONFIG /ALL command:
– Provides network connection details
– To access this information:
• Click Start
• Point to All Programs
• Click Accessories
• Click Command Prompt
• Type IPCONFIG /ALL
• Press Enter
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 21
Figure 11-7 Network connection details
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 22
Viewing TCP/IP Parameters in Fedora
13
• Use GUI tools or Terminal window
• To display Ethernet Device settings:
– Click System, point to Administration, click Network type your password, and then click Edit, or
– Use the nm-tool command in a Terminal window, or
– Use ifconfig –a command
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 23
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux
Figure 11-8 Ethernet Device settings
Courtesy Course
Technology/Cengage Learning
24
Figure 11-9 Network Manager tool
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 25
Accessing Network Resources
• Accessing network resources in Windows 7
– Workgroup:
• Provides a basis for file and printer sharing
• Automatically created when peer-to-peer network is created
• Default: WORKGROUP
– Homegroup:
• Makes it easy to share libraries and printers
• Protected with a password
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 26
Accessing Network Resources
(continued)
• Network option on the Start menu:
– Displays shortcuts to shared computers, printers, and other resources on the network
• To open the Network window:
– Click Start and then click Network
• To see shares another computer is offering:
– Type \\servername\ in Windows Search text box
– Click server name
• To see the shares another computer is offering:
– Type NET VIEW \\servername
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 27
Figure 11-10 Network resources shown in workgroup
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 28
Figure 11-11 Shares on the Host01 computer
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 29
Figure 11-12 The NET VIEW command shows shares on the other computer
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 30
Accessing Network Resources
(continued)
• UNC notation use:
– Requires that you know name or IP address of server and share
• To open a folder to a network location:
– Type the UNC in the search text box
• To access the files:
– Click UNC displayed in the search results text box
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 31
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux
Figure 11-13 Accessing a network share from the
Search window
Courtesy Course
Technology/Cengage Learning
32
Accessing Network Resources
(continued)
• To access a network share from command prompt:
– Double-click the command Prompt icon
– Type: NET USE [drive letter | *]
\\computer name\share name
– You may specify a drive letter or permit Windows 7 to provide one:
• Example: NET USE N: \\Windows7\History
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 33
Accessing Network Resources in
Fedora 13
• To access a share, you must mount the share
• After you create a directory for mount destination:
– Type mount command
– Specify UNC for share, logon credentials, and destination directory
– Once share completes:
• Change directory to mount destination
• Issue an ls command to view the files
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 34
Figure 11-14 Mounting a Windows share in Linux
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 35
Accessing Network Printers
• It makes good economic sense to:
– Share a printer
– Make it available to several users on a network
• Network administrators:
– Responsible for setting up shared printers on the network
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 36
Folder and File Sharing Permissions
• Managing Windows NT File System permissions
– You must be able to view folder and file permissions
– Only authorized users can access local and network folders and files
• NT File System required
– To share folders and files with other network users
– Only NTFS:
• Permits user accounts and user groups to be linked to folder and file permissions
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 37
Managing Windows NT File System
Permissions (continued)
• Using local user groups
– Used to simplify management and authorization of network resource
– Groups are created to:
• Define sets of user accounts that require access to the same resources
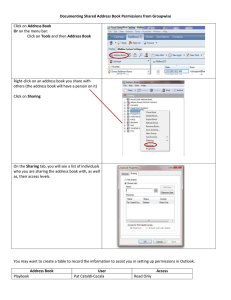
• Viewing shared folder permissions
– When sharing folder with network users, administrators:
• Must specify the level of access
• Balance security with functionality
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 38
Managing Windows NT File System
Permissions (continued)
Table 11-1 Windows 7 shared folder permissions
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 39
Managing Windows NT File System
Permissions (continued)
• Assigning NTFS permissions
– Administrators secure folders and files on an NTFS volume
– NT file system is required to use NTFS permissions
– Assign file permissions to control access to files
• Multiple NTFS permissions
– More effective to assign permissions to user groups
– Permissions assigned at file level override those assigned at folder level
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 40
Managing Windows NT File System
Permissions (continued)
Table 11-2 NTFS folder permissions
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 41
Managing Windows NT File System
Permissions (continued)
Table 11-3 NTFS file permissions
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 42
Managing Windows NT File System
Permissions (continued)
• Permission inheritance
– Inheriting permissions of parent folder by default
– Options to prevent inheritance:
• Copy inherited permissions from parent folder
• Remove inherited permissions and retain only assigned permissions
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 43
Figure 11-16 Permission inheritance
Courtesy Course
Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 44
Combining Shared Folder and NTFS
Permissions
• Administrators gain the highest level of security and control
• NTFS:
– Offers most flexible level of control
– Can be assigned to resources on an individual basis
• To determine effective permissions for a given network resource:
– Combine shared folder permissions
– Combine NTFS folder permissions
– Determine which permission is the most restrictive
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 45
Figure 11-17 The result of combining shared folder and NTFS permissions
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 46
Moving and Copying Files in NTFS
Volumes
• Files/folders inherit permissions from the destination folder
• When files/folders are moved within NTFS partition:
– They do not need to be re-created
• When you move a file/folder between NTFS volumes:
– It must be created on the destination volume
• FAT16 and FAT32 file systems
– Do not supports NTFS permissions
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 47
Viewing Fedora 13 File Permissions
• Each file and directory:
– Has permissions for owner, group, and everyone else
• Permissions for each group:
– Consist of three (binary) bits
• 10th bit is the sticky bit
• To show the file permissions:
– Use the ls command with the –l option
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 48
Viewing Fedora 13 File Permissions
(continued)
Figure 11-19 File permissions in Fedora 13
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 49
Viewing Fedora 13 File Permissions
(continued)
Figure 11-20 Viewing file permissions in Fedora 13
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 50
Figure 11-21 Listing file permissions in Fedora 13
Courtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 51
Viewing Fedora 13 File Permissions
(continued)
Figure 11-22 Displaying file permissions in Fedora 13
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 52
The User Identification Attribute
• File permissions bits:
– Include an execute permission bit for the file owner, the group, and others
• When the execute bit is set for the owner:
– The SUID bit (set user ID) is set to s
• Permission allows user/process that runs the file to have same access to system resources as owner
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 53
The Sticky Bit
• Ensures that:
– Only owner who created a file in directory can delete file and prevent malicious/accidental deletion
• When sticky bit is set:
– A t appears as the third character of the Others permission bits
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 54
Summary
• Network :
– Computers interconnected by communication paths
• To enable communications in a routed network:
– Computer must have an IP address, subnet mask, gateway IP address, and DNS IP address
• Network resources, folders, files, and printers are shared on the network
• File permissions:
– Enable users to access needed files
– Enable groups to share project files and folders
Guide to Parallel Operating Systems with Windows 7 and Linux 55