Standard Grade Physics Electronics Ink Exercise G1 1. The diagram
advertisement

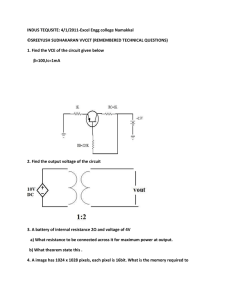
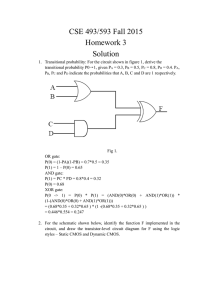
Standard Grade Physics 1. Electronics Ink Exercise G1 The diagram below shows a symbol used to represent a component in an electronic circuit. Which of the following does the symbol represent? A a NOT gate B an AND gate C an OR gate D A light dependent resistor (LDR) E A light emitting diode (LED) (KU1) 2. Which of the following is an output device? A LDR 3. B LED C microphone D solar cell E thermistor (PS1) An intercom system is used so that parents can hear a baby crying in the bedroom. The block diagram for the system is shown below. (a) Which of the following devices would be suitable as (i) the input device X ; (ii) output device Y loudspeaker bulb (KU1) (PS1) microphone LED (b) The output signal from the amplifier is displayed on an oscilloscope and is shown below. (i) (ii) Signals may be classified as digital or analogue. Which type is the above signal? (KU1) When the input signal to the amplifier has a value of 0.01 volt, the value of the output signal is 1.5 volts. Calculate the voltage gain of the amplifier. (KU2) 4. Three members of a school electronics club are planning their next projects. One project is to build a light meter. A second project is to build a circuit which will control the opening and closing of curtains from a distance. The third project is to build a sound operated baby alarm. The members use a catalogue to select components for their projects. The catalogue has the following list giving details of input and output devices. (a) Which of the devices listed is a suitable input device for the baby alarm? (PS1) (b) Name two devices from the list which are output devices (PS2) (c) Name, from the list, a suitable output device for the curtain control circuit. (PS1) (d) State the useful energy change which takes place in the solar cell. (KU1) (e) The light meter project involves the use of the light dependent resistor (LDR) in a circuit as shown below. Calculate the current in the circuit when the LDR is exposed to light. 5. (PS3) The diagram below shows a calculator which is powered by a solar cell. (a) State the energy transfer occurring in the solar cell. (KU1) (b) The circuit powered by the solar cell has a resistance of 100 ohms. The solar cell produces a voltage of 0.5 volt. Calculate the current in the solar cell circuit. (KU2) (c) Name a suitable output device which could be used in the display of the calculator. (PS1) TOTAL 19 Standard Grade Physics 2. Electronics Ink Exercise G2 (a) A thermistor is connected to a 3 volt d.c. supply in the circuit shown below. The table gives some information about the thermistor. Calculate the reading on the ammeter when the thermistor is placed in a warm room. (PS3) (b) The thermistor is used as a temperature probe and is placed in a chicken inside an oven as shown in figure 1. The thermistor is connected to an LED as shown in the circuit diagram in figure 2. The LED in the circuit is visible from the outside of the oven. 3. (i) What is the name of the component marked X in figure 2? (ii) What happens to the LED when the temperature reaches a high value? (iii) What is the purpose of resistor R which is connected in series with the LED? (KU1) Study the logic systems A and B below. A B Explain which system should be used in each of the following cases. (KU1) (PS1) (a) A bank alarm can be switched on by either of two employees using the switches shown. (PS2) (b) A paper cutting guillotine works only when the operator uses both hands to press two switches at the same time. (PS2) 4. An automatic light circuit for a porch is being constructed. The design for the circuit uses two sensors, so that the lamp in the circuit will only operate when it is dark and a person approaches the porch. One sensor detects heat from a person’s body. The second sensor detects the presence of visible radiation. (a.) There is a choice of three sensors as follows : infrared detector light dependent resistor ultraviolet detector (i) Which sensor should be used to detect body heat? (PS1) (ii) Which sensor should be used to detect visible radiation? (PS1) (b) The diagram below shows part of the circuit that is designed. The diagram shows the inputs from the sensors and from the on/off switch for the circuit. The circuit has two logic gates X and Y. The symbol for gate X is not shown. (i)(A) What type of logic gate is Y? (KU1) (B) Copy and complete the truth table for the logic gate that you have named in (b)(i)(A). (ii) What type of logic gate is X? (KU2) (PS1) TOTAL 16 Standard Grade Physics Electronics Ink Exercise C1 1. Part of an electronic system is shown below: The resistance of the light dependent resistor (LDR) in different lightning conditions is shown below. Calculate the voltage across the 1000Ω resistor when the LDR is in darkness. (KU2) 2. In the washing machine shown in figure 1, an electric motor is used to turn the drum. Before the clothes are washed, the machine fills with water which is then heated to the correct temperature. Figure 2 shows part of the control circuit for the washing machine. When the machine fills to the correct water level, A changes from logic 0 to logic 1. When the water reaches the correct temperature, B changes from logic 0 to logic 1. When the output from gate Y is at logic 1, the motor is ON. When the output from gate Z is at logic1, the heater is ON. a. What type of gate is X? (KU1) b. Give an example of: (i) an input device which could be used as a temperature sensor; (ii) an output device which could be used as the motor switch. (KU2) c. A table may be constructed to show the logic levels at P, Q, R and S and to show whether the heater and motor are switched on or off in a number of cases. Case 1: just after the machine is switched on and begins to fill with cold water. Case 2: just after the water reaches the correct level. Case 3: jus after the water reaches the correct temperature. Copy and complete the table for case 2 and case 3. (PS4) 3. The electronic system shown below is used as a light meter. A voltage is generated when light falls on the solar cell. The voltage is then amplified and the output displayed on a voltmeter. d. Copy and complete the block diagram below to show the parts of the system. (KU1) e. The solar cell is connected to the amplifier as shown below. If the voltage generated by the solar cell is 0.4mV, calculate voltage V1. (PS2) TOTAL 12 Standard Grade Physics Electronics Ink Exercise C2 1. A tape recorder is represented by the block diagram shown below. (a) The amplifier system produces 0.02 W of power in the headphones which have a resistance of 18 Ω. Calculate the voltage applied to the headphones (PS2) (b) The amplifier system has a voltage gain of 20. Calculate the size of the voltage signal produced by the playback head. (PS2) 2. The diagram for an alarm system is shown below. The alarm system is designed to operate if someone steps on a pressure pad or opens a door. When someone stands on the pressure pad sensor, the logic level at X changes from 0 to 1. When the door is opened, the logic level at Y changes from 0 to 1. f. Copy and complete the table below to show the logic levels at P, Q, R and S when the logic levels at X and Y are as indicated. (PS2) g. The pupil could have designed the alarm system using only one logic gate. Name the gate he could have used. (KU1) h. Two possible circuits for the door switch are shown below. When the door closes, the switch closes. Explain which circuit should be used in the above system. (PS2) 3. (a) Figure 1 shows two logic gates X and Y. (i) Name logic gate X and draw its truth table. (KU2) (ii) Name logic gate Y and draw its truth table. (KU2) (b) A pupil uses the logic gates, shown in figure 1, when designing an electronic lock system. The system contains six light detectors illuminated by a light source. When a card with holes in it is inserted between the light source and the detectors, as shown in figure 2, it can act as a “key” by allowing light to reach only some of the detectors. A set of logic gates connected to the detectors can provide the correct output voltage to open the lock. The logic gates are connected as shown in figure 3. Each detector gives a “high” logic output when light shines on it. The effect of using the card is shown in figure 3. (i) What are the logic levels at points L and M? (ii) What is the logic level at point N? (iii) Name a suitable output device which could be connected to the system at N. (c) (PS2) (PS1) (PS1) The pupil wishes to use a different card as the “key”. This card is shown in figure 4. What change would have to be made to the circuit shown in figure 3 before this card would open the “lock”? (PS2) TOTAL 19