PHYSICS LABORATORY
advertisement

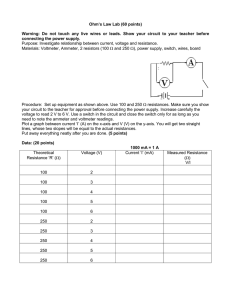
T.C. MARMARA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCES PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY - II DEPARTMENT: NAME: SURNAME: NUMBER: 2 T.C.MARMARA UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY –I I MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO: EXPERIMENT NAME: THE DATE: GROUP NO: NAME: NUMBER: DELIVERY TIME: REPORT NOTE: 2 3 EXPERIMENT.2 SERIAL-PARALLEL CONNECTION RESISTANCE CALCULATING OF RESISTANCES & EQUIVALENT Goal:1.) Calculation of equivalent resistance Theory: Calculating Equivalent Resistance: Resistances may connect to circuit serial or parallel. Equivalent resistance of circuit can be calculated with formulas given below for serial or parallel connection. Req ( serial ) R1 R2 R3 R4 Req ( parallel ) 1 1 1 1 1 R1 R2 R3 R4 In a serial circuit, current and voltage on each resistance is: In a parallel circuit, current and voltage on each resistance is: 3 4 Experimental Setup: Apparatus: 1.)Board 2.)Various resistances 3.)DC voltage source 4.)Digital multimeter 5.)Connectors EXPERIMENTAL SETUP AND MEASUREMENTS: 1.) Calculate resistance’s value that you will use via the table and measure them with multimeter. 2.) Connect resistance as schemes above. Measure and record equivalent resistance by multimeter before apply voltage to circuit. 3.) Apply ‘supply voltage’ to all of circuit.(Max. 5V) 4.) Build four connection scheme that given below on board and measure voltage value on each resistance. Calculate passing current and fill the table. Scheme(1) V 1: V2: V3: R 1: R2: R3: I 1: I2: I3: V 1: V2: V3: R 1: R2: R3: I 1: I2: I3: V 1: V2: V3: R 1: R2: R3: I 1: I2: I3: V 1: V2: V3: R 1: R2: R3: I 1: I2: I3: Equivalent resistance 1: Scheme(2) Equivalent resistance 2: Scheme (3) Equivalent resistance 3: Scheme (4) Equivalent resistance 4: 4 Experimental 5 Theorical Req1: Req2: Req3: Req4: Figure 1- Parallel - Serial Connection of Resistances Calculations: 1.) Calculate equivalent resistance for each scheme and compare initial equivalent resistance value with the value you get. Then calculate your percentage error. 2.) Compare current passing all branches of circuits and voltage on all branches of circuits with total current passing in circuits and applied voltage on whole circuit. If there is a difference, specify reasons of this difference. 3.) Build serial and parallel circuits randomly and then measure their equivalent resistance. Later, compare these values with your theorical values. 4.) Interpret your conclusions. 5 6 EXPERIMENT 2. SERIAL-PARALLEL CONNECTION OF RESISTANCES & EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE CALCULATING-NOTES: 6