Computer Engineering
advertisement
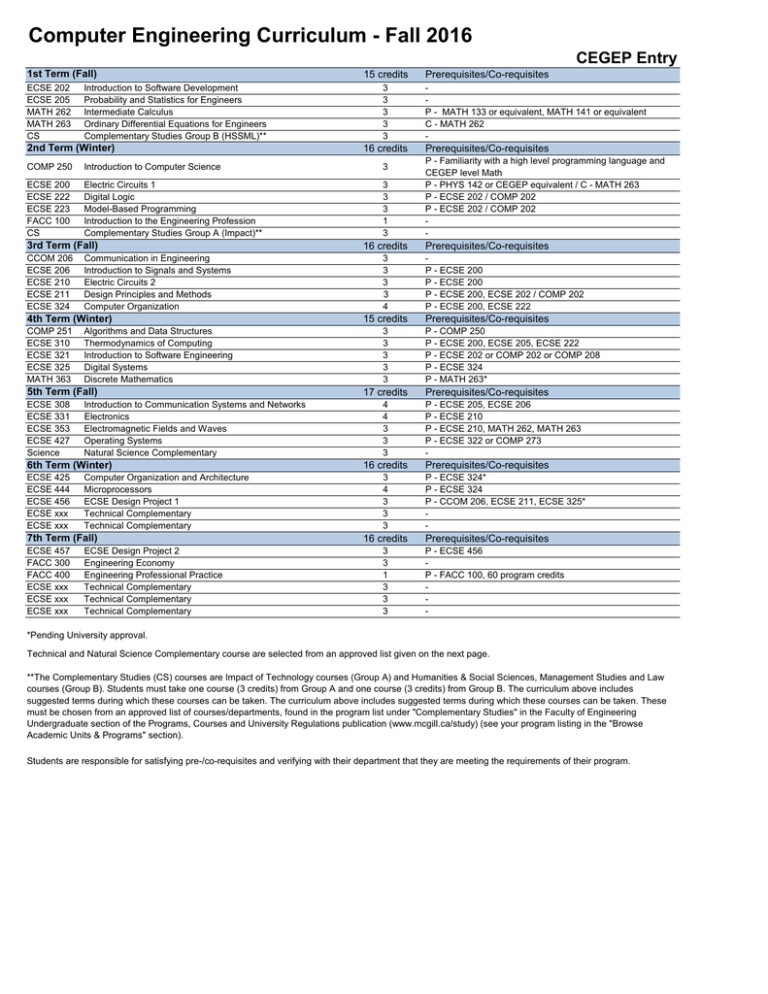
Computer Engineering Curriculum - Fall 2016 CEGEP Entry 1st Term (Fall) ECSE 202 ECSE 205 MATH 262 MATH 263 CS Introduction to Software Development Probability and Statistics for Engineers Intermediate Calculus Ordinary Differential Equations for Engineers Complementary Studies Group B (HSSML)** 2nd Term (Winter) 15 credits 3 3 3 3 3 16 credits COMP 250 Introduction to Computer Science 3 ECSE 200 ECSE 222 ECSE 223 FACC 100 CS Electric Circuits 1 Digital Logic Model-Based Programming Introduction to the Engineering Profession Complementary Studies Group A (Impact)** 3 3 3 1 3 3rd Term (Fall) CCOM 206 ECSE 206 ECSE 210 ECSE 211 ECSE 324 Communication in Engineering Introduction to Signals and Systems Electric Circuits 2 Design Principles and Methods Computer Organization 4th Term (Winter) COMP 251 ECSE 310 ECSE 321 ECSE 325 MATH 363 Algorithms and Data Structures Thermodynamics of Computing Introduction to Software Engineering Digital Systems Discrete Mathematics 5th Term (Fall) ECSE 308 ECSE 331 ECSE 353 ECSE 427 Science Introduction to Communication Systems and Networks Electronics Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Operating Systems Natural Science Complementary 6th Term (Winter) ECSE 425 ECSE 444 ECSE 456 ECSE xxx ECSE xxx Computer Organization and Architecture Microprocessors ECSE Design Project 1 Technical Complementary Technical Complementary 7th Term (Fall) ECSE 457 FACC 300 FACC 400 ECSE xxx ECSE xxx ECSE xxx ECSE Design Project 2 Engineering Economy Engineering Professional Practice Technical Complementary Technical Complementary Technical Complementary 16 credits 3 3 3 3 4 15 credits 3 3 3 3 3 17 credits 4 4 3 3 3 16 credits 3 4 3 3 3 16 credits 3 3 1 3 3 3 Prerequisites/Co-requisites P - MATH 133 or equivalent, MATH 141 or equivalent C - MATH 262 - Prerequisites/Co-requisites P - Familiarity with a high level programming language and CEGEP level Math P - PHYS 142 or CEGEP equivalent / C - MATH 263 P - ECSE 202 / COMP 202 P - ECSE 202 / COMP 202 - Prerequisites/Co-requisites P - ECSE 200 P - ECSE 200 P - ECSE 200, ECSE 202 / COMP 202 P - ECSE 200, ECSE 222 Prerequisites/Co-requisites P - COMP 250 P - ECSE 200, ECSE 205, ECSE 222 P - ECSE 202 or COMP 202 or COMP 208 P - ECSE 324 P - MATH 263* Prerequisites/Co-requisites P - ECSE 205, ECSE 206 P - ECSE 210 P - ECSE 210, MATH 262, MATH 263 P - ECSE 322 or COMP 273 - Prerequisites/Co-requisites P - ECSE 324* P - ECSE 324 P - CCOM 206, ECSE 211, ECSE 325* - Prerequisites/Co-requisites P - ECSE 456 P - FACC 100, 60 program credits - *Pending University approval. Technical and Natural Science Complementary course are selected from an approved list given on the next page. **The Complementary Studies (CS) courses are Impact of Technology courses (Group A) and Humanities & Social Sciences, Management Studies and Law courses (Group B). Students must take one course (3 credits) from Group A and one course (3 credits) from Group B. The curriculum above includes suggested terms during which these courses can be taken. The curriculum above includes suggested terms during which these courses can be taken. These must be chosen from an approved list of courses/departments, found in the program list under "Complementary Studies" in the Faculty of Engineering Undergraduate section of the Programs, Courses and University Regulations publication (www.mcgill.ca/study) (see your program listing in the "Browse Academic Units & Programs" section). Students are responsible for satisfying pre-/co-requisites and verifying with their department that they are meeting the requirements of their program. Technical Complementary Courses - Computer Engineering Technical Complementaries 15-19 credits 5 courses must be taken, chosen as follows: - 3 courses (minimum 9 credits) from List A - The remaining 2 courses (minimum 6 credits) from List A or List B List A 9-17 credits from the following: COMP 424 ECSE 335 ECSE 412 ECSE 416 ECSE 420 ECSE 421 ECSE 422 ECSE 424 ECSE 428 ECSE 429 Artificial Intelligence Microelectronics Discrete Time Signal Processing Telecommunication Networks Parallel Computing Embedded Systems Fault Tolerant Computing Human-Computer Interaction Software Engineering Practice Software Validation Credits 3 4 3 4 3 3 3 3 3 3 Prerequisites/Co-requisites P - COMP 206 / ECSE 321, MATH 323 or equivalent, and COMP 251 P - ECSE 331 P - ECSE 304 or ECSE 306 P - COMP 250, ECSE 205, ECSE 308 / ECSE 316 P - ECSE 427 P - ECSE 322, ECSE 323 P - ECSE 322 P - ECSE 322 or (COMP 251 and COMP 273) P - ECSE 321 or COMP 335 P - ECSE 321 or COMP 303 List B 0-8 credits from the following: COMP 557 ECSE 307 ECSE 403 ECSE 408 ECSE 415 ECSE 431 ECSE 435 ECSE 436 ECSE 450 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Linear Systems and Control Control Communication Systems Introduction to Computer Vision Introduction to VLSI CAD Mixed-Signal Test Techniques Signal Processing Hardware Electromagnetic Compatibility 3 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 3 P - COMP 206, COMP 251, MATH 223 P - ECSE 206, ECSE 210 P - ECSE 307 P - ECSE 205, ECSE 308 P - ECSE 304 or ECSE 306 or instructor permission P - ECSE 323, ECSE 330 P - ECSE 304, ECSE 334 P - ECSE 322, ECSE 323, ECSE 304 / 306 P - ECSE 221, ECSE 334, ECSE 352 / ECSE 353 Natural Science Complementary Courses - Computer Engineering Students from CEGEP are required to complete one 3-credit course at the 200-level or higher, chosen from the following science departments, approved by the Undergraduate Programs Office in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering: Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences (ATOC) Biology (BIOL) Chemistry (CHEM) Earth and Planetary Sciences (EPSC) Earth System Science (ESYS) Physics (PHYS) Last update: June 7, 2016 For the official program listing, see the Programs, Courses and University Regulations publication (www.mcgill.ca/study).