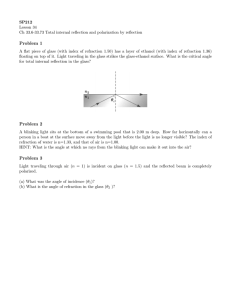
θi =θ2
advertisement
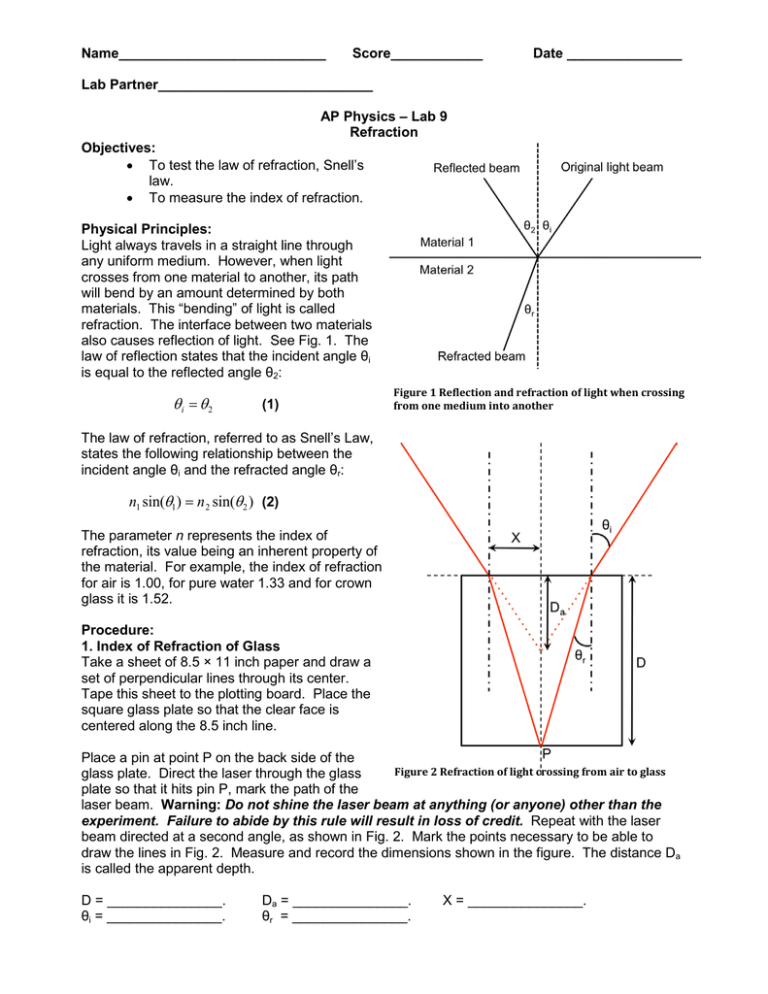
Name___________________________ Score____________ Date _______________ Lab Partner____________________________ AP Physics – Lab 9 Refraction Objectives: • To test the law of refraction, Snell’s law. • To measure the index of refraction. Physical Principles: Light always travels in a straight line through any uniform medium. However, when light crosses from one material to another, its path will bend by an amount determined by both materials. This “bending” of light is called refraction. The interface between two materials also causes reflection of light. See Fig. 1. The law of reflection states that the incident angle θi is equal to the reflected angle θ2: θi = θ2 (1) Figure 1 Reflection and refraction of light when crossing from one medium into another The law of refraction, referred to as Snell’s Law, states the following relationship between the incident angle θi and the refracted angle θr: n1 sin(θ1 ) = n 2 sin(θ 2 ) (2) The parameter n represents the index of refraction, its value being an inherent property of the material. For example, the index of refraction for air is 1.00, for pure water 1.33 and for crown glass it is 1.52. Procedure: 1. Index of Refraction of Glass Take a sheet of 8.5 × 11 inch paper and draw a set of perpendicular lines through its center. Tape this sheet to the plotting board. Place the square glass plate so that the clear face is centered along the 8.5 inch line. Place a pin at point P on the back side of the Figure 2 Refraction of light crossing from air to glass glass plate. Direct the laser through the glass plate so that it hits pin P, mark the path of the laser beam. Warning: Do not shine the laser beam at anything (or anyone) other than the experiment. Failure to abide by this rule will result in loss of credit. Repeat with the laser beam directed at a second angle, as shown in Fig. 2. Mark the points necessary to be able to draw the lines in Fig. 2. Measure and record the dimensions shown in the figure. The distance Da is called the apparent depth. D = _______________. θi = _______________. Da = _______________. θr = _______________. X = _______________. Compute the value of the index of refraction for class according to the formula: n2 = n1 sin(θ i ) sin(θ r ) (3) Record this index of refraction and compare it with the theoretical value nt = 1.52. Calculated index of refraction = _________________ %diff = n t − n calc ×100 = __________________ nt 2. Index of Refraction of Water Take a sheet of 8.5 × 11 inch paper and draw a set of perpendicular lines through its center. Place this sheet on the plotting board and secure it with masking tape. Draw five lines on the paper, representing incident rays with angles 10°, 25°, 40°, 50°, and 60° so that they all meet at the intersection of the perpendicular lines. See Fig. 3. Fill the plastic semi-disk container with water and place it so that the flat side is centered along the 8.5 inch line. Trace the curved edge on the paper. Direct the laser beam toward the Figure 3 Index of refraction of water flat side of the semi-cylinder along the line that makes a 10° experiment angle from the normal to this flat side. Mark the point where the light exits the semi-cylinder on the curved side. Repeat this process for each incident angle. You will have five dots on the curved side of the semi-cylinder so make sure you mark the corresponding incident angle for each one. Remove the container and draw lines through these points and the center of the paper (where the perpendicular lines intersect). These are the refracted light beams. Measure the angles of refraction (θr) and complete Table 1 below. Using Graphical Analysis software plot a graph of sin(θi) on the vertical axis versus sin(θr) on the horizontal axis and find the slope of the line. Compare this slope with the accepted value of the index of refraction of water na = 1.33. Print out the graph and attach to this report. Table 1: Refraction in water. Incident angle θi Refracted angle θr sin(θi) sin(θr) 10° Slope of the line ncalc = _______________, %diff = n a − n calc ×100 = _________________. na Conclusions: Staple the two drawn sheets and one Graphical Analysis graph to this report. Explain in two or three sentences what you learned from this lab.