Lecture 18 Transistor Amplifiers (I) Common
advertisement

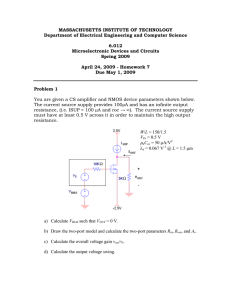
Lecture 18 Amplificateurs à Transistor (I) Common-Source Amplifier Outline • Amplifier fundamentals • Common-source amplifier • Common-source amplifier with current-source supply 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 1 Amplifier Fundamentals • • Source resistance RS is associated only with small signal sources Choose ID = ISUP ---> DC output current – IOUT = 0 – VOUT = 0 Input sources Intrinsic Amplifier V+ Load Voltage Input Supply Current ISUP RS vs + − VBIAS + − vIN = VBIAS + vs Current Input is iOUT = id ISUP RS iIN = IBIAS + is iD Input Active Device iD = f(input) + vOUT RL − IBIAS V− 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 2 2. Common-Source Amplifier: Consider the following circuit: V+=VDD RD iR signal source RS iD + vOUT vs VBIAS signal load RL V-=VSS • Consider intrinsic voltage amplifier - no loading •RS = 0 •RL ---> ∞ • VGS = VBIAS - VSS • VBIAS, RD and W/L of MOSFET selected to bias transistor in saturation and obtain desired output bias point (i.e. VOUT = 0). Watch notation: vOUT(t)=VOUT+vout(t) 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 3 Load line view of amplifier: load line IR=ID VDD-VSS VVGG -VSS -VDD - V=V =V SS- VSS BIAS ssDD RD VV -V - Vss GG BIAS SS -V VVGG -VSS =V BIAS ssT= VT 0 VSS VDD VOUT Transfer characteristics of amplifier: VOUT VDD VSS 0 Want: • • • • VT VDD-VSS VGG-VSS VBIAS - Vss Bias point calculation; Limits to signal swing Small-signal gain; Frequency response [in a few days] 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 4 Bias point: choice of VBIAS, W/L, and RD to keep transistor in saturation and to get proper quiescent VOUT. Assume MOSFET is in saturation: ID = W 2 µ nCox (VBIAS − VSS − VT ) 2L VDD − VOUT IR = RD If we select VOUT=0: V DD W 2 µ C (V − VSS − VT ) = ID = IR = RD 2 L n ox BIAS Then: VBIAS = 2I D W µn Cox L + VSS + VT Equation that allows us to compute needed VBIAS given RD and W/L. 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 5 VDD Signal swing: RD signal source + RS vOUT vs VBIAS - VSS • Upswing: limited by MOSFET going into cut-off. vout,max = VDD • Downswing: limited by MOSFET leaving saturation. VDS ,sat = VGS − VT = or 2I D W µn C ox L vout ,min − VSS = VBIAS − VSS − VT = Then: 6.012 Spring 2004 2I D W µn Cox L vout,min = VBIAS − VT Lecture 18 6 Generic view of the effect of loading on small-signal operation Two-port network view of small-signal equivalent circuit model of a voltage amplifier: Rin is input resistance Rout is output resistance Avo is unloaded voltage gain Rs Rout + + vs + vin - - input loading Voltage divider at input: Voltage divider at output: + Rin - Avovin RL vout - unloaded circuit output loading vs vin = Rin Rin + Rs Avo v in vout = RL Rout + RL vout RL Rin = A vo Loaded voltage gain: vs Rin + RS R L + Rout 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 7 Small-signal voltage gain Avo: draw small-signal equivalent circuit model: Remove RL and RS RD + + vt vgs - D G + gmvgs ro vout - - S + vt + gmvt (ro//RD) vout - - vout = −g mv t (ro // RD ) Then unloaded voltage gain: v out Avo = = −gm (ro // R D ) vt 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 8 Input Resistance • Calculation of input resistance, Rin: – Load amplifier with RL – Apply test voltage (or current) at input, measure test current (or voltage). For common-source amplifier: it + + vt - vgs gmvgs (ro//RD) RL - vt it = 0 ⇒ Rin = = ∞ it No effect of loading at input. 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 9 Output Resistance • Calculation of output resistance, Rout: – Load amplifier with RS – Apply test voltage (or current) at output, measure test current (or voltage). – Set input source equal zero For common-source amplifier: it + RS + vgs gmvgs (ro//RD) - - vt v gs = 0 ⇒ gm v gs = 0 ⇒ v t = it (ro // RD ) vt Rout = = ro // RD it 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 10 Two-port network view of common-source amplifier Voltage Amplifier Rs Rout + + vs + vin - - input loading + Rin - Avovin RL vout - Intrinsic circuit output loading Rin v out RL Avo = RL + Rout Rin + RS vs RL vout = −gm (ro // RD // RL ) = −g m(ro // RD ) RL + ro // RD vs 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 11 Current Source Supply I—V characteristics of current source: iSUP + vSUP 1 roc ISUP iSUP _ vSUP Equivalent circuit models : iSUP + vSUP ISUP roc roc _ large-signal model • • • small-signal model iSUP = 0 for vSUP ≤ 0 iSUP = ISUP + vSUP/ roc for vSUP > 0 High small-signal resistance roc. 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 12 3. Common-source amplifier with currentsource supply V DD iSUP signal source iD RS + vOUT vs VBIAS signal load RL - VSS Loadline View iSUP=ID load line VBIAS-VSS=VDD-VSS ISUP VBIAS-VSS VBIAS-VSS=VT 0 VSS 6.012 Spring 2004 VDD VOUT Lecture 18 13 Use PMOS for current source supply VDD VB iSUP signal source iD RS vOUT vs VBIAS VSS Bias point: Assume both transistors in saturation VOUT = 0 ⎛W⎞ 2 I SUP = −I Dp = ⎜ ⎟ µ p Cox VDD − VB + VTp ⎝ 2L ⎠ p ( ) ⎛W⎞ 2 I SUP = I Dn = ⎜ ⎟ µ nCox (VBIAS − VSS − VTn ) ⎝ 2L⎠ n 2I SUP VBIAS = + VSS + VT ⎛ W⎞ ⎜ ⎟ µnC ox ⎝ L ⎠n 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 14 VDD Signal swing: VB iSUP signal source iD RS vOUT vs VBIAS VSS • Upswing: limited by PMOS leaving saturation. VSD,sat = VSG + VTp = 2 I SUP ⎛ W⎞ ⎜ ⎟ µ p Cox ⎝ L⎠ p VDD − vout,max = VDD − VB + VTp vout,max = VB − VTp • Downswing: limited by NMOS leaving saturation. • Same result as with resistive supply current. vout,min = VBIAS − VT 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 15 3. Common-source amplifier with currentsource supply (contd.) Current source characterized by high output resistance: roc. Significantly higher than amplifier with resistive supply. p-channel MOSFET: roc = 1/λIDp VDD VB iSUP signal source iD RS vOUT vs VBIAS VSS • Voltage gain: Avo = -gm (ro//roc). • Input resistance :Rin = ∞ • Output resistance: Rout = ro//roc. 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 16 Relationship between circuit figures of merit and device parameters Remember: W µ nCox L 1 L ro ≈ ∝ λn I D I D gm = 2I D Then: Circuit Parameters |Avo| Device* gm(ro//roc) Parameters ↓ I ↑ SUP Rin Rout ∝ r //r o oc - ↓ W↑ ↑ - - µnCox ↑` ↑ - L↑ ↑ - ↑ * adjustments are made to VBIAS so that none of the other parameters change CS amplifier with current source supply is a good voltage amplifier (Rin high and |Avo| high), but Rout high too ⇒ voltage gain degraded if RL << ro//roc. 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 17 What did we learn today? Summary of Key Concepts for CS amplifier • • • Bias Calculations Signal Swing Small Signal Circuit Parameters – – – – • Voltage Gain - AVO Transconductance - Gm Input Resistance - Rin Output Resistance - Rout Relationship between small signal circuit and device parameters 6.012 Spring 2004 Lecture 18 18