Sunlight is composed of energy that is visible to humans and energy
advertisement

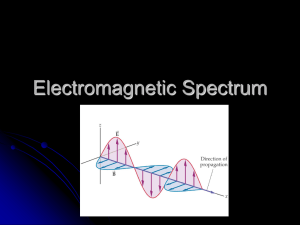
BELLRINGER On your BR page, draw this wave and correctly label the components labeled A – D. (It should be in your notes from yesterday) BELLRINGER A. B. C. D. Crest Trough Amplitude Wavelength AGENDA Today: The EM Spectrum: - Review of yesterday’s info - EM. Spectrum Notes - Begin EM Spectrum Foldable/Booklet (due complete and correct before any Jedi signatures will be given) Tomorrow: - First ½ - Finish foldable - Second ½ - Kahoot (EM waves, spectrum (Only for those finished with foldable)) REVIEW FROM YESTERDAY Which of the following waves has the longest wavelength? REVIEW FROM YESTERDAY Which of the following waves has the longest wavelength? B REVIEW FROM YESTERDAY Which of the following waves would have the highest frequency? REVIEW FROM YESTERDAY Which of the following waves would have the highest frequency? A REVIEW FROM YESTERDAY Which wave has the greatest energy (and therefore most likely to cause harmful radiation)? REVIEW FROM YESTERDAY Which wave has the greatest energy (and therefore most likely to cause harmful radiation)? A, because it would hit you with the most waves per second. Remember, energy of a wave = # of waves hitting you per second. THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM (NOTES ON PAGE 41) Depending on the frequency and therefore wavelength and energy, a wave falls somewhere along a spectrum. THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM (NOTES ON INB 41) Depending on the frequency and therefore wavelength and energy, a wave falls somewhere along a spectrum. THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM We use many of these waves for modern technology. RADIO (LONGEST WAVES = LOWEST ENERGY) • Emitted by: • Astronomical Objects • Radio and TV Station Transmitters • Detected by: • Ground based radio telescopes • Radio receivers • *If you turn on a radio, it will convert the radio wave energy into sound energy. MICROWAVES • Higher frequency (shorter wavelength) than radio waves • Emitted by: • Microwave Ovens • Cell Phones • Gas clouds collapsing into stars • Detected by • • • • Food (heated) Cell phones Radar (systems) Microwave Telescopes INFRARED (HEAT OR THERMAL) ARE YOU A SOURCE OF INFRARED? YES YOU ARE! • Emitted by • • • • Sun and stars (Near) TV Remote Controls Food Warming Lights (Thermal) Everything with thermal energy emits these waves • Detected by • Infrared Cameras • Your skin • Snakes VISIBLE LIGHT • Emitted by EACH COLOR IS A DIFFERENT SIZE WAVE. RED THE LONGEST & VIOLET THE SHORTEST • The sun and other astronomical objects • Light bulbs • Anything that emits light • Detected by • • • • Cameras (film or digital) Human eyes Plants (red light) Telescopes ULTRAVIOLET (UV) SUNBURN • Emitted by • Tanning booth • The sun • UV lamps • Detected by • Space based UV detectors • UV Cameras • Emitted by • • • • Airport luggage scanners X-ray machines CAT scan machines Radioactive minerals • Detected by • X-ray film and machines • Space based X-ray detectors • CCD detectors X-RAYS GAMMA RAYS (VERY SHORT EM WAVES, BUT VERY ENERGETIC!) Emitted by • Radioactive materials • Solar flares • Exploding nuclear weapons • Gamma-ray bursts Detected by • Medical imaging detectors • Geiger counters • Gamma detectors and satellites EM. SPECTRUM BOOK 1. Turn to pg 633 in your book, and make the 8-layer book shown. 1. Make sure you draw the EM spectrum on the outside as shown on page 633 (low frequency at the top, getting higher as you go top to bottom). 2. On each flap, fill in the following components: 1. “These waves have more energy than ___________ , but less energy than _____________.” (Ex: Radio: “These waves have more energy than NONE, but less energy than MICROWAVES.”) 2. 3 uses for that type of wave (can be found in notes, or section 16-3) 3. A picture of something that emits that wave 4. A picture of something that detects that type of wave.