Conservation of Energy WS KEY
advertisement
Physics: Energy
Worksheet 6: Conservation of Energy
KE::: (Y2) mv2
5
678
PEg'" mgh
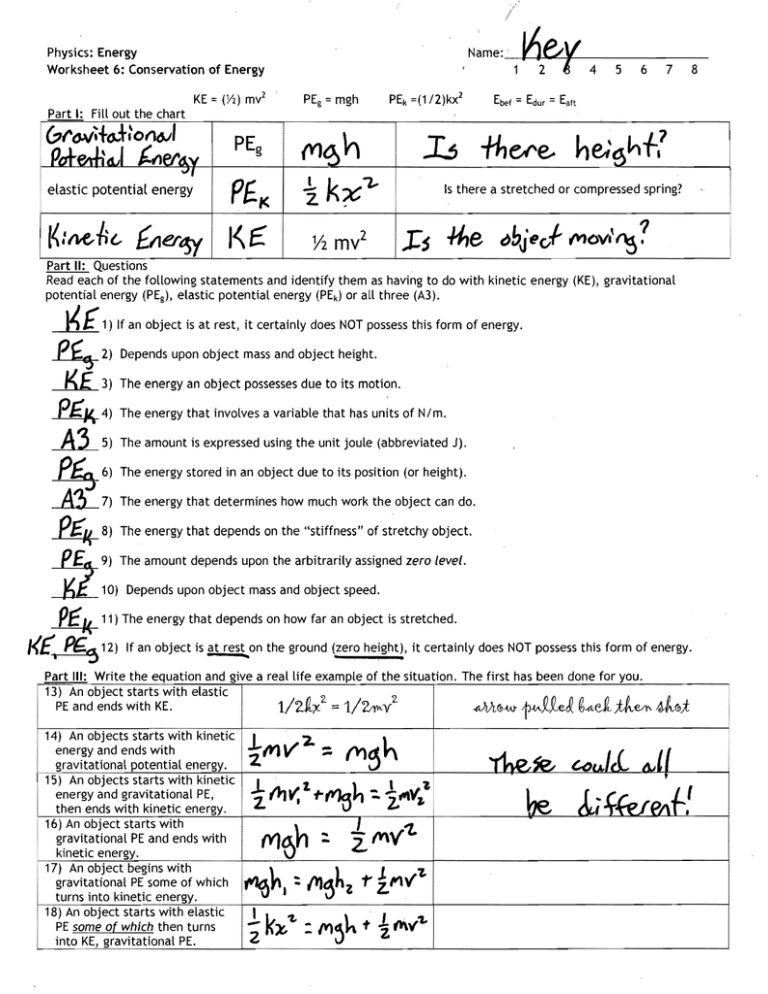
Part I: Fill out the chart
PEg
elastic potential energy
h
.1 KX'"
Z .
(Y)
Is there a stretched or compressed spring?
Part II: Questions
Read each of the following statements and identify them as having to do with kinetic energy (KE), gravitational
potential energy (PEg), elastic potential energy (PEk ) or all three (A3).
---.l{( 1) If an object is at rest, it certainly does NOT possess this form of energy.
~ 2)
K£
Depends upon object mass and object height.
3) The energy an object possesses due to its motion. ~ 4)
The energy that involves a variable that has units of N/m. ~ 5)
The amount is expressed using the unit joule (abbreviated J). p§-
6) The energy stored in an object due to its position (or height). A?J
7) The energy that determines how much work the object can do.
24
8) The energy that depends on the "stiffness" of stretchy object. ~ 9)
~ 10)
The amount depends upon the arbitrarily assigned zero level. Depends upon object mass and object speed. PIEk 11) The energy that depends on how far an object is stretched.
K£'. ~~
12) If an object is at reston the ground (zero height), it certainly does NOT possess this form of energy.
Part III: Write the equation and give a real life example of the situation. The first has been done for you.
14) An objects starts with kinetic
energy and ends with
gravitational potential energy.
15) An objects starts with kinetic
energy and gravitational PE,
then ends with kinetic energy.
16) An object starts with
gravitational PE and ends with
kinetic energy.
i 17) An object begins with
. gravitational PE some of which
turns into kinetic energy.
18) An object starts with elastic
PE some of which then turns
into KE, gravitational PE.
I
Part IV: Problems
19) A ball slides down the frictionless track shown below. The ball has no ve
- ~ .• Gyt.e
~II Co/I'f
'5ef
d/Iy h~h('l" fhot, #.;$.'
.......... -­ -c:-- - - - ­
F
oes the ball rise on the opposite incline?
B
b) At what point(s) in the diagram is the speed at a maximum?
8
c) At what pOint(s)is the kinetic energy at a maximum?
---=-­
~€
d) At what point(s) is the speed zero?
I
B
-=-­
(IE
e) At what point(s) is the potential energy at a minimum?
f) At what point(s) is the potential energy at a maximum?.r:f'
';he kIf fl,f
to
6.
t1,e 6tlS WC?/' wolA/&.- be. 6.
~ g) At what point(s) is the momentum at a maximum?
20) A pendulum is pulled sideways so that it is raised a vertical distance of 2 m above its resting position. Find the
maximum speed the pendulum reaches after being released.
Kf
21) An archer pulls back on a 0.25 kg arrow 1.5 m using bow. He then shoots the arrow and it leaves the bow traveling
at 120 mIs, what is the spring constant of the bow?
!Jlatf
lkG •
P~.:
(t'lcl
II
PEK
i kx t
vr:"
r~ - '"'f
I<
KE. Pf.1<
(I. S)'Z. k ~ (o.Z.5~ZO)-'-'
Kf£
2
.::.
'2. 2.251< =3ft,OO
li--k-:'-}(p(X>-ij
mV 22) A man standing on top of a 30 m tall building drops a brick. Determine the speed of the brick just before it hits
the ground.
pl
$I",+-
11(6
U
I..LKE
(,a Xoo)
0('..
'G~ ~h:
~
"&.
z.I'1V
if
-: :. .!. V -z.
2.
= (r,/)()
23) How high will a 60kg girl go if she stretches a trampoline (100 N/m) 1.4 m?
~I(JI'+
~
PE~ PE-J(
~(tcL
I. .
f'£~ P£.,..
PEl< : f£<!>
ik~~:
Me h
~(,()(/t.l.lf)-" : (~XJ{)'i.h)
·1
2..'1-. ~ ~ =-V
1
24) The frictionless car below is moving at 4 m/s at position A (50 m above ground level). It has a mass of 1000 kg and
is rolling along the hills in neutral. Point B is at ground level.
A \I'-),.~
-¥&
~~/~
a) What is the total energy of the car at point A?
K!+- ~
i
PI V1.
i(I6/JIJX'f)-Z"'(/~~)fi"
~~J"
A
II I
J<~ P~ ®t.
GOI"l
f!ip> .,. Sof)(X)()
--- --
1
B
---------------------------------­
h =10
b) What is the total energy of the car at point B?
[9l9oa:?~ [ ~ &Jefll,y ~5 fhe~.'
c) How fast will the car be moving when it reaches position B (at ground level)?
'hI. q "";j
KG:.
KG:.
fbBCXJ() d
I
All +he" flJEY43Y:-S h'1E,
frlV''"
'I.
'i. fJorx,)v
v"z' ':
1()11o
3/.Q"'A
d) What is the maXim'Arrh:n:;e ;;~th;~the Pf;! r e a c ; : ; t :d~:xJO) h
[h:~.91'1
I
[
f'1-=
/CU> /;'3
G6~fX)O=~h
25) At point "A" on the hill, there is a skier at rest.
A
SOfl(£() :
I L~
J<E'~ KE. P6~ £"~y
h:f;;().9ri
D
A
8
V":.
U
8m
KE I'EC)
B
a) Find the skier's maximum speed. Where on the hill does she achieve this speed?
o.l., A :: E(Jf't{)y (4,+ 8
Sfdf B
p~~
I<E
PtS~:: i~-z... v1.: lIfO
= .l- V
The ~ o.s fk 1.fa;.~\(lt!J he'5ht!
uoX/Z)
b) How far vertically up the other hill will the skier bf-able to go?
12..('1 I
V:.IZ.(P~
I
v=8.qt*l41
26) A water balloon is shot upwards with a velocity of 55 m/s. How high does it travel?
\Ii,
}(£: ~
{rtGl
Swr
I
L1<, PE5
P~
J
...i'
• .," :. ",,(
nr
,r
,,.5
l(~S)"t = UiJ) h
h
2­
h :: IS I (l1
27) A man standing on top of a 30 m tall building throws a brick downwards with a velocity of 12 m/s. Determine the
speed of the brick just before it hits the ground.
KErt p~; .: K£.f
Err/.
Sf"f
V.f?- :. '"
I.KG p~
• lIt P(v," ~l, :: if'~"
I<E ~
J(.z)t." Oo"bo)
7 Z.
\I~ ~ 11.3 "'A
1"
=. -£V.f'l.
Z.
28) A 80 kg kid seeking attention jumps off of a garage roof onto a trampoline. If he is traveling at 8 m/s just before
he begins to stretch the 120 N/m trampoline, how far will the trampoline stretch before it flings him upwards?
~&-f
I~ £:: P£I{
£*,.J.
U
LA--
I.
til
;1:nY1t."
ttZ. fD 7 = X.*'L
ik~~
(8t;'f..B)'1. :: (ll()))(.7,.
1<6 P6k
ff:: :. KG
IX~'.S3(>J
.
29) An archer pulls back on a 0.2 kg arrow 1.0 m using a 60 N/m bow. He then shoots the arrow. What is the velocity
K6
~
l{1
the
a~~lhird 01 the
G PI ,.,
~s')15m) + Y,12m!s)'
Of~he
ik~"L
+
IV~
fEk Y,
iMV'~""
ik(;x)t.
M'-'t.J)'l.::. ;iftJ.iJv L *"ftw'U.1J)"t.
V7.:.
7. 3 ~h
$3. ",(p
Part v: Backwards Problems
.t,\'" 1) Draw a picture of the work shown, and 2) give the equation being solved 30)
( 20 Nj m )
31)
=
( 08m)
.
=
(O.2kg)(Sm/s)2
(
)2
O.Sm
(4m/s)2
2(10m/s2)
32) lO.lm/s = .jZ(lOm/sIlZ)(Sm) + l/Z(Zm/s)AZ
33) 448N/
m
;::: 2[(2kg)(lOmlsA2)(3m)-1/2(2kg)92m/s)A2]
(.5m)A2
I


