Reinforcing Bar Supports
Use the right supports to prevent problems, enhance durability, and maintain
structural integrity
M
ost design specifications call for reinforcing bars to be precisely and accurately
spaced. The most common way of
spacing reinforcing bars is through
the use of reinforcing bar supports.
These supports come in a va ri e t y
of configurations for various applications and can be made of metal,
concrete, fiber-reinforced cement,
plastic, or other material. The ma-
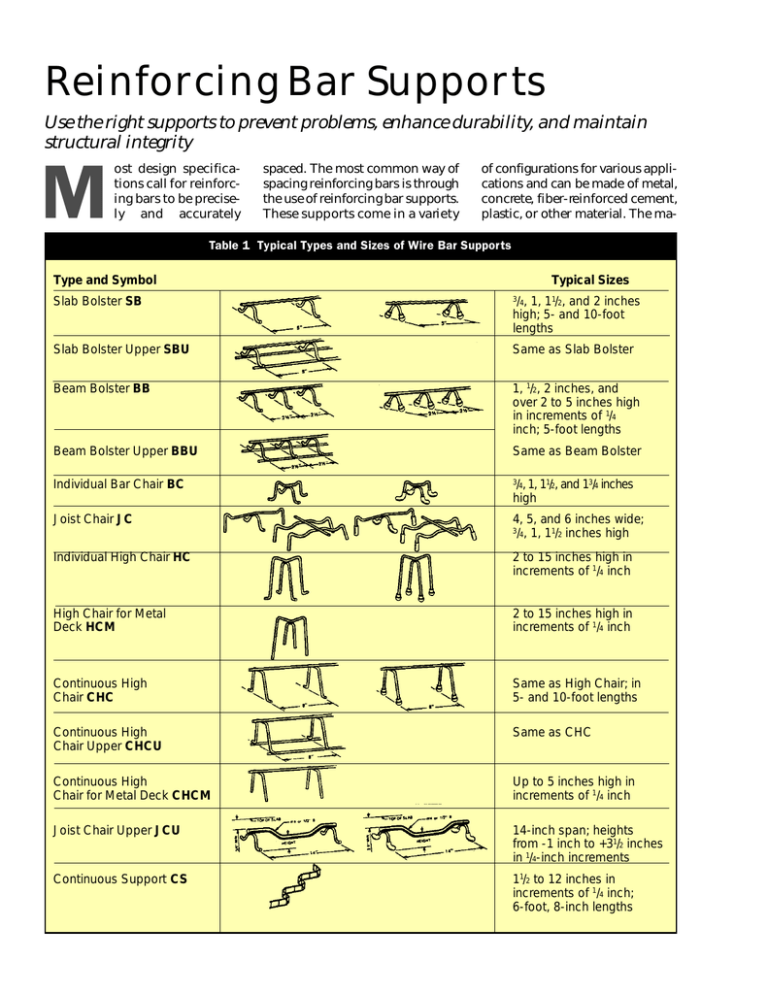
Table 1 Typical Types and Sizes of Wire Bar Supports
Type and Symbol
Typical Sizes
Slab Bolster SB
3/4, 1, 11/2, and 2 inches
high; 5- and 10-foot
lengths
Slab Bolster Upper SBU
Same as Slab Bolster
Beam Bolster BB
1, 1/2, 2 inches, and
over 2 to 5 inches high
in increments of 1/4
inch; 5-foot lengths
Beam Bolster Upper BBU
Same as Beam Bolster
Individual Bar Chair BC
34
Joist Chair JC
/ , 1, 11/2, and 13/4 inches
high
4, 5, and 6 inches wide;
/ , 1, 11/2 inches high
34
Individual High Chair HC
2 to 15 inches high in
increments of 1/4 inch
High Chair for Metal
Deck HCM
2 to 15 inches high in
increments of 1/4 inch
Continuous High
Chair CHC
Same as High Chair; in
5- and 10-foot lengths
Continuous High
Chair Upper CHCU
Same as CHC
Continuous High
Chair for Metal Deck CHCM
Up to 5 inches high in
increments of 1/4 inch
Joist Chair Upper JCU
14-inch span; heights
from -1 inch to +31/2 inches
in 1/4-inch increments
Continuous Support CS
11/2 to 12 inches in
increments of 1/4 inch;
6-foot, 8-inch lengths
jority of the information in this article is derived from Reference 1.
Wire Bar Supports
Metal bar supports usually are
made of plain or stainless steel wire
and are one of the most common
types used (Table 1). Lower portions of wire supports may have a
plastic coating to prevent rusting,
or are manufactured in whole or
part of stainless steel. Both types
can be used where light grinding
(1/16 inch or less) or sandblasting of
the concrete will be done.
Plastic-coated wire bar supports
(Class 1—maximum protection) are
intended for use in situations of
moderate to severe exposure. The
plastic coating usually is applied by
the manufacturer by dipping or by
using premolded slip-on plastic tips.
No matter which method is used, inspect the coating or tip before use
to ensure that it will not chip, crack,
deform, peel, or come loose under
ordinary job conditions.
Stainless steel protected bar
supports (Class 2—moderate protection) are for use in moderate-exposure applications. One type of
stainless steel support is fabricated
from steel wire and has a stainless
steel tip or leg extension attached
to each leg. Tipped bar supports
generally provide a minimum of 1/4
inch of stainless steel protection
from the form surface, while supports with leg extensions generally
provide a minimum of 3/4 inch of
protection. Legs on other types of
wire bar supports are fabricated
THE
MOST COMMON WAY OF
SPACING REINFORCING BARS
IS THROUGH THE USE OF
REINFORCING BAR SUPPORTS.
entirely from stainless steel.
Bright basic wire bar supports
(Class 3—no protection) have no
p rotection against rusting and
a re intended for use where surface blemishes can be tolera t e d
or where the supports do not
come in contact with exposed
concrete surfaces.
Concrete Bar Supports
Precast concrete bar supports
(Table 2) are normally available in
three styles: plain, with wires, and
doweled. Plain concrete bar supports are used to support bars off
the ground. Concrete bar supports
usually come with two wires cast
into the support’s center. The wires
are used to hold the support
against vertical forms or to hold the
concrete bar support in place by tying it to reinforcing bars.
Doweled concrete bar supports
are cast with a 21/4-inch-deep hole
in the center. The hole usually is
large enough so that a #4 reinforcing bar can be inserted into it. The
reinforcing bar thus inserted usually has a 90-degree bend at its top.
This allows reinforcing steel to be
placed across the horizontal portion of the bent bar. At the same
time, the concrete bar support can
be used to support bottom bars off
the ground by placing them on the
shoulders of the bar support.
Fiber-reinforced Supports
Cementitious fiber- re i n f o rc e d
bar supports (Table 3) are available
in two types: plain and with wire.
Most are chemically inert and bond
naturally to the concrete. Both
types can be used for both hori zo ntal and vertical reinforcing steel
Table 2 Typical Types and Sizes of Precast Concrete Bar Supports
Type and Symbol
Typical sizes (inches)
Plain Block
PB
A—3/4 to 6
B—2 to 6
C—2 to 48
Wired Block
WB
A—3/4 to 4
B—2 to 3
C—2 to 3
Tapered Wired Block
TWB
A—3/4 to 3
B—3/4 to 21/2
C—11/4 to 3
Combination Block
CB
A—2 to 4
B—2 to 4
C—2 to 4
D—fits #3 to #5 bar
Dowel Block
DB
A—3
B—3 to 5
C—3 to 5
D—hole to accommodate a #4 bar
Table 3 Typical Types and Sizes of Cementitious Fiber-reinforced Bar Supports
Type and Symbol
Typical Sizes
(inches)
Description
Slab Bolster
SB
3/4 to 3 high;
2, 3, 12, 36 long
Supports lower slab
reinforcing steel; also
comes in circular shape
for architectural work
and square shape for
heavy reinforcement
Beam Bolster
BB
same as above
Supports lower beam
bars and heavy slab bars
Bar Chair
BC
34
Supports bars in slab
and deck construction;
comes with or without
tie wire in three types:
single, double, and triple cover
/ to 2 high
Single Cover
High Chair
HC
Double Cover
34
/ to 3 high
Supports upper slab
bars directly or supports
lower slab bars; comes
with or without tie wires
Triple Cover
34
Clip-on Spacers
CS
/ to 2 concrete
cover
Vertical Spacers
VS
34
Double Clips
Available with double or
single clips; provides
necessary cover between
vertical bars and formwork
Single Clip
/ to 3 concrete
cover
support. Many supports of this type
are available in configurations that
offer multiple support heights from
the same support.
All-plastic Bar Supports
Many all-plastic bar supports
(Table 4) can be used for both horizontal and vertical re i n f o rc i n g
steel due to their snap-on action or
other method of attachment. Allplastic supports offer the advantages of being lightweight, nonp o ro u s, and chemically inert to
c o n c re t e. Properly designed allplastic supports should have
rounded seating areas to pre ve n t
their punching holes in formwork.
They also should not deform under
load when subjected to normal
temperatures encountered during
use, nor should they shatter or severely crack under impact loading
when used in cold weather.
According to one report (Ref. 2),
because all-plastic bar supports
and spacers are subject to temperature effects, they should have at
least 25% percent of their gross
plane area perforated to compensate for the difference in the coefficient of thermal expansion between the plastic and concrete. The
same report also notes that allplastic supports should be placed
no closer than 12 inches apart
along a bar.
All-plastic supports do not rust,
therefore eliminating blemishes on
concrete surfaces. These supports
Available with hooks for
attaching to bars;
provides cover between
vertical bars and
formwork; triangular in
shape and 12 inches long
are said to be especially suitable
where moderate to severe exposure
will be encountered or when grinding of the concrete is necessary. In
addition, all-plastic supports may
be used to support epox y- c o a t e d
reinforcing bars.
Supports for Epoxy-coated Bars
Ep ox y-coated re i n f o rcing bars
have become a widely used corros i o n - p rotection system for re i nf o rced concrete stru c t u re s. Sp ecial types of bar supports should
be used with epox y-coated bars.
This is done to prevent damaging
the coating on the bars duri n g
field placement and to pre vent a
potential source of corro s i o n
w h e re the bar supports contact
Table 4 Typical Types and Sizes of All-plastic Bar Supports
Type and Symbol
Bottom Spacer BS
Typical Sizes
(inches)
3/4 to 6 high
Description
Generally for horizontal work;
not recommended for ground
or exposed-aggregate finish
Bottom Spacer,
Clamp-on BS-CL
34
Generally for horizontal work;
provides bar clamping action;
not recommended for ground
or exposed-aggregate finish
High Chair HC
34
For use on slabs or panels
High Chair,
Variable HC-V
21/2 to 61/4
For horizontal and vertical
work; provides for different heights
Wheel Spacer
3/8 to 3 concrete
cover
Generally for vertical work;
bar clamping action and minimum
contact with forms; applicable for
column reinforcing steel
/ to 2 high
/ to 5 high
the coated bars.
To prevent problems when using
epoxy-coated reinforcing bars, the
Concrete Reinforcing Steel Institute
recommends the following:
1. Wire bar supports should be
coated with dielectric (nonconducting) material, such as epoxy or
plastic, compatible with concrete,
for a distance of at least 2 inches
from the point of contact with the
epoxy-coated reinforcing bars, or
2. Bar supports should be made
of dielectric material. In addition,
if precast concrete blocks with em-
bedded wire ties or precast concrete doweled blocks are used, the
wires or dowels should be epoxycoated or plastic-coated, or
3. Reinforcing bars that are used as
support bars should be epoxy-coated. In walls reinforced with epoxycoated bars, spreader bars (where
specified) also should be epoxy-coated. Proprietary combination bar
clips and spreaders used in walls with
epoxy-coated bars should be made
of corrosion-resistant material or
coated with dielectric material.
References
1. Manual of Standard Practice, Chapter 3—Bar Supports, Concrete Reinforcing Steel Institute, 933 N. Plum
Grove Rd., Schaumburg, Ill. 60173.
2. “Selection of Bar Spacers for Reinforced Concrete,” Concrete, November 1968, Cement and Concrete Association, London, England.
PUBLICATION #C940569
Copyright © 1994, The Aberdeen Group
All rights reserved