Lecture 16
advertisement

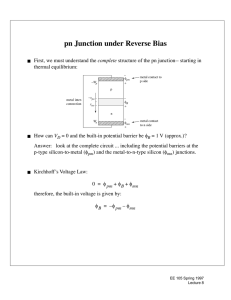
Lecture 16 The pn Junction Diode (III) Outline • Small-signal equivalent circuit model • Carrier charge storage –Diffusion capacitance Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini; Chapter 6, Sections 6.4 - 6.5 6.012 Spring 2007 Lecture 16 1 I-V Characteristics Diode Current equation: ( ) ⎡ I = Io ⎢e ⎢ ⎣ I V Vth ⎤ −1⎥ ⎥ ⎦ lg |I| 0.43 q kT =60 mV/dec @ 300K Io 0 0 V Io linear scale 6.012 Spring 2007 0 V semilogarithmic scale Lecture 16 2 2. Small-signal equivalent circuit model Examine effect of small signal adding to forward bias: ⎛ q( V+v) ⎞ ⎡ ⎛ q (V+v )⎞ ⎤ ⎜ ⎟ ⎢ ⎜⎝ kT ⎟⎠ ⎥ I + i = Io ⎢e −1⎥ ≈ I oe ⎝ kT ⎠ ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ If v small enough, linearize exponential characteristics: ⎡ (qV ) (qv )⎤ ⎡ (qV )⎛ qv ⎞ ⎤ kT kT kT I + i ≈ I o ⎢e e ⎥ ≈ I o ⎢e ⎜1 + ⎟⎥ ⎝ kT ⎠ ⎥⎦ ⎢⎣ ⎥⎦ ⎢⎣ = Io Then: qv ( ) ( ) e +I e qV kT o qV kT kT qI i= •v kT From a small signal point of view. Diode behaves as conductance of value: qI gd = kT 6.012 Spring 2007 Lecture 16 3 Small-signal equivalent circuit model gd gd depends on bias. In forward bias: qI gd = kT gd is linear in diode current. 6.012 Spring 2007 Lecture 16 4 Capacitance associated with depletion region: ρ(x) p-side (a) −xp +qNd n-side x xn vD = V D −qNa QJ = −qNaxp ρ(x) +qNd p-side −x −x p p (b) n-side x xn xn vD = VD + vd > VD--> xp < xp,| qJ | < | QJ | −qNa qJ = −qNaxp qj = qNa∆xp ∆ρ(x) = ρ(x) − ρ(x) + qNd Xd p-side (c) xn xn −xp −xp qj = qj − Qj > 0 = −qNaxp − (−qNaxp) = qNa (xp −xp) = qNa∆xp n-side x − qNa −qj = −qNd ∆xn Depletion or junction capacitance: dqJ C j = C j (VD ) = dv D Cj = A 6.012 Spring 2007 VD qε s N a N d 2(N a + N d )(φ B − VD ) Lecture 16 5 Small-signal equivalent circuit model gd Cj can rewrite as: qε s N a N d Cj = A • 2(N a + N d )φ B or, Cj = φB (φ B − VD ) C jo 1− Under Forward Bias assume VD φB VD ≈ φB 2 C j = 2C jo Cjo ≡ zero-voltage junction capacitance 6.012 Spring 2007 Lecture 16 6 3. Charge Carrier Storage: diffusion capacitance What happens to majority carriers? Carrier picture thus far: ln p, n Na Nd po no p n ni2 Nd ni2 Na 0 x If QNR minority carrier concentration ↑ but majority carrier concentration unchanged? ⇒ quasi-neutrality is violated. 6.012 Spring 2007 Lecture 16 7 Quasi-neutrality demands that at every point in QNR: excess minority carrier concentration = excess majority carrier concentration (p-type) pp(x) = Na + np(x) nn(x) = Nd + pn(x) ppo = Na metal contact to p region pn(xn) = pno . eVD/Vth pn(x) np(x) np(−Wp) = npo metal contact to n region nno = Nd np(−xp) = npo . eVD/Vth −Wp ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; carrier concentrations (cm−3) (n-type) 0 −xp 0 xn pn(Wn) = pno Wn x Mathematically: pn (x) − pno = n n (x) − n no Define integrated carrier charge: 1 q Pn = qA (pn (x n ) − pno ) • (W n − x n ) 2 W n − x n n i2 ⎡ qVkT ⎤ = qA e −1⎥ = −q Nn ⎢ ⎣ ⎦ 2 Nd 6.012 Spring 2007 Lecture 16 8 Now examine small increase in V: ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; metal contact to p region p-type n-type nn(xn) [for VD + vd] pp(−xp) [for VD + vd] dqPp pp(−xp) [for VD] nn(xn) [for VD] ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; carrier concentrations (cm−3) −dqNn pn(xn) [for VD + vd] np(−xp) [for VD + vd] pn(xn) [for VD] −dqNp np(−xp) [for VD] 0 −xp −Wp 0 xn dqPn metal contact to n region Wn x Small increase in V ⇒ small increase in qPn ⇒ small increase in |qNn | Behaves as capacitor of capacitance: Cdn = 6.012 Spring 2007 dqPn dV = qA VD Lecture 16 Wn − xn n q e 2 N d kT 2 i ⎡ qVD ⎤ ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ kT ⎦ 9 Similarly for p-QNR: Cdp = Wp − xp n q = qA e 2 N a kT 2 i dqNp dV VD ⎡ qVD ⎤ ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ kT ⎦ Both capacitors sit in parallel ⇒ total diffusion capacitance: C d = Cdn + Cdp Complete small-signal equivalent circuit model for diode: gd 6.012 Spring 2007 Lecture 16 Cj Cd 10 Bias dependence of Cj and Cd: C Cd C Cj 0 0 V • Cj dominates in reverse bias and small forward bias ∝ 1 φB − V • Cd dominates in strong forward bias ∝e 6.012 Spring 2007 Lecture 16 ⎡ qV ⎤ ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ kT ⎦ 11 What did we learn today? Summary of Key Concepts Large and Small-signal behavior of diode: • Diode Current: I = Io • [ ] (e − 1) qV kT Conductance: associated with current-voltage characteristics – gd ∝ I in forward bias, – gd negligible in reverse bias • Junction capacitance: associated with charge modulation in depletion region Cj ∝ • 1 φB − V Diffusion capacitance: associated with charge storage in QNRs to maintain quasi-neutrality. Cd ∝ e 6.012 Spring 2007 Lecture 16 ⎡ qV ⎤ ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ kT ⎦ 12