Material Safety Data Sheet Neodymium-Iron
advertisement
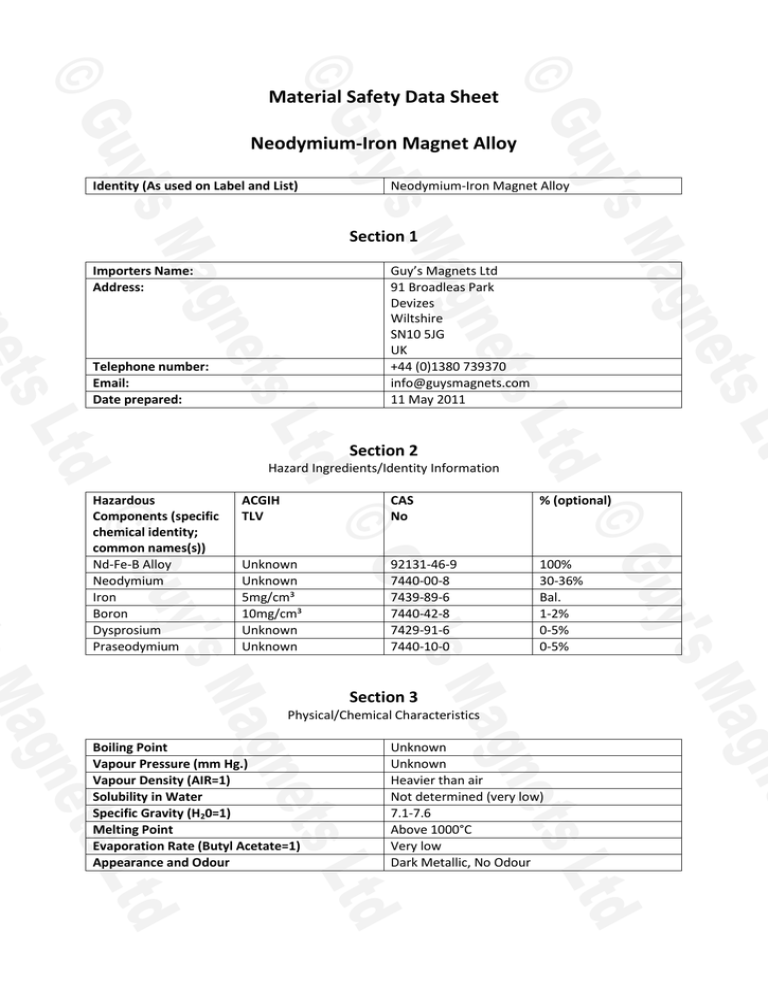
Material Safety Data Sheet Neodymium-Iron Magnet Alloy Identity (As used on Label and List) Neodymium-Iron Magnet Alloy Section 1 Importers Name: Address: Guy’s Magnets Ltd 91 Broadleas Park Devizes Wiltshire SN10 5JG UK +44 (0)1380 739370 info@guysmagnets.com 11 May 2011 Telephone number: Email: Date prepared: Section 2 Hazard Ingredients/Identity Information Hazardous Components (specific chemical identity; common names(s)) Nd-Fe-B Alloy Neodymium Iron Boron Dysprosium Praseodymium ACGIH TLV CAS No % (optional) Unknown Unknown 5mg/cm³ 10mg/cm³ Unknown Unknown 92131-46-9 7440-00-8 7439-89-6 7440-42-8 7429-91-6 7440-10-0 100% 30-36% Bal. 1-2% 0-5% 0-5% Section 3 Physical/Chemical Characteristics Boiling Point Vapour Pressure (mm Hg.) Vapour Density (AIR=1) Solubility in Water Specific Gravity (H20=1) Melting Point Evaporation Rate (Butyl Acetate=1) Appearance and Odour Unknown Unknown Heavier than air Not determined (very low) 7.1-7.6 Above 1000°C Very low Dark Metallic, No Odour Section 4 Fire and Explosion Hazard Data Flash Point (Method Used) Flammable Limits LEL UEL Extinguishing Media Special Fire Fighting Procedures Unusual Fire and Explosion Hazards N/A N/A N/A N/A Dry chemicals for fighting magnesium or metal fires Isolate and contain burning materials. Smother with Argon gas or non-reactive dry chemicals. Avoid water. Do not use Halon. For solid dense magnet: none. Powders from chipping, crushing, grinding, slicing etc: may ignite spontaneously and burn intensely. Rare earth metal powders burn vigorously in halogen or oxidizing atmospheres Section 5 Reactivity Data Stability Unstable Stable X Conditions to Avoid Acids, highly active oxidisers Hydrogen may be released when powders react with water May occur Will not occur X Conditions to avoid Incompatibility (Materials to Avoid) Hazardous Decomposition or Byproducts Hazardous Polymerisation Section 6 Health Hazard Data Route(s) of Entry: Health Hazards (Acute and Chronic) Carcinogenicity: Signs and Symptoms of Exposure Medical Conditions Generally Aggravated by Exposure Emergency and First Aid Procedures Inhalation? YES Skin? YES Ingestion? NO Entry through skin injuries may irritate and produce granulomas NTP? NO IARC Monographs? NO OSHA Regulated? NO Skin or eye irritations Skin cuts, abrasions, punctures Remove victim from dust and fume environment. Flush skin and eyes with water. Section 7 Precautions for Safe Handling and Use Steps to be taken in case material is released or spilled Waste disposal method Precautions to be taken in Handling and Storing Other precautions Fine chips and powders should be gathered up by a damp mop or broom. Do not use a vacuum cleaner. Metal recycling. Powders may ignite and burn. Store under inert gas or vacuum. Storage in water may generate hydrogen gas. Use water during machining processes to control sparking of the swarf. Section 8 Control Measures Respiratory Protection (Specify Type) Ventilation: Protective Glvoes Eye Protection Other Protective Clothing or Equipment Work/Hygienic Practices Use dust mask whenever dust is present Local Exhaust: Use for dust and iron fumes when machining or pulverizing Special: N/A Mechanical (General): N/A Other: N/A Use Use Garments to protect skin from direct contact Avoid skin injuries. If powders generated are inhaled, train workers in safe practices for combustible powders. Magnetised parts are strongly attracted to each other and to steel – handle firmly to avoid injury causing impacts.