WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria
advertisement

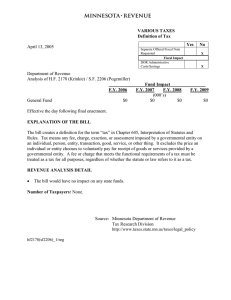
1 WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria Risk Factor Risk Factor Subcategory Description Low Medium High Considerations Compliance Trends Severity Risk the entity’s violation(s) Violation(s) pose no higher than pose on the reliability of minimal risk the BES. Violation(s) pose no higher than moderate risk Compliance Trends Repeats Multiple violations of the same Standard and Requirement No repeat violations Repeat violations with different root causes Compliance Trends Area of Concern No violations associated with an Area of Concern Compliance Trends Violation Cluster Violations since the previous audit for Requirements associated with an Area of Concern given at previous audit or spot check Violations of different Standards and Requirements that are the result of the same set of circumstances No violation clusters Violation cluster(s) of less than five violations Generation Portfolio Generating Facilities and Fuel Type Entity has just one generating facility Entity has multiple generating facilities at same geographical location Entity has multiple generating facilities in geographically dispersed location. Generation Portfolio Name Place Generation Capacity 0-1000 MW 1000-6000 MW Greater than 6000 MW Generation Portfolio Renewable Portfolio Maintenance Challenges based on number of generating facilities, and its geographical location Amount of generation that entity owns or is within its foot print Renewable generation in BA footprint < 10% generation in BA footprint is renewable generation 10-25% generation in BA footprint is renewable generation > 25% generation in BA footprint is renewable generation Generation Portfolio Distributed Generation The amount of generation An entity has < 800 MWs of distributed that is not visible to the entity generation that is not telemetered but is required to be balanced An entity has 800-2000 MW of distributed generation that is not telemetered An entity has more than 2000 MW of distributed generation that is not telemetered Generation Portfolio Ancillary resources Ancillary Power Plant Some of the generating units owned by the All the generating unit owned by entity can Entity performs periodic testing to ensure the generating unit can be used entity can be used for Reserve Sharing be used for Reserve Sharing Purposes for Reserve Sharing purposes. The risk should be reduced. Purposes Revised November 20, 2015 Entity does not own any units that can be used for Reserve Sharing Purposes Violation(s) pose severe risk Risk may be lower if higher risk violations occurred before the last audit, if higher risk violations were mitigated within a reasonable amount of time, and/or there are no root cause trends (violations with the same root cause). Consideration should also be given if entity has performed a root cause analysis and WECC has discussed the analysis. Repeat violations with the same root More weight to be given to repeat violations since the last audit. cause Consideration should also be given if entity has performed a root cause analysis and WECC has discussed the analysis. Another consideration is whether or not the violation is for a zero-defect Requirement One or more violations associated with Risk may be lower if higher risk violations occurred before the last an Area of Concern audit, if higher risk violations were mitigated within a reasonable amount of time, and/or there are no root cause trends (violations with the same root cause). Consideration should also be given if entity has performed a root cause analysis and WECC has discussed the analysis. Violation cluster(s) of five or more Consideration should be given if both O&P and CIP Requirements violations were impacted by the circumstances. Consideration should also be given if entity has performed a root cause analysis and WECC has discussed the analysis. The risk can be reduced based on Generator’s equivalent Forced outage rate. If the Equivalent forced outage rate is less than 5, the risk can be reduced. If an entity has wind and solar forecasting tools that are considered in its planning studies, the risk of renewable generation integration should be reduced. Risk should be reduced, if entity is taking steps to account of distributed generation or entity’s operators are being trained to balance the system for distributed generation that is not visible on their scads system. 2 WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria Risk Factor Generation Portfolio Risk Factor Subcategory Description Reserve Sharing Managing Reserves Low Internal Resources within an entity's footprint are adequate for maintaining reserves and Entity is participant of Reserve Sharing Group Medium Internal Resources within an entity's footprint are adequate for maintaining reserves OR Entity is participant of Reserve Sharing Group Blackstart Resources Blackstart Availability Entity owns or has access to Blackstart Resources Entity owns Blackstart units AND Entity operates all Blackstart units for peaking or other non-Blackstart uses, as needed Entity owns Blackstart units Entity owns Blackstart units but operates all AND of them during Blackstart emergencies only Entity operates some of the Blackstart units for peaking or other non-Blackstart uses while other units are only operated for Blackstart emergencies Emergency Preparedness General Preparedness Peak Load to Generation ratio The entity's peak load is 800 MW or less and availability of Blackstart resources An entity has peak load greater than 800 MW and Peak Load / Generation ratio is less than or equal to 1 OR Entity has Peak Load greater than 800 MW and Peak Load/Generation ratio is less than or equal to 2 and the entity owns or operates Blackstart resource High Considerations Internal Resources within an entity's If an entity does not have studies to ensure that the reserves will be footprint are not adequate for maintaining available from reserve sharing pool on that day based on the system reserves condition, risk can be increased. OR An entity does not participate in Reserve Sharing Group. An entity has peak load greater than 800 If an entity is a load serving entity, the risk can be reduced even if the load MW and Peak Load / Generation ratio is to generation ratio is greater than one. greater than 1 and entity does not own or operate Blackstart resource OR Entity has Peak Load greater than 800 MW and Peak Load/Generation ratio is greater than 2 and entity owns or operates Blackstart resource Transmission Portfolio Transmission Portfolio Transfer Paths Does the entity have a transfer path? Entity does not have a WECC transfer path Entity owns or operates an element of WECC Transfer Path but does not own or operate an element of WECC Major Transfer Path. Transmission Portfolio Transmission Length Length of entity’s transmission lines Entity has less than 1000 miles of transmission lines Entity has between 1000 and 4000 miles of Entity has greater than 4000 Miles of transmission line transmission lines Transmission Portfolio Transmission Voltage The entity does not own or operate transmission lines larger than 161 kV Entity owns or operates transmission lines greater than 161 kV, but none larger than 345kV One line identified as a Critical Asset Transmission Portfolio Voltage levels that the entity owns or operates within its system. Critical Transmission Lines Transmission lines identified as a Critical Asset and amount of load on the lines. Revised November 20, 2015 No transmission lines are identified as a Critical Asset. If any Blackstart unit experienced a startup forced outage failure while testing or during any other time it is required to generate, then the risk for failure during an emergency is much higher and the risk rating may be increased. Entity owns or operates an element of WECC Major Transfer Path Entity owns or operates transmission lines larger than 345 kV Review any unplanned transmission outages, Loss of Load events, Misoperations and Violation History for any common trends related to transmission portfolio. Transfer limits on Transfer Paths range from 17MW to 11,200MW with an interconnection average of approximately 2,023MW. If the path transfer limit is less than the 2,023MW average, the risk can be reduced to low for a Transfer Path for medium for a Major Transfer Path. If entity only has transmission lines less than or equal to 230 kV or if the entity did not have any sustained forced outages on its transmission lines since the last audit, the risk may be reduced. If the entity has less than 50 miles of transmission lines 345kV to 500kV, the risk may be reduced. More than one line is identified as a Critical If the entity's transmission system is highly resilient and a line outage Asset would have minimal impact, risk rating may be reduced. Alternatively, risk rating may be raised if the entity's system is particularly vulnerable to a line outage. 3 WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria Risk Factor BPS Coordination Risk Factor Subcategory Description Coordination based on Number of interconnections number of entity has and amount of Interconnections coordination required to be done Low Entity has interconnections with single entity Medium Entity has one interconnection with multiple entities BPS Coordination Geographical location Geographical location of entity in the Western Interconnection Entity’s system is not critical to adjacent entities as it is not being used as a flow through system for power flow Entity’s system is critical to adjacent entities as it is being used as a flow through system for power flow BPS Coordination Coordination with neighbors Geographical location and responsibilities as per registration Entity is registered as a GO, TO, TP, DP, LSE, Entity is a BA, TOP, or GOP for its own TSP, PA or RP Generation and Transmission asset Entity is registered as an RC OR Entity is registered as a BA, TOP or GOP, and entity has other Generation, Transmission assets not owned by the entity in its footprint System Geography System Geography Type of Terrain Entity has no areas of challenging system geography (e.g. desert or plains with no vegetation) Transmission lines are exposed to a large amount of challenging system geography, wildfire risk, and/or invasive vegetation (e.g. rugged terrain, high growth rate vegetation, dense forest) Load Management Resource Flexibility to manage load profile changes Entity’s ability to adjust the Entity has not identified any change in load Entity identified a change in load profile resources as per the changes profile since last audit since last audit in the demand. AND Entity has sufficient resource mix that can react quickly to meet sharp changes in net demand Entity identified a change in load profile If an entity monitors load profile in its planning assessments and is since last audit prepared to address the challenges faced by it, risk rating may be AND reduced. Entity does not have sufficient resource mix that can react quickly to meet sharp changes in net demand System Modeling and Usage Critical Facility Identification Identification of critical facilitie Entity’s Planning Authority or Transmission Planner has not identified critical transmission or generation facilities that impact the reliability of entity’s system. Entity’s Planning Authority or Transmission Planner has identified one critical facility within entity’s system that impact the reliability of BES Entity’s Planning Authority or Transmission Is PA testing the study models provided by Transmission Planners and Planner has identified multiple critical Resource Planners on the periodic basis? If yes, the risk rating may be facilities within entity’s system that impact reduced. the reliability of BES System Modeling and Usage Planning Authority Identification of Planning Authority footprint Entity is a Planning Authority and models the information of its neighboring entities even though it does not formally identify the entity in their Planning Authority Area. Entity is a Planning Authority for itself, but Risk should be reduced if a Planning Authority is modeling neighboring does not identify entities within its Planning Planning Authority’s information. Authority Area. OR Entity is not a Planning Authority and does not identify Planning Authority Area it is required to be under. Revised November 20, 2015 Entity has a formal Transmission Planning process and identifies the entities that should be within its Planning Authority Area. Or Entity is not a Planning Authority but is in agreement with the Planning Authority to which it should belong to. Entity has a moderate amount challenging system geography (e.g. wet lands, low growth rate vegetation, lakes, rivers) High Entity has more than one interconnections with multiple entities Considerations 1. If any areas of concern or major events are associated with vegetation management issues, risk rating may be increased 2. If additional "above and beyond" resources (e.g. LiDAR, drones, or other monitoring technology) are integrated, risk rating may be reduced 4 WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria Risk Factor System Modeling and Usage System Modeling and Usage Risk Factor Subcategory Description Low Medium High System Modeling WECC Base Case utilization for Entity uses WECC base case for its planning Entity reviews WECC’s base case but Entity uses its own base cases for its system modeling assessments develops its own base case for its planning planning assessments assessments Network Application Real Time Contingency Entity uses RC hosted RTCA application for Entity uses RC hosted RTCA application for Entity does not have RTCA application. Usage Analysis (RTCA) utilization contingency analysis contingency analysis AND OR Has its own RTCA tool for contingency Entity uses its own RTCA tools for analysis contingency analysis System Modeling and Usage Planning Studies in Operating Horizon Understand the type of planning studies performed by the entity to take pre contingency actions Entity performs daily studies for understanding system conditions and identifying pre contingency actions to be taken Entity reviews its seasonal studies daily but does not perform actual studies for understanding system conditions and identifying pre contingency actions to be taken System Modeling and Usage Modeling Consistency Modeling consistency between planning and operating horizon Entity has a formal process to ensure operation model and planning model have the same modeling assumptions and both the models are in sync Entity does not have a formal process to Entity does not review its planning and ensure operation model and planning operations model to ensure consistency models have same modeling assumptions within the models but the models are reviewed periodically to maintain consistency within the models Equipment Categories Special Protection Scheme Type of SPS that entity has (SPS)/Remedial Action and periodic review of SPS Scheme (RAS) design Revised November 20, 2015 Entity owns or operates SPS classified Entity owns or operates SPS classified under Local Area Protection Scheme (LAPS) under Wide Area Protection Scheme and entity reviews SPS design periodically (WAPS) and reviews its SPS design periodically OR Entity owns or operates SPS that is classified under LAPS and does not review its design periodically Considerations If an entity participates in regional committees and coordinates its base case, the risk rating may be reduced. If an entity has other operational models that assist in real-time reliability tools like RTCA, State Estimation, real-time voltage and/or transient stability analysis the risk rating may be reduced. If an entity is using its own RTCA tool for contingency analysis, risk rating may be reduced if entity’s RTCA is more granular than Peak RC’s hosted application. Entity does not review seasonal studies daily unless they have significant changes to the system which requires an entity to perform studies for understanding system conditions and identifying pre contingency actions to be taken Entity owns or operates SPS classified under WAPS and does not review its SPS design periodically OR Entity’s SPS is to mitigate post transient voltage stability and is on a WECC Major Transfer Path 1. Review the number of Misoperations the entity had for SPS. Review root causes and corrective actions taken by entity for these Misoperations. 2. Review how many times SPS has operated since the last audit. 3. If the SPS is for Transient Instability issues to mitigate post transient voltage overload, the inherent risk is high. 4. If the SPS is for Thermal Overload the risk may be reduced to medium if it is WAPS or low if it is LAPS. 5. Review whether the misoperation is part of a NERC Event Analysis Program categorized event. If the entity participates, the risk rating may be reduced. a. Does the entity participate in the Event Analysis Program? b. If the event Category 2 or greater, does the entity participate in the Compliance Self-Assessment program per the annual CMEP? 5 WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria Risk Factor Equipment Categories Risk Factor Subcategory Description Low Under Frequency Load Entity’s participation in Entity participates in WECC’s Off-Nominal Shedding (UFLS) WECC’s Off-Nominal UFLS Program Frequency Load Shedding Plan and frequency of review of its UFLS Medium Entity does not participate in WECC’s OffNominal UFLS program but has its own UFLS program that is coordinated with its Balancing Authority The entity reviews its UFLS program design annually Equipment Categories Under Voltage Load Shedding (UVLS) Entity’s history of UVLS operation and location Entity has no UVLS capability UVLS is used for local equipment protection UVLS is used to prevent voltage collapse or 1. Review the amount of firm load shed by the entity if UVLS operates. voltage instability. 2. Review whether the entity has operated UVLS since its last audit. 3. Review whether the entity had any Misoperations associated with UVLS since the last audit. 4. If an entity sheds less than 100 MW of firm load and has not operated its UVLS and has not had any Misoperations since its last audit, the risk rating may be reduced. 5. Entity reviews UVLS program design periodically Equipment Categories Equipment Maintenance Maintenance Schedule Entity does periodic review and/or maintenance for its major BES equipment OR Entity has a policy for maintaining spares for critical major BES equipment Entity does not have a policy for maintaining spares for critical major BES equipment Entity does not perform periodic review and/or maintenance for major BES equipment Misoperations Having formal Root Cause Having formal Root Cause Analysis process Analysis process Average Timeframe of implementation of Corrective Action Plans Entity has performed root cause analysis but root causes have not been identified for all Misoperations On an average, the entity implemented Corrective Action Plans for its Misoperations within one month Majority of entity’s Misoperations have "unknown" root cause Misoperations Entity has performed root cause analysis and identified a root cause for all Misoperations Average Timeframe of On average, the entity implemented implementation of Corrective Corrective Action Plans for its Action Plans Misoperations within 24 hours Misoperations Average system restoration time due to a Misoperation. Average system restoration time due to a Misoperation. On average, partial system restoration time On average, partial and full system following Misoperation was less than 24 restoration time following Misoperation hours was greater than 24 hours 1. If a misoperated device was left out of service but the entity had a workaround to restore the system immediately, the risk rating may be reduced even if it takes longer to put the device in to service Misoperations Main Causes of Misoperation Main Causes of Misoperation Entity had Misoperations due to human error Entity had a repeat misoperation of the same device due to an insufficient Corrective Action Plan 1. If an entity had Misoperations on a WECC Major Transfer Path, SPS, UFLS, or UVLS device, risk rating may be increased 2. If the misoperation happened because of a failure to follow commissioning procedures, risk rating may be increased Revised November 20, 2015 On average, full system restoration time following Misoperation was less than 24 hours High Entity does not participate in WECC’s OffNominal UFLS program but has its own UFLS program AND The entity does not review its UFLS program design annually Considerations 1. Review the amount of firm load shed by the entity if UFLS operates. 2. Review whether the entity has operated UFLS since its last audit. 3. Review whether the entity had any Misoperations associated with UFLS since the last audit. 4. Review coordination of SPS with neighboring entities. 5. If an entity sheds less than 100 MW of firm load and has not operated its UFLS and has not had any Misoperations since its last audit and coordinates it’s SPS with neighboring entities, the risk rating may be reduced. 1. Major BES equipment includes Transformers, Circuit Breakers, Circuit Switchers, Phase Shifters, Generators and Turbines 2. Where equipment failures occur, does the entity conduct root cause analysis and develop appropriate and reasonable corrective action plans? On an average, the entity took longer than 1. If the entity had to delay implementing the Corrective Action Plan due one month to implement Corrective Action to outage scheduling issues, the risk rating may be reduced Plans for Misoperations 2. Review whether the entity has provided quarterly updates to WECC for any Corrective Action Plan open for more than 60 days Entity had Misoperations due to lack of maintenance or testing procedures 6 WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria Risk Factor Risk Factor Subcategory Description Reportable Events Type of reportable event Type of reportable event Low Medium High Entity had a Category 1 or Category 2 event Entity had a Category 3 or Category 4 event Entity had a Category 5 event since its last since its last audit since its last audit. Entity has performed audit Self-Assessment for the event. Considerations 1. If Corrective Actions were completed on any Category 2 or higher events and closure letters were sent by WECC to the entity, the risk rating may be reduced. Reportable Events Compliance SelfAssessment status for all Events Reportable Events Impact of the event on neighboring entities Compliance Self-Assessment status for all events Entity performed Compliance SelfAssessment for all events 1. If the entity performed Compliance Self-Assessment for all the events and shared their assessment with WECC, the risk rating may be reduced. Impact of the event on neighboring entities The event only affected one entity Reportable Events Root Cause Analysis of the Root Cause Analysis of the event event Reportable Events Compliance Violation identified as part of the event Entity did not have events with the same root cause Compliance Violation No compliance violations were found as a identified as part of the event result of the event Entity only performed Compliance SelfAssessment for Category 2 and higher events Multiple entities were affected by the event and entity coordinated the assessment with the affected entities Entity did not perform a Compliance SelfAssessment on any events Entity had multiple events with the same root cause at the same time Entity had multiple events with the same root cause at different times Multiple entities were affected by the event 1. If the entity has made recent changes to its processes and now but the entity did not coordinate the coordinates the assessment with WECC and affected entities, the risk assessment with affected entities rating may be reduced. 1. Review whether the entity has a formal Root Cause analysis process and shares with neighbors and operational WECC committees. 2. If an entity implemented Root Cause analysis process recently, the risk rating may be reduced. 3. If the entity has a Root Cause analysis program or corrective actions document, risk rating may be reduced. A compliance violation was identified and Entity had a repeat compliance violation as 1. If the root cause of the repeat violation is different from the previous Self-Reported as a result of internal analysis a result of the event that was Self-Reported violation, the risk rating may be reduced. by the entity or identified during audit Workforce Capability Knowledge loss due to Annual turnover rate for annual employee turnover systems operators and relay technicians for critical positions Turnover for system operators and relay technicians is less than 8% annually OR Entity reports a high level of redundancy built into their staffing model Turnover for system operators and relay technicians is between 8% and 20% annually OR Entity reports some redundancy built into their staffing model Turnover for system operators and relay technicians is greater than 20% annually 1. Upon review of past audit results, areas of concern, violation history, and event and misoperation analysis, are any operational or compliance failures identified as a result of personnel or organizational changes? 2. Does the entity identify any risks related to the retention of institutional knowledge? 3. Does the entity demonstrate redundancy among critical personnel (through cross training, apprenticeship programs, over-staffing, etc.) to mitigate the effects of employee turnover? 4. If the entity is well prepared to handle turnover, risk rating may be reduced. 5. If the entity has a history of problems associated with turnover, the risk rating may be increased. Workforce Capability Quality of new hires Average years of job experience for newly hired system operators and relay technicians is greater than 10 years OR Entity has an internal training program to develop new talent Average years of job experience for newly hired system operators and relay technicians is between 5 and 10 years Entity reports difficulties in filling vacancies OR Average years of job experience for newly hired system operators and relay technicians is less than 5 years 1. Does the entity identify any risks related to staffing qualified personnel? 2. Upon review of past audit results, areas of concern, and violation history, are any area of concern/recommendations identified with training programs? 3. If entity has a history of problems associated with insufficient knowledge among staff, the risk rating may be increased. Revised November 20, 2015 Ability to fill vacancies with experienced personnel, understanding that most entities will fill vacancies with a blend of new and experienced personnel 7 WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria Risk Factor Workforce Capability Risk Factor Subcategory Description Impact of Aging Workforce Entity plans to mitigate impact of aging workforce Low Medium Entity identified risks related to aging Entity identified risks related to aging workforce and identified formal plans to workforce but has not identified any plans meet projected work force needs for meeting projected workforce needs OR Entity did not identify risks related to aging workforce over the next 5 years BES Cyber System Identification Reliability Coordinator BCS Highest risk rating of Reliability Coordinator BCS. Entity does not perform the functional obligations of the Reliability Coordinator Entity does not perform the functional obligations of the Reliability Coordinator Entity has at least one High Impact BCS at a No Considerations. Control Center or backup Control Center used to perform the functional obligations of the Reliability Coordinator. BES Cyber System Identification Balancing Authority BCS Risk rating of Balancing Authority BCS. Entity has Low impact BCS Entity has at least one Medium impact BCS at a control center used to perform the functional obligations of the Balancing Authority, per the criteria outlined in attachment 1: 2.3, 2.6, or 2.9 Entity has at least one High impact BCS at a Review BPS Coordination risk factor. Is there a discrepancy in the risk control center used to perform the factor rating and the BCS risk factor? If so, consider modifying this risk functional obligations of the Balancing factor. Authority, per the criteria outlined in attachment 1: 1.2 BES Cyber System Identification Transmission BCS Risk rating of Transmission BCS. Entity has Low impact BCS Entity has at least one Medium impact BCS, Entity has at least one High impact BCS at a Review Transmission portfolio and registered functions risk factors. Is per the criteria outlined in attachment 1: Control Center or backup Control Center there a discrepancy in the risk factor ratings and the BCS risk factor? If so 2.2, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9, 2.10 and 2.12 used to perform the functional obligations consider modifying this risk factor. of the Transmission Operator per the criteria outlined in attachment 1: 1.3. BES Cyber System Identification Generation BCS Risk rating of Generation BCS. Entity has low Impact BCS Entity has at least one Medium impact BCS, per the criteria outlined in attachment 1: 2.1, 2.3, 2.6, and 2.11., but entity has no High impact BCS Entity has at least one High impact BCS at a Review Generation portfolio and registered functions risk factors. Is there Control Center or backup Control Center a discrepancy in the risk factor ratings and the BCS risk factor? If so, used to perform the functional obligations consider modifying this risk factor. of the Generator Operator per the criteria outlined in attachment 1: 1.4. BES Cyber System Identification High Impact High Impact Details < 4 High impact bcs > 4 - 6 High impact bcs >6 high impact bcs Physical location of BCS may be evaluated to reduce risk (multiple BCS in one ESP/PSP may present a smaller attack surface) BES Cyber System Identification Medium Impact Medium Impact Details < 6 Medium Impact BCS 6-8 MIBCS > 8 MIBCS Physical location of BCS may be evaluated to reduce risk (multiple BCS in one ESP/PSP may present a smaller attack surface) BES Cyber System Identification Low Impact Low Impact Details <10 LIBCS 10-15 LIBCS > 15 LIBCS Physical location of BCS may be evaluated to reduce risk (multiple BCS in one location may present a smaller attack surface) Physical Access Threats Have you identified any threats which apply to your PSPs/facilities? Threats have been assessed and none were Threats have been assessed, and there Threats have not been assessed have been threats identified which apply to identified which apply to your PSPs/facilities your PSPs/facilities Revised November 20, 2015 High Considerations 1. What, if any formal programs has the entity implemented to address projected workforce needs due to retirements and aging workforce? a. Are those programs sufficient to address the risk? 2. If analysis determines that the entity is taking appropriate steps to mitigate anticipated staffing challenges, risk rating may be reduced. Consider the threats you identified for the entity or if the entity has identified any of its own threats which apply. What measures have been taken to mitigate the vulnerability associated with the identified threats. 8 WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria Risk Factor Physical Access Risk Factor Subcategory Description Low PSP changes Changes made to the PSP The entity has not had any PSP changes since last audit (redesign, add since the last audit or remove access points, new PACS, etc.) Physical Access PSPs by site Number of PSPs by site < 3 sites Physical Access PSP design Geographic dispersion of the PSPs PSPS are within 5 mile radius Cyber Security Incidents Threats Threats identified and information received from other sources Threats, both internal and external, are identified and documented Threats, both internal and external, are NOT identified and documented Consider the threats identified for the entity which apply (high, medium, or low risks?); steps taken to mitigate the risk of identified threats; how the entity performs an assessment to identify potential threats? Cyber Security Incidents Cyber Security Incidents Impact and Likelihood Identified Impacts and Likelihood Information used to determine risk Potential business impacts and likelihoods are identified Threats, vulnerabilities, likelihoods, and impacts are used to determine risk Potential business impacts and likelihoods are NOT identified Threats, vulnerabilities, likelihoods, and impacts are NOT used to determine risk Less risk might exist if an entity knows its impacts and likelihood of events. This can help focus its defenses around the BCS. An entity might be more likely to protect BCS if it has an idea of the threats and vulnerabilities which exist on the BCS; how an entity identifies and prioritizes risk. Do personnel know their roles for response? Cyber Security Incidents Detection Monitoring External service provider Cyber Security Incidents NERC Alerts Entity owned devices which apply to a NERC Alert External service provider activity is monitored to detect potential cyber security incidents Low impact BCS devices impacted by a NERC alert Cyber Security Incidents Loss of EMS/ SCADA Any loss of EMS/SCADA (full or partial) experienced by an entity since the last audit The entity has not had a loss of EMS/SCADA The entity has had a loss of EMS/SCADA for The entity has had a loss of EMS/ SCADA for Length of the outage (30 min or longer, but no reliability issues might be a since the last audit less than 30 minutes since the last audit 30 minutes or more since the last audit lower risk), effect of the outage, steps entity has taken to prevent a similar outage. Another consideration to be looked at, and favorably, is the entity’s participation in NERC’s EA program and cause coding. Did the EMS/SCADA outage cause any reliability issues or system monitoring issues? System Management Legacy Systems The entity’s use of outdated computer software or hardware, known as a legacy system, within the ESP The entity is not using any legacy systems Risk Revised November 20, 2015 Medium High Considerations The entity has had minor PSP changes since The entity has had major PSP changes since Type of change (completely new PACS, total redesign of PSP, removing or the last audit the last audit adding a significant amount of access points) can modify the risk. The more significant the change the higher the risk could be. Consider the steps taken to manage the changes and security measures taken during the change. 3 to 7 more than 7 More than 7 PSPs but they are constraints to the sites, the risk can be reduced. PSPs are within 6- 20 mile radius PSPs greater than 20 mile radius Size of the guard force, MOUs with local law enforcement, local law enforcement response time. External service provider activity is NOT monitored to detect potential cyber security incidents Medium impact BCS devices impacted by a High impact BCS devices impacted by a NERC alert NERC alert The entity is using legacy system(s), but the The entity is using legacy system(s) that system(s) is/are still supported by the is/are not being supported by the vendor vendor If the entity monitors external activity, it might be more likely to detect and prevent incoming attacks and threats. Does the entity have any devices which are part of a NERC alert? Consider the location of the devices and if the devices have been patched or otherwise mitigated. Devices which might be protected by other means may not be vulnerable to the weakness describe in the NERC Alert. Also consider how the entity uses NERC alerts. Does the entity adapt its program to handle these alerts? The entity has a plan to replace the software, the entity is aware of new vulnerabilities found on the legacy software and addresses them accordingly 9 WECC Inherent Risk Assessment Risk Factor Criteria Risk Factor System Management Risk Factor Subcategory Description EMS/SCADA Version How up-to-date the entity’s EMS/SCADA is System Management Network changes Changes to the network (such The entity has not had any network as hardware/software changes since the last audit upgrades, replacement, etc.) the entity has made since the last audit System Management Personal Devices ( BYOD, CYOD, COPE) How the entity handles employee devices on the network Revised November 20, 2015 Low The entity’s EMS/SCADA is at the most current version OR The entity’s EMS/SCADA software version is supported by the vendor Medium High The entity’s EMS/SCADA is not at the most current version released by the vendor AND The entity’s EMS/SCADA software is not supported by the vendor Considerations Risk could be higher if EMS/SCADA is not being run on the platform (OS, hardware, database, etc.) recommended by the vendor. Also should be considered is entity’s change management system for EMS/SCADA changes (having a dedicated test environment may lower risk) The entity has had minor network changes The entity has had major network changes Type of change (new hardware, new OS, OS upgrade (moving from a.0 to since the last audit since the last audit a.1 vs a.0 to b.0)) may lower risk, a smaller Compliance history with CIP003-3 R6 (CIP-010-2 R1) may lower risk. Addititionally, if the entity has External Interactive Access (EIA) that was impacted by the changes that may increase the risk, or lower the risk of changes if EIE is not allowed or modified by the changes in scope. The entity has a policy which does not allow The entity has a policy which does allow such devices on the network and has steps such devices on the network and specifies to ensure no such device exists on the how these devices will be handled network The entity does not have a policy OR The entity's policy does not specify how such devices will be handled Separate network for personal devices, alerts when new device is on network, use of host-based Data Loss Prevention