That tingling feeling - Singapore General Hospital
advertisement
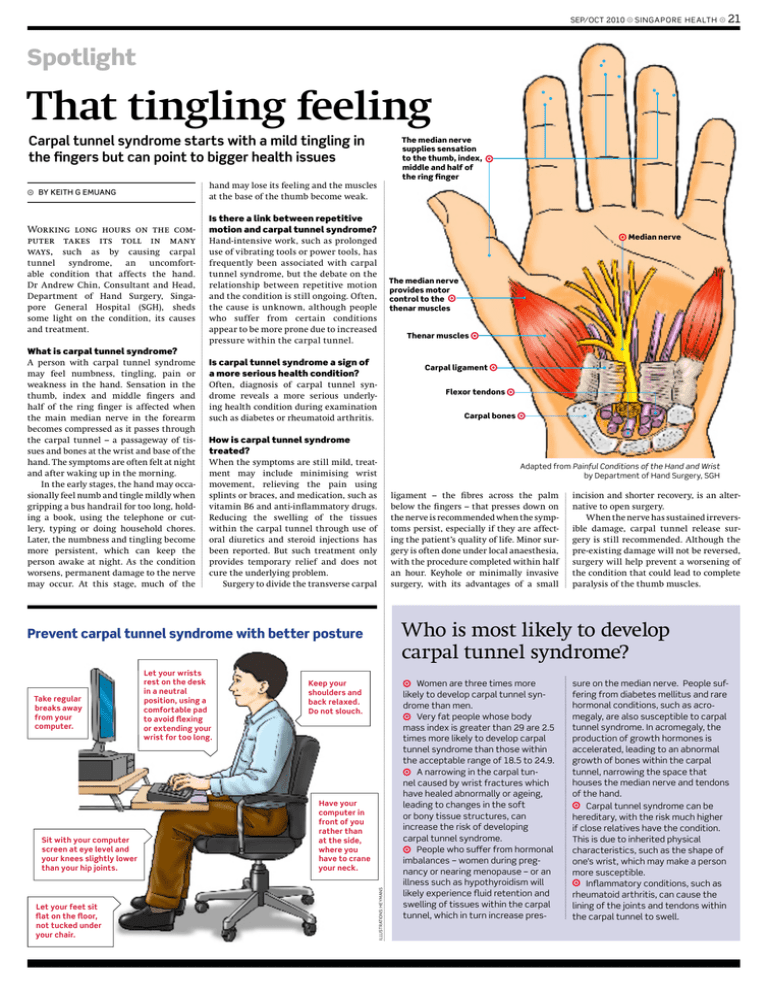
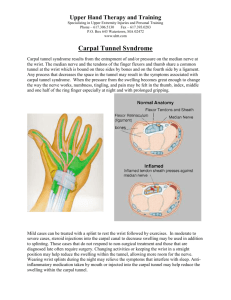
sep⁄ oct 2010 singapore he alth 21 Spotlight That tingling feeling Carpal tunnel syndrome starts with a mild tingling in the fingers but can point to bigger health issues The median nerve supplies sensation to the thumb, index, middle and half of the ring finger hand may lose its feeling and the muscles at the base of the thumb become weak. By Keith G Emuang Working long hours on the computer takes its toll in many ways, such as by causing carpal tunnel syndrome, an uncomfortable condition that affects the hand. Dr Andrew Chin, Consultant and Head, Department of Hand Surgery, Singapore General Hospital (SGH), sheds some light on the condition, its causes and treatment. What is carpal tunnel syndrome? A person with carpal tunnel syndrome may feel numbness, tingling, pain or weakness in the hand. Sensation in the thumb, index and middle fingers and half of the ring finger is affected when the main median nerve in the forearm becomes compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel – a passageway of tissues and bones at the wrist and base of the hand. The symptoms are often felt at night and after waking up in the morning. In the early stages, the hand may occasionally feel numb and tingle mildly when gripping a bus handrail for too long, holding a book, using the telephone or cutlery, typing or doing household chores. Later, the numbness and tingling become more persistent, which can keep the person awake at night. As the condition worsens, permanent damage to the nerve may occur. At this stage, much of the Is there a link between repetitive motion and carpal tunnel syndrome? Hand-intensive work, such as prolonged use of vibrating tools or power tools, has frequently been associated with carpal tunnel syndrome, but the debate on the relationship between repetitive motion and the condition is still ongoing. Often, the cause is unknown, although people who suffer from certain conditions appear to be more prone due to increased pressure within the carpal tunnel. Median nerve The median nerve provides motor control to the thenar muscles Thenar muscles Is carpal tunnel syndrome a sign of a more serious health condition? Often, diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome reveals a more serious underlying health condition during examination such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis. Carpal ligament Flexor tendons Carpal bones How is carpal tunnel syndrome treated? When the symptoms are still mild, treatment may include minimising wrist movement, relieving the pain using splints or braces, and medication, such as vitamin B6 and anti-inflammatory drugs. Reducing the swelling of the tissues within the carpal tunnel through use of oral diuretics and steroid injections has been reported. But such treatment only provides temporary relief and does not cure the underlying problem. Surgery to divide the transverse carpal Adapted from Painful Conditions of the Hand and Wrist by Department of Hand Surgery, SGH ligament – the fibres across the palm below the fingers – that presses down on the nerve is recommended when the symptoms persist, especially if they are affecting the patient’s quality of life. Minor surgery is often done under local anaesthesia, with the procedure completed within half an hour. Keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, with its advantages of a small Who is most likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome? Prevent carpal tunnel syndrome with better posture Sit with your computer screen at eye level and your knees slightly lower than your hip joints. Let your feet sit flat on the floor, not tucked under your chair. Keep your shoulders and back relaxed. Do not slouch. Have your computer in front of you rather than at the side, where you have to crane your neck. illustrations: heymans Take regular breaks away from your computer. Let your wrists rest on the desk in a neutral position, using a comfortable pad to avoid flexing or extending your wrist for too long. incision and shorter recovery, is an alternative to open surgery. When the nerve has sustained irreversible damage, carpal tunnel release surgery is still recommended. Although the pre-existing damage will not be reversed, surgery will help prevent a worsening of the condition that could lead to complete paralysis of the thumb muscles. Women are three times more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome than men. Very fat people whose body mass index is greater than 29 are 2.5 times more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome than those within the acceptable range of 18.5 to 24.9. A narrowing in the carpal tunnel caused by wrist fractures which have healed abnormally or ageing, leading to changes in the soft or bony tissue structures, can increase the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. People who suffer from hormonal imbalances – women during pregnancy or nearing menopause – or an illness such as hypothyroidism will likely experience fluid retention and swelling of tissues within the carpal tunnel, which in turn increase pres- sure on the median nerve. People suffering from diabetes mellitus and rare hormonal conditions, such as acromegaly, are also susceptible to carpal tunnel syndrome. In acromegaly, the production of growth hormones is accelerated, leading to an abnormal growth of bones within the carpal tunnel, narrowing the space that houses the median nerve and tendons of the hand. Carpal tunnel syndrome can be hereditary, with the risk much higher if close relatives have the condition. This is due to inherited physical characteristics, such as the shape of one’s wrist, which may make a person more susceptible. Inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause the lining of the joints and tendons within the carpal tunnel to swell.