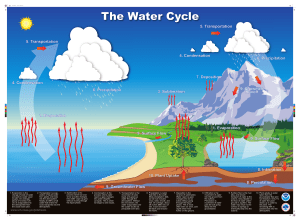
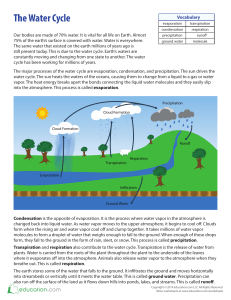
The volume of water in the biosphere remains fairly constant through
advertisement

CS_Ch9_Environment 2/28/05 4:41 PM Page 586 A Vote for Ecology Bio Words water (hydrologic) cycle: the cycle or network of pathways taken by water in all three of its forms (solid, liquid, and vapor) among the various places where is it temporarily stored on, below, and above the Earth’s surface evaporation: the process of changing from a liquid to a gas condensation: the process of changing from a gas to a liquid precipitation: water that falls to the Earth’s surface from the atmosphere as liquid or solid material in the form of rain, snow, hail, or sleet runoff: the part of the precipitation appearing in surface streams groundwater: water contained in pore spaces in sediments and rocks beneath the Earth’s surface infiltration: the movement of water through pores or small openings into the soil and porous rock aquifer: any body of sediment or rock that has sufficient size and sufficiently high porosity and permeability to provide an adequate supply of water from wells long cycle t cycle condensation ens ns precipitation THE WATER CYCLE cond con ondensation atm water vapor life processes precipitation evaporation evaporation vap va runoff infiltration groundwater The volume of water in the biosphere remains fairly constant through time. In fact, the water that you used today has been around for hundreds of millions of years. It has probably existed on the Earth’s surface as a liquid, a solid, and a vapor. However, water is always moving from place to place. It is forever changing from one state to another.This complicated movement of the Earth’s water is called the water cycle or hydrologic cycle. Some of the pathways of this cycle are shown in the diagram above. One of the largest reserves of water on Earth is found in the oceans. The oceans contain about 97% of the Earth’s water. Other surface water includes lakes, rivers, estuaries, marshes, and swamps. By contrast, the atmosphere holds less than 0.001% of the Earth’s water. This means that rapid recycling of water must take place between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere. By absorbing heat energy from the Sun, some of the water on the Earth’s surface changes to water vapor by evaporation. It rises upward into the atmosphere until it reaches a point where the 586 Active Biology