Introduction to Smith Charts
advertisement

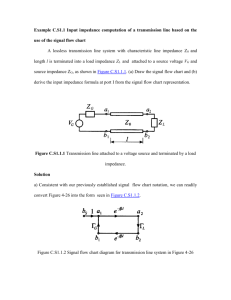
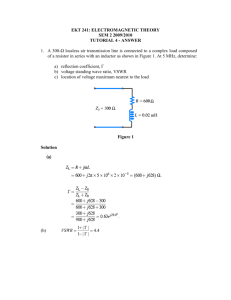
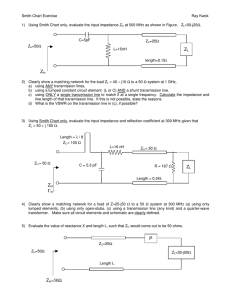
Introduction to Smith Charts Dr. Russell P. Jedlicka Klipsch School of Electrical and Computer Engineering New Mexico State University Las Cruces, NM 88003 September 2002 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 Smith Chart Summary A Smith Chart is a conformal mapping between the normalized complex impedance plane ( z = r + j x ) and the complex reflection coefficient plane. First, the normalized impedance is given as zL = Z L RL + j X L = Zo Zo Consider the right-hand portion of the normalized complex impedance plane. All values of impedance such that R $ 0 are represented by points in the plane. The impedance of all passive devices will be represented by points in the right-half plane. The complex reflection coefficient may be written as a magnitude and a phase or as real and imaginary parts. Γ L = Γ L e ∠Γ L = Γ Lr + jΓ Li Remember that 0 ≤ Γ L ≤ 1 and the p 'L is measured with respect to the positive real 'r axis. The reflection coefficient in terms of the load, ZL, terminating a line, Zo is defined as ΓL = Z L − Zo Z L + Zo Rearranging the above equation we get Page 1 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 Z L = Zo 1+ Γ L 1− Γ L So we get the conformal mapping by dividing through by Zo (remember 'L is complex). z L = rL + j x L = 1+ Γ L 1− Γ L Substituting in the complex expression for 'L and equating real and imaginary parts we find the two equations which represent circles in the complex reflection coefficient plane. 2 ( ) r Γ Lr − L + Γ Li − 0 1 + rL (Γ Lr ) 2 2 1 = 1 + rL 1 1 = − 1 + Γ Li − xL xL 2 2 2 The first circle is centered at rL ,0 1 + rL whose location is always inside the unit circle in the complex reflection coefficient plane. The corresponding radius is 1 1 + rL So it is observed that this circle will always be fully contained within the unit circle. The radius can never by greater than unity. The second circle is centered at 1 1, xL whose location is always outside the unit circle in the complex reflection coefficient plane. Note that the center of these circles will always be to the right of the unit circle. The corresponding radius is 1 . The radius can vary between 0 and infinity. xL Page 2 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 The first circles, those centered on the real axis, represent lines of constant real part of the load impedance (rL is constant, xL varies). The circles whose centers reside outside the unit circle represent lines of constant imaginary part of the load impedance (xL is constant, rL varies). Circles centered at the match point ( ZL = Zo, or 'L = 0 ) are equidistance from the origin (| 'L | = constant) and are called constant VSWR circles. This related quantity is defined as Vmax 1 + Γ L VSWR = = Vmin 1 − Γ L Note that the VSWR can vary between 1 ≤ VSWR ≤ ∞ . The phase of the reflection coefficient is given by the angle from the right-hand horizontal axis. We have -180° # p'L # +180°. Above the horizontal axis is positive, below negative. Page 3 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 When we place these other circles on the REFLECTION COEFFICIENT PLANE we call it a SMITH CHART. It can also be referred to as an: impedance chart admittance chart immittance chart (impedance and admittance) Page 4 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 Page 5 of 22 08/22/02 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 Normalized Impedance The transmission line of characteristic impedance, Zo, is terminated in a load impedance, ZL. If the characteristic impedance is Zo = 50 + j 0 S and the load impedance is ZL = 100 + j 100 S, the normalized load impedance is zL = 100 + j100 = 2 + j2 50 Now enter this on the Smith Chart as shown in below. Page 6 of 22 ( dim ensionless) EE521 Lecture 3 Page 7 of 22 08/22/02 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 VSWR Circles To construct the VSWR circle for a lossless line, place the compass center at the center of the Smith Chart ( ZL = Zo, or 'L = 0 ) and construct a circle through zL. To read off the VSWR on the line, note the intercept of the VSWR circle with the right-half zero reactance line (it is the horizontal line that bisects the top and bottom of the chart. For the previous example, this is shown in Figure 2 where we read off the VSWR as VSWR = 4.3 Let’s check this against the calculated VSWR. First, compute the reflection coefficient. Γ = Z L − Z o (100 + j100) − 50 = Z L + Z o (100 + j100) + 50 Taking the magnitude we find Γ = 0.62 . Then the VSWR is VSWR = 1+ Γ = 4.265 1− Γ This tells us that the graphically obtained value (VSWR = 4.3) is accurate to about one significant figure. Page 8 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 Page 9 of 22 08/22/02 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 Load Admittance The load admittance is the reciprocal of the load impedance. YL = For the previous example, we find YL = 1 ZL 1 = 0.005 − j 0.005 Siemens 100 + j100 Normalized Load Admittance The normalized load admittance is the reciprocal of the normalized load impedance which can be expressed as 1 YL 100 + j100 yL = = = 0.25 − j 0.25 1 Yo 500 ( dim ensionless) We can find this more easily by noting that yL is on the constant VSWR circle at a point diametrically opposed from zL. This is shown in Figure 3. Page 10 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 Page 11 of 22 08/22/02 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 Input Impedance The input impedance to the line of characteristic impedance, Zo, a length R from the load, ZL, is found via the equation. 2π Z L + jZ o tan λ Zin = Z o 2π Z o + jZ L tan λ l l Where 8 is the wavelength on the transmission line. Consider the following example with ZL = 100 + j 100 S. Zin = 100 (100 + j100) + j100 tan π 4 = 100 1 + j 2 = 200 − j100 Ω π j1 100 + j(100 + j100) tan 4 Now consider this process on the Smith Chart. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Enter the normalized load impedance, zL = 1 + j 1 Construct the constant VSWR circle. Travel clockwise (transform towards the generator) on the circle by a distance equivalent to the line length, starting at zL . Remember the distance on the Smith Chart is in terms of wavelength. Specifically, wavelength on the transmission line, which is not necessarily the free space wavelength. One full revolution is 8/2. The outer scale is calibrated in wavelengths. Read off zin. In this case, zin = 2 - j 1. Compute Zin = zin * Zo = ( 2 - j 1 ) * 100 = 200 - j 100 S. Page 12 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 Page 13 of 22 08/22/02 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 Input Admittance Use the Smith Chart to find the input admittance. Consider the example above. 1. Enter the normalized load admittance on the VSWR circle. This is accomplished by entering the normalized load impedance, drawing the VSWR circle and marking the point diametrically opposed. 2. Travel clockwise (towards the generator) from yL on the VSWR circle by a distance equivalent to the line length. 3. Read off yin = 0.44 + j 0.2 4. Find Yin = yin * Yo = ( 0.44 + j 0.2 ) / (100) = 0.004 + j 0.002 Seimens. Let’s compare the result from the Smith Chart on the next page to the analytical result. From the example above we found Zin = 200 - j 100 S. Yin = 1 1 = = 0.004 − j 0.002 Zin 200 − j100 Page 14 of 22 Siemens EE521 Lecture 3 Page 15 of 22 08/22/02 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 Drill Problem # 1 Consider a load impedance, ZL = 100 - j 25 S, connected to a transmission line of characteristic impedance Zo = 50 S. The line is R = 3/8 8 long. Find the following quantities using the Smith Chart on the next page. a) zL = ______________ \ b) VSWR = ______________ c) yL = ______________ d) zin = ______________ e) Zin = ______________ f) yin = ______________ g) Yin = ______________ h) Check the answer in part e) using the analytical result. 2π Z L + jZ o tan l λ Zin = Z o 2π Z o + jZ L tan l λ Page 16 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 Page 17 of 22 08/22/02 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 Drill Problem # 2 Consider a load impedance, ZL = 0 - j 0 S, connected to a transmission line of characteristic impedance Zo = 50 S. The line is R = 1/4 8 long. Find the following quantities using the Smith Chart on the next page. a) zL = ______________ b) VSWR = ______________ c) yL = ______________ d) zin = ______________ e) Zin = ______________ f) yin = ______________ g) Yin = ______________ h) Check the answer in part e) using the analytical result. 2π l Z L + jZ o tan λ Zin = Z o 2π l Z o + jZ L tan λ Page 18 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 Page 19 of 22 08/22/02 EE521 Lecture 3 08/22/02 Drill Problem #3 Use the Smith Chart on the next page to find the input impedance to the parallel connected lines Zo1 = Zo2 = 70.7 S. Furthermore, ZL1 = ZL2 = 50 + j 0 S. The line lengths are R1 = R2 = 8/4. The characteristic impedance of the main line is Zo = 50 S to which the two parallel lines are connected, what is the VSWR on this main line? Drill Problem #4 Use the Smith Chart to find the input impedance to the parallel connected lines Zo1 = 50 S and Zo2 = 70.7 S. Furthermore, ZL1 = 50 + j 0 S and ZL2 = 100 + j 0 S. The line lengths are R1 = 8/2 and R2 = 8/4. The characteristic impedance of the main line is Zo = 50 S to which the two parallel lines are connected, what is the VSWR on this main line? Page 20 of 22 EE521 Lecture 3 Page 21 of 22 08/22/02 EE521 Lecture 3 Page 22 of 22 08/22/02