AC Current Presentation
advertisement

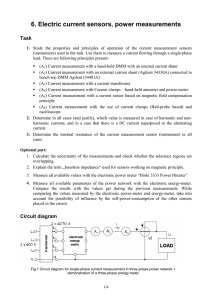
VERIFICATION OF MEASUREMENT OFAC ACCURRENT CURRENT MEASUREMENT USING COAXIAL WITH CURRENT SHUNTS COAXIAL CURRENT SHUNTS Bostjan Voljc1, Matjaz Lindic1, Rado Lapuh2 1 Bostjan Voljc, Mag. Matjaz Lindic SIQ - Slovenian Institute of Quality and Metrology, Ljubljana, Slovenia SIQ- Metrology - Slovenian Institute of Quality and 2 MIRS Institute of Republic of Slovenia, Metrology, Slovenia Ljubljana, Slovenia bostjan.voljc@siq.si, matjaz.lindic@siq.si bostjan.voljc@siq.si, matjaz.lindic@siq.si, rado.lapuh@gov.si 1 Overview 1. New direct ac current measurement method 2. Accuracy of the new method 3. Comparison of the new method • comparison between different shunts • comparison to ac-dc current transfer measurement method 4. Conclusion 2 New direct ac measurement technique • coaxial current shunts are suitable for ac-dc current transfer measurement and for direct measurement of ac current • direct measurement of ac current: method is based on the measurement of the ac voltage drop (Us) on resistance (Rs) of the coaxial current shunt • current shunts characterized for ac-dc current transfer difference, long term drift of its dc resistance and self heating effect • 6 coaxial current shunts covering range from 10 mA to 20 A in frequency range from 10 Hz to 30 kHz AC current source AC voltmeter Current shunt resistor 3 New direct ac measurement technique US Im = RS ⋅ (1 + δ drift + δ ac−dc + δ pwc ) where is the unknown ac current, • Im Us Rs δdrift • δac/dc is correction due to ac-dc difference of the shunt (from PTB calibration certificate), • δpwc is correction due to self heating of the current shunt (from measurement of temperature and power coefficient). • • • is measured ac voltage across the shunt, is dc resistance of the shunt, is correction of the dc resistance long term drift (from dc resistance calibration history), 4 Accuracy of the new method Shunt 100 mA 300 mA 1A 5A 10 A 20 A 10 Hz 54 54 56 57 62 70 20 Hz 44 45 47 49 55 63 40 Hz 29 29 33 37 47 54 1 kHz 29 29 33 37 47 54 Best measurement capabilities 10 kHz 29 29 34 37 47 62 5 Comparison between shunts • two coaxial current shunts were compared over the special current T-piece • additional 30 cm high current coaxial cable was used for each shunt to minimize interference between shunts • two shunts compared on the nominal current of the smaller shunt • following combinations were compared: AC current source Shunt 1 Shunt 2 source current 100 mA 300 mA 100 mA 300 mA 1A 300 mA 1A 5A 1A Shunt 1 Shunt 2 AC voltmeter 6 Comparison to ac-dc transfer technique • dc+, ac and dc- measurement sequence was used • from the same measuring results the ac current was calculated from equations for both methods: • ac-dc current transfer method 2U ac − U dc + − U dc − I ac = I dc ⋅ 1 + + δ ac − dc U dc + + U dc − • Im = • DC current source direct method U ac RS ⋅ (1 + δ drift + δ ac −dc + δ pwc ) Current switch AC current source common parameters: • ac-dc transfer difference (δac-dc) • ac voltmeter (Uac) AC/DC voltmeter 7 Results Shunt 1 0,1 A 0,3 A 1A Shunt 2 0,3 A 1A 5A source current 40 Hz Frequency 1 kHz 5 kHz 0,1 A 0,3 A 1A -14,0 -12,1 -0,8 -13,7 -11,2 -2,6 -14,1 -11,5 -1,4 10 kHz -14,4 -11,5 -2,8 Difference between measurement results obtained on two different coaxial current shunts in µA/A Shunt 0,1 A 0,3 A 1A 5A 40 Hz -6,6 9,4 10,6 5,9 Frequency 1 kHz 5 kHz -6,6 10,3 10,8 7,3 -7,5 9,6 9,9 5,9 10 kHz -8,8 8,7 8,9 4,9 Difference between the direct ac current measurement method and ac-dc transfer difference method in µA/A 8 Conclusion • results shows very well controlled behavior of both shunts and measurement method • deviations typically less than 1/3 of the stated uncertainty • measuring results of the comparison prove that the direct ac current measuring method is suitable and that the uncertainties stated are appropriate • uncertainty of the ac voltmeter presents the major uncertainty contribution • • minimizing its uncertainty would decrease also the uncertainty of the direct acc current measurement method between direct ac current measurement and ac-dc transfer difference method systematic deviations are observed • further investigation shall be made to identify and resolve these deviations