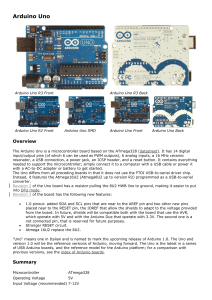
Arduino UNO R3 Analysis: Features & Architecture
advertisement
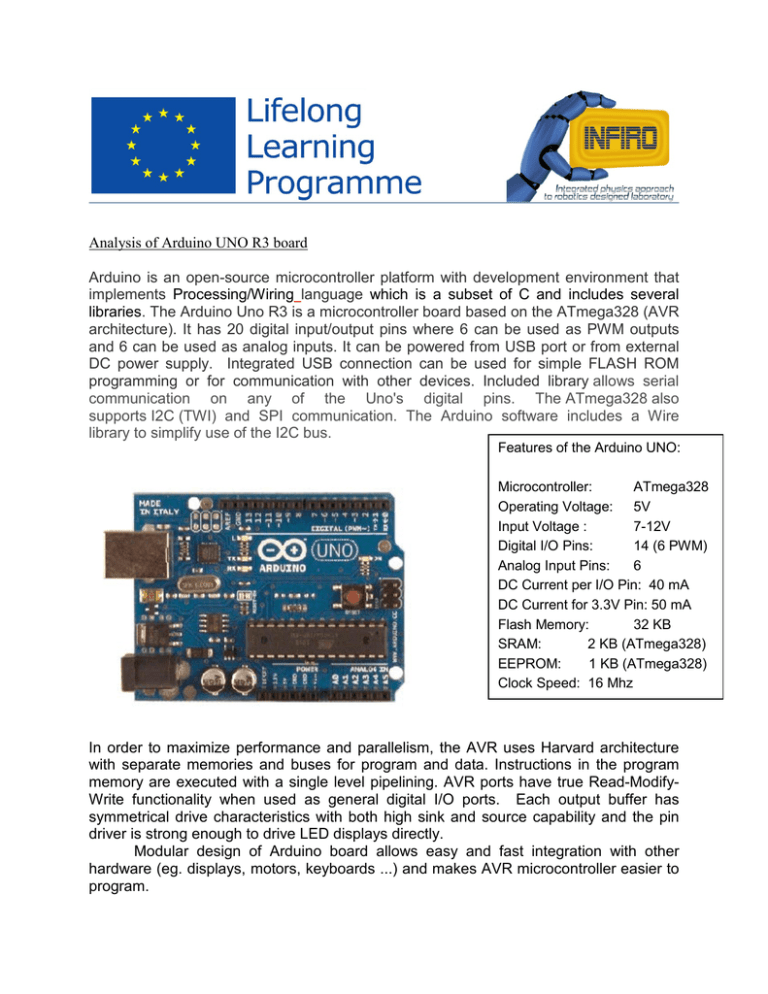
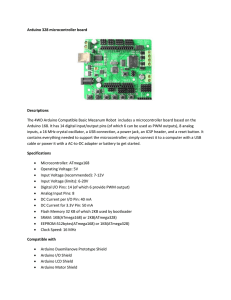
Analysis of Arduino UNO R3 board Arduino is an open-source microcontroller platform with development environment that implements Processing/Wiring language which is a subset of C and includes several libraries. The Arduino Uno R3 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328 (AVR architecture). It has 20 digital input/output pins where 6 can be used as PWM outputs and 6 can be used as analog inputs. It can be powered from USB port or from external DC power supply. Integrated USB connection can be used for simple FLASH ROM programming or for communication with other devices. Included library allows serial communication on any of the Uno's digital pins. The ATmega328 also supports I2C (TWI) and SPI communication. The Arduino software includes a Wire library to simplify use of the I2C bus. Features of the Arduino UNO: Microcontroller: ATmega328 Operating Voltage: 5V Input Voltage : 7-12V Digital I/O Pins: 14 (6 PWM) Analog Input Pins: 6 DC Current per I/O Pin: 40 mA DC Current for 3.3V Pin: 50 mA Flash Memory: 32 KB SRAM: 2 KB (ATmega328) EEPROM: 1 KB (ATmega328) Clock Speed: 16 Mhz In order to maximize performance and parallelism, the AVR uses Harvard architecture with separate memories and buses for program and data. Instructions in the program memory are executed with a single level pipelining. AVR ports have true Read-ModifyWrite functionality when used as general digital I/O ports. Each output buffer has symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability and the pin driver is strong enough to drive LED displays directly. Modular design of Arduino board allows easy and fast integration with other hardware (eg. displays, motors, keyboards ...) and makes AVR microcontroller easier to program.