Lecture Slides (Download) - Department of Energy Science and
advertisement

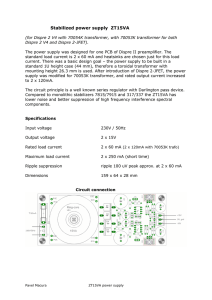
EN 206 1/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation EN 206 - Power Electronics and Machines Transformers Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Suryanarayana Doolla Department of Energy Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay suryad@iitb.ac.in Lecture Organization - Modules EN 206 2/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Introduction and Power Semiconductor Switches Module 1: Transformers Module 2: AC/DC converter / Rectifier Module 3: DC machines and Drives Module 4: DC/DC converter Module 5: Induction Machine Module 6: DC/AC converter / Inverter Module 7: AC/AC converter / Cyclo converter Module 8: Synchronous Machine Module 9: Special Topics: Machines, HVDC, APF Review of Last Class EN 206 3/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Transformers Phasor diagram for ideal transformer and no load condition, impedance transformation Equivalent circuit SC and OC Test of a Transformer Voltage Regulation EN 206 4/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Definition: It is defined as change in voltage from no load to full load, as a percentage of rated terminal voltage at full load. FL Voltage Regulation = VNLV−V FL Problem-1 EN 206 5/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Short circuit measurements done on a 2200/220V transformer rated 500 kVA provide the following values of equivalent resistance and reactance, respectively, referred to low-voltage (secondary) side: Re2 = 2mΩ, xe2 = 6mΩ Calculate (a) Rated secondary current (b) Full-load equivalent resistance voltage drop I2 Re2 , Full load equivalent reactance voltage drop I2 Re2 . (c) Induced voltage when the transformer is delivering rated current to a unity PF load. (d) Voltage regulation at UPF. (e) Voltage regulation for rated load at 0.8pf lagging. (f) Voltage regulation for rated load at 0.8pf leading. VR - Analysis EN 206 6/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer It is practically impossible to determine voltage regulation for a transformer. In such case the results of SC test shall be used to determine the voltage regulation. It is possible to have zero percent or negative voltage regulation depending on magnitude of leading pf. Losses in a Transformer EN 206 7/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Constant loss: Core loss: Assumed to be constant for rated voltage and frequency. Depends on flux density of the core, magnetic properties of the material, resistivity of core material, volume of core material. Stray load loss: Leakage flux present in a transformer induce eddy currents in the conductors, tanks, channels, bolts etc. These eddy currents give rise to stray load loss. Dielectric loss: This loss occurs in the insulating materials (transformer oil, solid insulation of HV transformers) Variable losses: These are due to ohmic losses in the primary and secondary of transformer when it is loaded (no load neglected). Under normal operating conditions, the variation of mutual flux is not more than 2 to 3%, consequently, core losses are assumed to be constant throughout. Efficiency EN 206 8/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Both SC and OC test data is required to calculate efficieny of a transformer. Efficiency (η): OutputPower (kW ) OutputPower (kW )+Losses(kW ) = Po Po +Losses = V2 I2 cosθ2 V2 I2 cosθ2 +(Pc +I22 Re2 ) Maximum efficieny of a transformer occurs at load when fixed losses are equal to variable losses. “Try the proof at home”. q Pc = I22 Re2 =⇒ I2 = Pc Re2 All Day Efficiency: In a transformer where the load changes continuously with time (ex. distribution transformer), all day efficieny is defined as DailyLosses(kWh) ADE=1- DailyOutput(kWh)+Dailylosses(kWh) Autotransformer EN 206 9/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer A transformer in which a part of winding is common to both the primary and secondary circuits, is called an auto-transformer. In an autotransformer primary and secondary winding are not isolated. Working mmf in a transformer remains substantially constant at its no load value. The primary must draw additional current from the source, in order to neutralize the effect of load current. Autotransformer - Analysis EN 206 10/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer mmf of winding AB= I1 (N1 − N2 ) = (I2 − I1 )N2 = ICB N2 = mmf of winding CB Transformer action takes place between winding AB and BC Transformed VA = VAB IAB = (V1 − V2 )I1 . Transformed VA/Input VA = V1 −V2 V1 =1−k Autotransformer - Advantages & Disadvantages EN 206 11/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Advantages High efficiency Low leakage impedance and has superior voltage regulation when compared to a two winding transformer of same output Requires less conductor compared to a two winding transformer (k < 1). Disadvantages Isolation or direct electrical connection If the ratio of transformation is far from unity, the economic advantages of auto transformer over two winding transformer decreases. Three Phase Transformer EN 206 12/19 Prof. Doolla Three phase supply for rectifiers, less ripple occurs in the rectified output Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Simplicity, low cost, reliability, efficiency and safety Three phase to two phase is mutually convertible. Six and twelve phase circuits are obtained from Z circuits. Most commonly used circuits ∆ or Y . Others include inter connected Y arrangement, Open Delta (V connection), Tee connections, Scott-Connection. Delta - Delta connection EN 206 13/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer The transformation ratio of all the transformers must be the same, otherwise circulating currents round the winding will be present even under no load condition The impedance of all the units should be the same to ensure equal load sharing Secondary voltages are in phase with primary Delta - Delta connection EN 206 14/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer The voltages does not get unbalanced due to unbalancing in the loads. Cross section of the wire is reduced as Iph = IL √ 3 If one of the three transformers gets burnt, the delta-delta system continues functioning uninterrupted. Star - Star connection EN 206 15/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Line voltage = phase current √ 3× phase voltage and line current = No phase shift between primary and secondary voltages With an unbalanced load on the secondary winding, the phase voltage on the load side changes unless the neutral point is earthed. The neutral is also unstable because of third harmonic component in the exciting currents, and also due to unequal magnetizing currents for the three units. Star - Delta connection EN 206 16/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer The coil in star winding will carry full current but voltage across them will be √13 of line voltage Delta coils, carry only line voltage √1 3 of the line current but whole of Generally used at substation end of the transmission line where the incoming voltage is to be stepped down for consumption purposes. 30o phase shift is observed between corresponding primary and secondary terminal voltages. Cannot be paralleled with ∆ − ∆ and Y-Y. Delta - Star connection EN 206 17/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Generally used for step-up the voltages Most generally employed (both single phase and three phase circuits) Low voltage distribution systems. 300 phase shift is observed between corresponding primary and secondary terminal voltages. Cannot be paralleled with ∆ − ∆ and Y-Y. Open Delta and Scott Connection EN 206 18/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Open Delta: It is extensively used in distribution systems Initial stages of rural electrification The two transformers will carry an overload of 15.5% as a whole which is acceptable. Scott Connection: A poly phase system may be transformed to another polyphase system. General application of Scott connection involves 3∅ to 2∅ and 2∅ to 3∅ transformation. Summary EN 206 19/19 Prof. Doolla Introduction Votlage Regulation Efficiency Auto Transformer Three Phase Transformer Transformers Voltage regulation and efficiency of a transformer. All day efficiency of a distribution transformer. Auto Transformer (principle of operation, equivalent circuit, advantages and disadvantages) Three Phase Transformer Next Class AC/DC Converter Thank you!! For Further Reading: Transformer Engineering: Design and Practice Authors: S.V. Kulkarni and S.A. Khaparde Publisher: Marcel Dekker (Taylor & Francis Group), New York, May 2004 ISBN: 0-8247-5653-3 Electric Machinery: A. E. Fitzgerald, C. Kingsley, S. D. Umans. Publisher: TMH, New Delhi, India, 2009