NYSERDA School Power…Naturally
advertisement

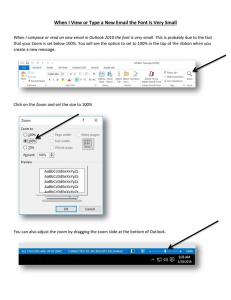
GIS Lessons and Tools for a New Energy Generation Help Guide This document provides an outline on the tools included in the Solar, Wind and Energy Overview online applications and provides information on using the geospatial tools contained in the Online mapping interfaces. Table of Contents By checking the boxes next to the names of the layers (e.g. Generated Renewable by State) turns the layers on making them visible or turns them off. By clicking on the [+] next to the layer name, the layer will expand displaying the legend for the layer. By clicking the [-], the legend will collapse. Layers are static and cannot be moved up or down to change their location. Tools Zoom Bar – By selecting the plus or minus button, the user can zoom in or out. The clicking on the sliding bar, the user can dynamically control the zoom scale. Zoom In – This tool can be used 2 ways. By selecting the tool the user can single click on the map to zoom in step by step on the point the cursor is located over. The user may also click, hold and draw a box over the area on the map in which they wish to zoom. Zoom Out – This tool like zoom in can be used 2 ways. By selecting the tool the user can single click on the map to zoom out step by step on the point the cursor is located over. The user may also click, hold and draw a box over an area on the map in which they wish to zoom away from. This lesson was made possible by the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA), in cooperation with the Institute of Geospatial Technology (IAGT), teachers from the Hannibal School District (Hannibal, New York), and the Environmental Science Research Institute (ESRI). 1 Pan – This tool is used to move the map. By clicking, holding, and moving the cursor the map can be dragged in any direction. Full Extent – By clicking this button the map will return to the same view as when it opened. Zoom to previous extent – This tool allows the user to Go Back to the last zoom level of the map. It is a lot like the back button in a web browser. Zoom to last extent – This tool allows the user to return to the previous zoom level of the map. It is a lot like the forward button in a web browser. Remove Graphics\Results – This tool allows the user to remove any graphics or query results with one click of a button. Identify Feature – This tool allows the user to query features on the map. The tool returns the information from all the layers visible on the map. The user can then select which layer they are interested in and see the database information associated with the feature in a form that lists the information by field name. Scale Bar – This shows the ground distance covered for a certain length on the map. The scale bar will change as the user zooms in and out. Zoom to Scale Tool – Clicking on the blue scale ratio numbers activates the Zoom to Scale tool. Enter the desired scale level in the dialog box and click Scale. The map then zooms to the scale entered. Map Menu Print – This menu item opens the Print dialog box. Within the dialog box the user can enter a map title, select a map template, select a map width, and resolution. Upon clicking Create print page the user will be returned a printable map inside a web browser window. Export (Image) – This will allow you to export a digital image of the map interface for the image that is in the view window. No legends will be included in this export box. This lesson was made possible by the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA), in cooperation with the Institute of Geospatial Technology (IAGT), teachers from the Hannibal School District (Hannibal, New York), and the Environmental Science Research Institute (ESRI). 2 This tool can be used to have students show the maps they have created. The image will be available in a .zip format. Add GeoRSS Feed – This is a way to add additional data to the online interface. This data can be dynamic and constantly changing. Add Local Data – Data you have stored on your local computer can be uploaded and added to the map interface. You can upload GPS waypoints, or even other shapefiles. Add Map Resource – A map resource might be another existing online map that has been made available over the internet. You can add this map to the existing online data. Unless you have access to other resources that publish map resources, this is something that will likely not be of interest. Manage Map Resources – This is where all map resources, including those currently in the online table of contents can be managed. View Menu Accordion Menu – This menu item returns the Table of Contents on the right hand side of the application if the window has been closed or minimized. Overview Map – This menu item returns the Overview Map window to the lower right corner of the application if it has been closed or minimized. Results – This menu item opens the Results window on the bottom of the application if the window has been closed or minimized. This lesson was made possible by the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA), in cooperation with the Institute of Geospatial Technology (IAGT), teachers from the Hannibal School District (Hannibal, New York), and the Environmental Science Research Institute (ESRI). 3 Selection Menu The tools within the Selection menu are geospatial tools that are commonly used in any GIS software program. These tools allow you to select features based on a specific value, proximity to another feature, or by location. Select by Attribute – This tool allows you to select a group of features, such as schools, based on an attribute, or a common piece of information stored in the table of the dataset. You must select the Input Layer you wish to select features from. In the Attribute Selection, you are creating a query or equation for selecting features. Select one of the Attributes that are provided in the drop down. The dropdown attributes are unique to each Layer selected above. The operation is where you determine if you are looking for a specific name or a range of vales (i.e. cities with a population greater than 20,000). Value allows you to see all the values listed for the Attribute you have selected. Select Get Sample Values to make sure you have the spelling of a name correctly. Once you have your query built, you must Add to Query Expression. This will place your query in the Query Expression box. Now you can Query full extent and see the results that are returned in the Results box that appears at the bottom of the screen Select by Feature Buffer – This tool allows you to select certain features that are within a distance of another feature. For example you could see what schools are within a certain distance of the SPN School locations. Once you fill in the dropdowns, you will select a feature using the point or rectangle tool and then Show intersecting features. 1. Find data is the data you are looking for, such as all schools. 2. Intersecting with is the feature you want to use as your focus point from with a buffer will be drawn This lesson was made possible by the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA), in cooperation with the Institute of Geospatial Technology (IAGT), teachers from the Hannibal School District (Hannibal, New York), and the Environmental Science Research Institute (ESRI). 4 Select by Location – This tool allows you to select features on the map based on their location. Use any of the Select by functions as indicated by the black arrows and red shapes to select features. The features you select will appear in the Results box that will appear at the bottom of the screen. Select by Point Buffer – This tool allows you to select all features that are within a certain distance of any point you specify on the screen. Select the layer of the features you wish to find. Specify the distance. Click on the Specify point tool and then select a location on the map. The features from the layer you selected will return in the Results box that will appear at the bottom of the screen. Tools Menu These tools allow you do draw shapes, graphics and labels on the map. You can also measure distances and change the symbology of certain features. Draw Graphic – allows you to place a graphic anywhere on the map, such as an airport, pinpoint, box, or school. Draw Label – allows the placement of text you wish to view on the map. Specify the font, size, color and text before you place on the map. You can also delete a specific label or delete all labels. Draw Shape – allows points, lines or shapes to be drawn on the map. Specify the type and width before drawing the shape. You can also delete a specific or all shapes. Measure – you can get X,Y coordinates of a particular location or you can measure between features. If you have multiple segments, double click to get the total distance. Map Symbology Editor - Symbolize a layer based on a chosen attribute. You may specify the number of ranges and specify values and colors for each. Preferences Menu Set Selection Symbols – This menu item allows the user to set the visual parameters of selected items. The default color for selected items is cyan. Here the user can change the selection color for the remainder of there visit to the site. This lesson was made possible by the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA), in cooperation with the Institute of Geospatial Technology (IAGT), teachers from the Hannibal School District (Hannibal, New York), and the Environmental Science Research Institute (ESRI). 5