Varactor-Tuned Oscillators Technical Data
advertisement

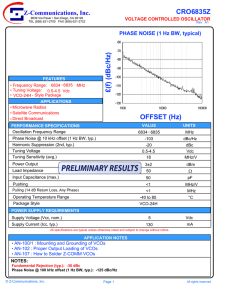
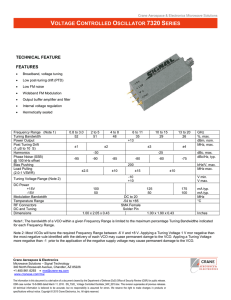
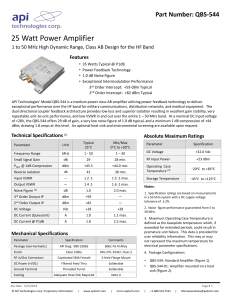
H Varactor-Tuned Oscillators Technical Data VTO-8000 Series Features • 600 MHz to 10.5 GHz Coverage • Fast Tuning • +7 to +13 dBm Output Power • ±1.5 dB Output Flatness • Hermetic Thin-film Construction Description HP VTO-8000 Series oscillators use a silicon transistor chip as a negative resistance oscillator. The oscillation frequency is determined by a silicon abrupt varactor diode acting as a voltage-variable capacitor in a thin-film microstripline resonator. This provides extremely fast tuning speed, limited primarily by the internal impedance of the user-supplied voltage driver. Fast settling is another feature of the HP VTO-8000 Series oscillators. Typical settling times for the VTO-8090 are <200 kHz within one microsecond while the VTO-8950 settles to <2 MHz within two microseconds referenced to ten milliseconds. The VTO-8850 combines a bipolar transistor oscillator with a GaAs FET buffer stage. This GaAs FET buffer isolates the oscillator from variations in load impedance for low frequency pulling, allows the oscillator to run lighty-loaded for low phase noise content and provides +10 dBm of minimum output power over the full tuning range. The VTO-8000 Series varactor-tuned oscillators are packaged in TO-8 transistor cans for simple installation in a conventional 50-ohm microstripline PC board. They are ideal for most compact, lightweight commercial and military equipment designs. Test fixturing is also available for lab bench test applications. See the “Test Fixtures for TO-8 Packages” section for additional information and outlines. Applications Frequency agile systems, such as digitally controlled receivers and active jamming transmitters often use externally linearized varactor-tuned oscillators. HP oscillators are monotonic making external linearization easy using analog (opamp) or digital (EPROM) linearizing techniques. The HP VTO Series has been designed with a tuning input bypass capacitance which is sufficient to provide the necessary RF filtering action yet as low Pin Configuration TO-8V GROUND +V 3 TUNE 2 RFOUT 4 1 +DC VOLTAGE CASE GROUND as possible to maximize ∆V/∆T characteristics for excellent tuning speeds. Used in a phase locked loop PLL circuit, a VTO provides a receiver LO with stability equivalent to the reference oscillator (usually crystal controlled), yet variable in discrete steps or continuously depending on the PLL configuration. Another important aspect of VTOs used in an LO application is their power vs. frequency flatness (±1.5 dB). This assures that once a receiver mixer is biased for best dynamic range the local oscillator drive will remain constant throughout the tuning range without complex leveling circuitry. 2 Electrical and Performance Specifications Guaranteed Specifications @ 25°C Case Temperature (0° to +65°C Operating Temperature) Part Number Frequency Range, Min. Power Output into 50–ohm Load,Min. Power Output Variation @ 25°C, Max. Operating Case Temperature Range Frequency Drift Over Operating Temperature, Typ. Pulling Figure (12 dB Return Loss), Typ. Pushing Figure, +15 VDC Supply, Typ. Harmonics, Below Carrier, Typ. Spurious Output Below Carrier, Min. Tuning Voltage Low Frequency High Frequency Maximum Tuning Voltage Tuning Port Capacitance, Nom. Phase Noise, Singie Sideband, 1 Hz Bandwidth, Typ. 50 kHz From Carrier 100 kHz From Carrier Input Power ±1% Regulation Voltage, Nom. Current, Max. Case Style Part Number Frequency Range, Min. Power Output Into 50–ohm Load, Min. Power Output Variation @25°C., Max. Operating Case Temperature Range Frequency Drift Over Operating Temperature, Typ. Pulling Figure (12 dB Return Loss), Typ. Pushing Figure, +15 VDC Supply, Typ. Harmonics, Below Carrier, Typ. Spurious Output Below Carrier, Min. Tuning Voltage Low Frequency High Frequency Maximum Tuning Voltage Tuning Port Capacitance, Nom. Phase Noise, Single Sideband, 1 Hz Bandwidth, Typ. 50 kHz From Carrier 100 kHz From Carrier Input Power ±1% Regulation Voltage, Nom. Current, Max. Case Style VTO–8060 VTO–8080 600–1000 MHz 800–1400 MHz 20 mW/+13 dBm 20 mW/+13 dBm ±1.5 dB ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 0° to +65°C 8 MHz 10 MHz VTO–8090 VTO–8150 900–1600 MHz 20 mW/+13 dBm ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 10 MHz VTO–8200 1500–2500 MHz 2000–3000 MHz 10 mW/+10 dBm 10 mW/+10 dBm ±1.5 dB ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 0° to +65°C 18 MHz 30 MHz 25 MHz 5 MHz/V –15 dB –60 dB 25 MHz 6 MHz/V –15 dB –60 dB 25 MHz 6 MHz/V –15 dB –60 dB 35 MHz 6 MHz/V –15 dB –60 dB 35 MHz 6 MHz/V –18 dB –60 dB 3±1 VDC 40±8 VDC +60 VDC 180 pF 2±1.5 VDC 35±10 VDC +60 VDC 180 pF 2±1 VDC 48+8/–10 VDC +60 VDC 180 pF 2.5±1 VDC 47±8 VDC +60 VDC 90 pF 2+2/–1 VDC 20±4 VDC +45 VDC 45 pF –110 dBc/Hz –117 dBc/Hz –100 dBc/Hz –107 dBc/Hz –100 dBc/Hz –107 dBc/Hz –95 dBc/Hz –102 dBc/Hz –95 dBc/Hz –102 dBc/Hz +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V VTO–8240 VTO-8360 VTO–8430 VTO–8580 2400–3700 MHz 10 mW/+10 dBm ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 30 MHz 3600–4300 MHz 10 mW/+10 dBm ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 35 MHz 4300–5800 MHz 10 mW/+10 dBm ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 60 MHz 5800–6600 MHz 5 mW/+7 dBm ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 70 MHz 35 MHz 6 MHz/V –18 dB –60 dB 40 MHz 6 MHz/V –25 dB –60 dB 50 MHZ 6 MHz/V –25 dB –60 dB 70 MHz 8 MHz/V –25 dB –60 dB 2+2/–1 VDC 30±8 VDC +45 VDC 45 pF 8±2 VDC 24±4 VDC +30 VDC 45 pF 1.0 VDC Min 20.0 VDC Max. +30 VDC 45 pF 5±2.5 VDC 24+3/–5 VDC +30 VDC 45 pF –95 dBc/Hz –102 dBc/Hz –100 dBc/Hz –108 dBc/Hz –90 dBc/Hz –97 dBc/Hz –85 dBc/Hz –92 dBc/Hz +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V 3 Electrical and Performance Specifications Guaranteed Specifications @ 25°C Case Temperature (0° to +65°C Operating Temperature) Part Number Frequency Range, Min. Power Output Into 50–ohm load, Min. Power Output Variation @ 25°C., Max. Operating Case Temperature Range Frequency Drift Over Operating Temperature, Typ. Pulling Figure (12 dB Return Loss), Typ. Pushing Figure, +15 VDC Supply, Typ. Harmonics, Below Carrier, Typ. Spurious Output Below Carrier, Min. Tuning Voltage Low Frequency High Frequency Maximum Tuning Voltage Tuning Port Capacitance, Nom. Phase Noise, Single Sideband, 1 Hz Bandwldth, Typ. 50 kHz From Carrier 100 kHz From Carrier Input Power ±1% Regulation Voltage, Nom. Current, Max. Case Style VTO–8650 VTO–8810 VTO–8850 VTO–8950 6500-8600 MHz 10 mW/+10 dBm ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 100 MHz 8100–9100 MHz 10 mW/+10 dBm ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 110 MHz 8500–9600 MHz 10 mW/+10 dBm ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 110 MHz 9500–10500 MHz 10 mW/+10 dBm ±1.5 dB 0° to +65°C 160 MHz 15 MHz 10 MHz/V –20 dB –60 dB 8 MHz 12 MHz/V –15 dB –60 dB 10 MHz 15 MHz/V –25 dB –60 dB 20 MHz 10 MHz/V –20 dB –60 dB 2±1 VDC 20±5 VDC 30 VDC 26 pF 2 VDC Min. 16 VDC Max. +30 VDC 26 pF 5±2 VDC 13±5 VDC +30 VDC 26 pF 4±1 VDC 10 VDC Max. +15 VDC 26 pF –80 dBc/Hz –88 dBc/Hz –80 dBc/Hz –88 dBc/Hz –82 dBc/Hz –90 dBc/Hz –73 dBc/Hz –80 dBc/Hz +15 VDC 50 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 100 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 100 mA TO–8V +15 VDC 100 mA TO–8V Schematic +15 V Output Matching Series Feedback Varactor V Tune Tuning Port Capacitor Resonator RF Output 4 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 8 16 24 32 40 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC POWER OUTPUT, dBm 15 14 13 180 160 TUNING CURVE 140 120 100 80 60 MODULATION 40 SENSITIVITY 20 2.5 2.0 1.5 0 45 50 5 10 15 20 POWER OUTPUT, dBm 250 TUNING CURVE 2500 MODULATION SENSITIVITY 1500 0 8 16 24 32 45 50 Figure 4. VTO–8150 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. 40 50 48 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC Figure 5. VTO–8200 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. FREQUENCY, GHz 3500 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V POWER OUTPUT, dBm FREQUENCY, MHz POWER OUTPUT 2000 25 30 35 40 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC Figure 3. VTO–8090 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. 3000 48 POWER OUTPUT TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC 14 13 12 11 10 25 Figure 2. VTO–8080 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. FREQUENCY, GHz MODULATION SENSITIVITY MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V POWER OUTPUT, dBm FREQUENCY, GHz 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 TUNING CURVE 0 MODULATION SENSITIVITY 500 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V POWER OUTPUT, dBm TUNING CURVE 1000 45 50 POWER OUTPUT 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.0 .9 .8 125 1500 Figure 1. VTO–8060 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. 15 14 13 POWER OUTPUT 14 13 12 11 POWER OUTPUT TUNING CURVE 4.0 3.5 160 120 3.0 80 MODULATION SENSITIVITY 2.5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 40 45 50 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V 0 15 14 13 12 11 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V 160 140 120 TUNING CURVE 100 80 60 MODULATION 40 SENSITIVITY 20 FREQUENCY, MHz 1.1 1.0 .9 .8 .7 .6 .5 POWER OUTPUT MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V POWER OUTPUT, dBm 17 16 15 14 FREQUENCY, GHz Typical Performance @ 25ºC Case Temperature TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC Figure 6. VTO–8240 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. 5 20 10 15 20 25 1000 6500 TUNING CURVE 5500 4500 MODULATION SENSITIVITY 3500 0 30 8 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC 5.5 0 POWER OUTPUT, dBm 140 TUNING CURVE 120 100 80 MODULATION 60 SENSITIVITY 40 20 0 5 10 15 20 25 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC 600 MODULATION SENSITIVITY 5 0 4 8 12 16 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC 200 0 20 1000 TUNING CURVE 800 600 7 6 400 MODULATION SENSITIVITY 5 4 POWER OUTPUT, dBm POWER OUTPUT, dBm FREQUENCY, GHz TUNING CURVE MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V 1000 10 7 6 48 2 4 200 0 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC Figure 10. VTO–8650 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. POWER OUTPUT 9 8 40 POWER OUTPUT 0 Figure 9. VTO–8580 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. 15 14 13 14 13 12 11 10 8 FREQUENCY, GHz 6.0 32 Figure 8. VTO–8430 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. Figure 11. VTO–8810 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. FREQUENCY, GHz FREQUENCY, GHz 7.0 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V POWER OUTPUT, dBm POWER OUTPUT 6.5 24 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC Figure 7. VTO–8360 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. 13 12 11 10 16 200 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V 10 POWER OUTPUT 15 14 13 POWER OUTPUT TUNING CURVE 10 400 9 MODULATION SENSITIVITY 8 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 300 200 100 0 45 50 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V 5 13 12 11 10 9 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V 90 TUNING CURVE 80 70 60 MODULATION 50 40 SENSITIVITY 30 POWER OUTPUT, dBm 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V POWER OUTPUT FREQUENCY, MHz 11.5 11.0 10.5 FREQUENCY, GHz POWER OUTPUT, dBm Typical Performance (Continued) TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC Figure 12. VTO–8850 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. 6 POWER OUTPUT 800 12 FREQUENCY, GHz LOG £(f), dBc/Hz –20 13 12 11 10 11 TUNING CURVE 10 600 400 MODULATION SENSITIVITY 9 200 8 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 TUNING VOLTAGE, VDC 14 0 16 MODULATION SENSITIVITY, MHz/V POWER OUTPUT, dBm Typical Performance (Continued) 8650 8240 –40 –60 –80 –100 –120 –140 –160 8950 10k 100k 1M 1k FOURIER FREQUENCY, Hz Figure 14. Noise Comparison Single Sideband Phase Noise. Figure 13. VTO–8950 Power Output, Frequency and Modulation Sensitivity vs. Tuning Voltage. TO-8V Case Drawing .300 TYP .18 .150 TYP .017 +.002 –.001 GROUND RF OUT 3 .50 DIA 2 .300 TYP .45 DIA 4 .150 TYP GLASS RING .060 DIA TYP (3X) 1 CASE GROUND .22 MIN 10M V TUNE V+ APPROXIMATE WEIGHT 1.7 GRAMS NOTES (UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED): 1. DIMENSIONS ARE SPECIFIED IN INCHES 2. TOLERANCES: xx ± .02 xxx ± .010 7 Test Fixtures for TO-8 Packages (TF 801/802) Oscillators (VTO) Features • DC to 11 GHz Frequency Range • Connectorized Tuning Port and RF Output • Easy to Test Package • Repeatable Performance Applications • Engineering Characterization • Incoming Inspection • System Prototype • Demonstration of Device Performance Description clamp is placed over the device under test and secured by machine screws prior to testing. Orientation of pins can be verified by comparison with part (c) of Figure 15. It is recommended that both machine screws be used to fasten the ring clamp. Screws should be tightened down snugly with a jewelers type screwdriver. To facilitate testing and prototyping of products in the TO-8V package, a series of test fixtures is available. Designated the HP TF Series test fixtures, they feature rugged construction for precise, repeatable measurements. The TF Series test fixtures come supplied with mounting hardware to ensure excellent ground contact between the oscillator package and test fixture. This assures excellent contact between package pins and test fixture connector pins for reliable testing. The device under test is aligned according to Figure 15, and pushed fully down onto the fixture. The steel mounting ring TUNING VOLTAGE CONNECTOR .53 It should be noted that some output power variation may be seen, from unit data, at frequencies above 8 GHz. This is due to small differences in lengths of test fixture RF output connector pins. TUNING VOLTAGE .35 POWER INPUT CONNECTOR VTO IN PLACE For different connector options check the table in Figure 15 to identify the correct part numbers. + TUNING VOLTAGE PIN .83 DCPIN VDC .35 .45 GROUND .20 .55 .65 (a) GROUND .35 RFOUT .15 RFOUT .70 (b) (c) + TUNING VOLTAGE CONNECTOR OPTIONS .150 TYP .300 TYP GROUND 3 SERIES TUNING VOLTAGE RF OUTPUT TF-801 SMA SMA TF-802 SMA TYPE N Figure 15. TO-8 Test Fixture. GROUND TAB ON PACKAGE 2 .45 CASE GROUND 4 1 RFOUT .150 TYP +DC VOLTAGE (Bottom View) H For technical assistance or the location of your nearest Hewlett-Packard sales office, distributor or representative call: Americas/Canada: 1-800-235-0312 or 408-654-8675 Far East/Australasia: (65) 290-6305 Japan: (81 3) 3331-6111 Europe: Call your local HP sales office listed in your telephone directory. Ask for a Components representative. Data subject to change. Copyright © 1996 Hewlett-Packard Co. Obsoletes 5963-3264E Printed in U.S.A. 5964-9815E (3/96)