Phantom Load of Electronic Devices
advertisement

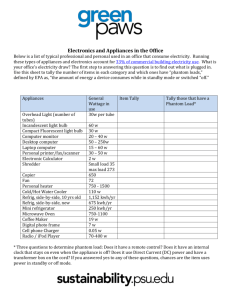
Phantom Load of Electronic Devices "Understand what a phantom load is and how it can be reduced." Key Points ● ● ● Phantom load results when electronic devices continue to draw power after they are turned off. Televisions, microwave ovens, and DVD players are common phantom load culprits. Unplugging devices when they are not in use is the best way to reduce phantom load. Many electronic devices continue to draw power after they are switched off. This waste of electricity is known as "phantom load." Devices that cause phantom loads can often be recognized by clocks or lights that continue to operate when the equipment is not "running." Common examples include DVD players and microwave ovens. Any device that uses a remote control, such as a television, causes a phantom load because it must use a small amount of energy to remain in a ready state. Small transformers are another common cause of phantom load. These are plastic, cubed-shaped boxes that plug into a wall outlet to help power devices such as answering machines. According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), the United States uses about 43 billion kWh of electricity per year as a result of this continuous, low-level energy use. The average home uses about 450 kWh per year of its total energy consumption to power phantom loads, or about $28 per year. In some home electric devices, 75% of total energy is consumed when the device is turned off. Below is a list of common devices that cause phantom load along with an estimate of their total annual energy consumption (turned on and off): Electronic Device Annual Energy Usage Television 222 kWh DVD Player 36 kWh VCR 47 kWh Answering Machine 35 kWh Cordless Phone 28 kWh Source: Energy 'Consumption of Consumer Electronics in U.S. Residences,' Consumer Electronics Association Televisions and VCRs are big contributors to phantom loads. Electricity use in televisions that are turned “off” costs the United States more than $750 million each year. The electricity is used to maintain the remote control and instanton features, and to keep the filaments in the picture tube warm 24 hours a day. The DOE offers the following tips for reducing phantom loads: ● ● ● ● If possible, unplug a device when it is not in use. Plug devices into a power strip and use the power strip to cut power when they are not in use. If possible, choose an appliance without a built-in clock or timer. While the displays only consume about 0.5 watts, the power supply in the appliance is converting 120 volts of alternating current to low-voltage direct current for the clock or timer. This is very inefficient and consumes 100 to 200 watt-hours per day. This is enough energy to run a compact fluorescent light bulb continuously for 10 hours. Avoid leaving appliances with small transformers plugged in while not in use. Also, consider purchasing all-in-one appliances, such as a phone with built-in answering machine and caller id display. This will reduce the number of small transformers plugged in. Blue Ridge Electric Cooperative Questline has been prepared solely for the purpose of providing helpful information to users of this service. The information has been compiled by Tech Resources, a contractor to Blue Ridge Electric Cooperative, however, no representation is made as to the completeness or accuracy of the information contained therein. In particular, some information may be incomplete, may contain errors or may be out of date. In addition, neither Tech Resources nor Blue Ridge Electric Cooperative endorses any product or service mentioned therein.