ELEG 646 Devices- Homework 1
advertisement
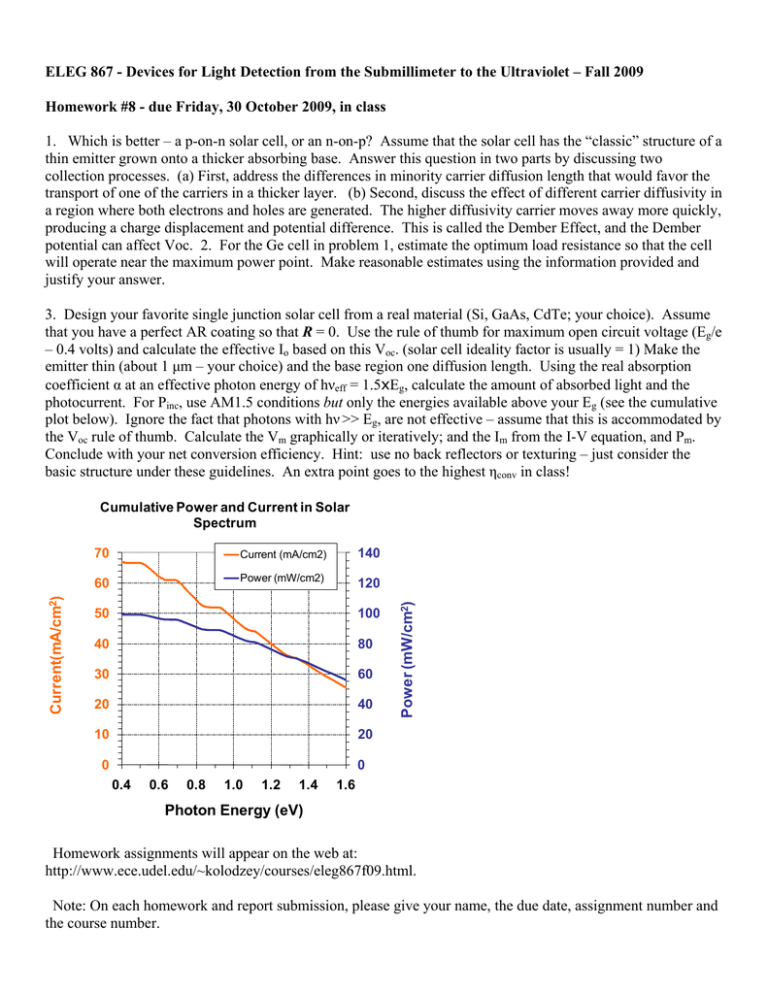
ELEG 867 - Devices for Light Detection from the Submillimeter to the Ultraviolet – Fall 2009 Homework #8 - due Friday, 30 October 2009, in class 1. Which is better – a p-on-n solar cell, or an n-on-p? Assume that the solar cell has the “classic” structure of a thin emitter grown onto a thicker absorbing base. Answer this question in two parts by discussing two collection processes. (a) First, address the differences in minority carrier diffusion length that would favor the transport of one of the carriers in a thicker layer. (b) Second, discuss the effect of different carrier diffusivity in a region where both electrons and holes are generated. The higher diffusivity carrier moves away more quickly, producing a charge displacement and potential difference. This is called the Dember Effect, and the Dember potential can affect Voc. 2. For the Ge cell in problem 1, estimate the optimum load resistance so that the cell will operate near the maximum power point. Make reasonable estimates using the information provided and justify your answer. 3. Design your favorite single junction solar cell from a real material (Si, GaAs, CdTe; your choice). Assume that you have a perfect AR coating so that R = 0. Use the rule of thumb for maximum open circuit voltage (Eg/e – 0.4 volts) and calculate the effective Io based on this Voc. (solar cell ideality factor is usually = 1) Make the emitter thin (about 1 μm – your choice) and the base region one diffusion length. Using the real absorption coefficient α at an effective photon energy of hνeff = 1.5xEg, calculate the amount of absorbed light and the photocurrent. For Pinc, use AM1.5 conditions but only the energies available above your Eg (see the cumulative plot below). Ignore the fact that photons with hν >> Eg, are not effective – assume that this is accommodated by the Voc rule of thumb. Calculate the Vm graphically or iteratively; and the Im from the I-V equation, and Pm. Conclude with your net conversion efficiency. Hint: use no back reflectors or texturing – just consider the basic structure under these guidelines. An extra point goes to the highest ηconv in class! 70 Current (mA/cm2) 140 60 Power (mW/cm2) 120 50 100 40 80 30 60 20 40 10 20 0 Power (mW/cm2) Current(mA/cm2) Cumulative Power and Current in Solar Spectrum 0 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 Photon Energy (eV) Homework assignments will appear on the web at: http://www.ece.udel.edu/~kolodzey/courses/eleg867f09.html. Note: On each homework and report submission, please give your name, the due date, assignment number and the course number.