Medical Respiratory Emergencies Signs of Inadequate Breathing
advertisement

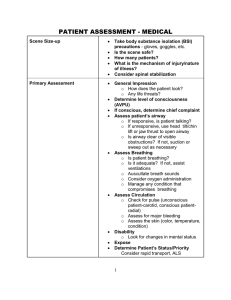
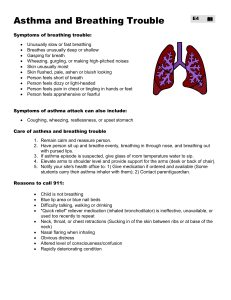
Signs of Inadequate Breathing Medical Respiratory Emergencies Breathing - It Does Your Body Good! • Rate: 12-20 adult; 15-30 child; 25-50 infant • Rhythm - irregular may be neurologic • Quality - sounds in the airway – Stridor - upper airway obstruction – Wheeze - bronchospasm – Snore - tongue in the airway • Depth - compared to Pt’s condition Signs of Inadequate Breathing • Skin condition – pale / palor - lack of blood flow – cyanosis - poorly oxygenated blood • Other physical findings: – retractions – nasal flaring – tripod position – see saw breathing Signs of Inadequate Breathing • First sign of hypoxia is: – Hold your breath: • Anxiety is the first sign of hypoxia • Changes in mentation are important clues to cerebral perfusion Assessment • Initial Assessment – LOC? - is there anxiety here? LOC – Airway - sounds ? – Breathing - breath with your Pt! – Circulation - expect ↑ in pulse rate, Skin? ( Think Compensation) Assessment • Focused – – – – Breath Sounds – listen for aliens AMPLE OPQRST - also, Pertinent Negatives Vital signs • Consider related problems • # of words per breath? • “How bad is this episode compared to normal?” 1 Treatment in General Respiratory Treatments • Airway - ensure it is adequate! • Oxygen - high flow , NRB time • Calm and reassure - reduce the body’s need for oxygen • Fowler’s position • Medications as indicated • Bag Valve Mask - RR <8 or >28; use common sense here • Oxygen – 10-15 lpm for respiratory distress Types of Respiratory Ailments • COPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease – a groups of diseases – from continued irritation of lungs – very often from exposure to cigarette smoke – progressive from one to the next – also sometimes the progression from asthma Emphysema • The “Pink Puffer” • Alveolar destruction / loss of elasticity • Airways close during exhalation before all the air is out • leads to air trapping • Volume expands giving Pt a barrel chested appearance – to increase oxygenation of tissues • BVM – to ensure adequate oxygen intake / CO2 removal (ventilation) • Albuterol – bronchodilator – For treatment of bronchoconstriction evidenced by wheezing / restricted airflow Chronic Bronchitis • The “Blue Bloater” • Chronic • caused by mucous plugging • Signs / Symptoms – Productive cough – Cyanosis “Blue” • Often leads to right sided heart failure – this produces peripheral (body) Edema - “Bloater” – Jugular Vein Distention zLung sounds – often Rhales / rhonchi and wheezing Emphysema • Breathing out against resistance helps hold open the airways longer • so Pt breaths out through pursed lips - “Puffer” • Long term hypoxia leads to increased hemoglobin production - gives a “pink” appearance • often very thin due to high energy cost of breathing • Lung sounds – inspiration often of greater volume than expiration, wheezes / ‘tight’ lung sounds 2 Oxygen use on COPDers • ‘Normal’ people breath when they have too much CO2 in them • COPDers breath when they have too little O2 in them • So what happens if you give them lots of O2? • You will NEVER withhold O2 from a respiratory Pt • Monitor rate AND depth of respirations - ventilate if needed Asthma • Pts often sit bolt upright to ‘stretch’ open airways. • Treatment will include assisting with Metered Dose Inhalers or Nebulizer Asthma • Irritation causes increased mucous production and spasms in the airway • Wheezing as air moves through narrowed passages Asthma vs. Status Asthmaticus • Asthma often relieves itself or is relieved by medications • Status asthmaticus isn’t relieved by med.s very Life-threatening • Fear the ‘quiet’ asthma attack • What is the difference? • Time! Be moving towards the hospital while treating - don’t wait for effects of med.s Pneumonia Break • From an infection - viral, bacterial • Bacterial secondary to aspiration has 80% mortality rate • S/S: – cough with thick, colored mucous – Hx of fever, infection – Areas of consolidation may be heard 3 Anaphylaxis • Allergic reaction, Allergic response, Anaphylaxis • The body is killing itself trying to defend itself – airway begins to swell shut and significant bronchoconstriction occurs • S/S – Anxiety,hives, itching throat and tongue, watery eyes/nose, sneezing, wheezing, SOB, Hypotension Pulmonary Embolism • Embolism that lodges in the lungs • blocks off part of the lungs from blood/air exchange • Increases pressure in the area • S/S: depend on size of blockage – – – – Sudden dyspnea from no apparent cause, pleuritic chest pain possible diminished lung sounds in area Hemoptysis from leaking alveoli Pulmonary Embolism • History may be the key – recent surgery – recent long-bone fx – confinement to bed for long period • All are events that could cause a clot that might break free and become and embolism • Other Risk factor group: – Female, smoker, use of oral birth control Spontaneous Pneumothorax • A non-traumatic pneumothorax • build up of air doesn’t allow the lung to expand • In this case, air comes from the lung itself • Congenital bleb bursts, allowing air to enter pleural space Spontaneous Pneumothorax • S/S: – – – – Sudden dyspnea with no other obvious cause pleuritic chest pain diminished or absent lung sounds on one side possible tracheal deviation - easily become tension pneumothorax • Usually in blond, blue-eyed, 20ish males 4 Hyperventilation Syndrome • ‘Syndrome’ indicates from no other medical cause… • rule everything else out! • Breathing too fast - generally emotional reasons • Air not in lungs long enough for exchange • Too much CO2 is removed • need to slow breathing down Hyperventilation Syndrome Hyperventilation Syndrome • • • • Chief Complaint: SOB possible head ache, chest pain (pleuritic) Hx of argument or other anxiety-causing event Lack of other abnormality!!! • Cluebirds: – tingling lips, nose, extremities – carpo-pedal spasms RULES TO LIVE BY: • Tx: – calm and reassure – oxygen if needed - may help calm, may not – may still be hypoxic – “breath with me” – ask questions that require long answers - you can’t breath and talk at the same time Childhood Diseases • Croup – a true childhood disease – barking seal cough - see H.O. • Epiglottitis – even in adults – muffled voice, drooling - see H.O. • don’t look in the mouth if you suspect these illnesses! • There is no such thing as Hyperventilation Syndrome in the Trauma Patient • No paper bags! BVM Use • 2 person is always better than 1 person • Slow and steady • Cryciod pressure - the Sellick Maneuver – to reduce gastric distention • 30 < RR >8 or to push past obstuctions / spasming airways 5 Pulse Oximetry Best Treatments • Measures bound hemoglobin • doesn’t even care if it’s bound to oxygen or something else • Oxygen - Can’t hurt, Might help, Heck of a crowd pleaser! • Calm and reassure reduces the problem from the other side - lowers oxygen demand on the body – CO binds to hemoglobin too • Only measures in the extremity the sensor is on • Treat the Pt, not the monitor... 6