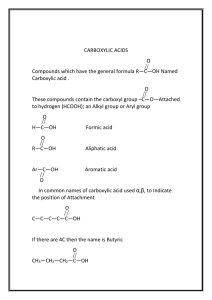
A list of tricks to help you remember the amino acids Structures

Structures
A list of tricks to help you remember the amino acids
Names (letter code) Side chain features/description
Aliphatic
H
H
C
NH
2
COOH
CH
3
H
C
NH
2
COOH
CH
3
CH
CH
3
CH
3
CH
CH
3
H
C
NH
2
COOH
CH
2
H
C
NH
2
COOH
CH
3
CH
2
CH
H
C
CH
3
NH
2
COOH
Glycine (G) hydrogen for R, most simple, optically inactive
Alanine (A) methyl for R, a simple functional group to start just
Valine (V) like “A” (in alanine) starts the alphabet
Leucine (L) valine extended by one methylene
Isoleucine (I) simple again, but shaped like the “V” in its name
lopsided valine....?
COOH
N
H
Proline (P) 3 carbon chain to proline’s own nitrogen, structurally “special” and found in turns
CH
3
HS
S
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
Sulfur-containing
H
C
NH
2
COOH
Methionine (M) special - starts every protein, 3 carbons with a thioether; methyl-blocked sulfhydryl...?
H
C
NH
2
COOH
Cysteine (C) “sulfhydryl alanine,” reactive, can form disulfides
© 2001 by Jeff Dahlseid
HO
CH
2
CH
2
Aromatic
H
C
NH
2
COOH
CH
2
Phenylalanine (F) alanine with a phenol group which you
KNOW is aromatic, the “Y” in phenyl can remind you which 3 amino acids with names beginning with T (the “T”s) are aromatics
H
C
NH
2
COOH
Tyrosine (Y) hydroxylated phenylalanine, one of 3 “T”s that has “Y” in its name so it is an aromatic
H
C
NH
2
COOH
N
H
Tryptophan (W) one of 3 “T”s with a “Y” so it is aromatic, will
“tryp” you up because it is hard to remember, has a 3 carbon start to N (or indole ring on
methylene)
Aliphatic hydroxyl
HO CH
2
H
C
NH
2
COOH
CH
3
OH H
C C COOH
H NH
2
Serine (S) “hydroxyl alanine”
Threonine (T) one of 3 “T”s, without “Y” so aliphatic (also its symbol is the first letter of its name like the other aliphatics), its “threo” parts are
methyl, hydroxyl, and hydrogen on a single C
© 2001 by Jeff Dahlseid
Acidic - negative charges
O
-
O
C CH
2
H
C COOH
NH
2
Aspartate (D) “carboxyl alanine” with acidic nature noted by suffix “ate”, the alphabetical ordering of the first letter of their names correlates with an increase in length of side chain
O
-
O
C CH
2
H
CH
2
C COOH
NH
2
Glutamate (E) aspartate plus one methylene, G is after A
NH
2
+
NH
3
C
NH
NH
2
+
(CH
2
)
4
(CH
2
)
3
H
C
NH
2
COOH
Basic - positive charges
H
C
NH
2
COOH
Arginine (R) 3 carbon chain linked to a C full of only N’s
(no H’s & C has 4 bonds) through an N
Lysine (K) 3 carbon chain plus one methylene to amino, it lies (“Lys”) about the 3 carbon trend
+
H
N
N
H
CH
2
H
C
NH
2
COOH
Histidine (H) 3 carbons to N and loop back through C ‘n’ N
NH
2
C
O
NH
2
C
O
CH
2
CH
2
H
Amide derivatives of acids - loose OH for NH
2
to loose charge
C COOH
NH
2
CH
2
H
C
NH
2
COOH
Asparagine (N) amide derivative of aspartate
Glutamine (Q) amide derivative of glutamate
For 3-D visualization, see: http://chemistry.gsu.edu/glactone/PDB/Amino_Acids/aa.html
For RasMol download, see: http://www.umass.edu/microbio/rasmol/
© 2001 by Jeff Dahlseid