Inter-institutional agreements
advertisement

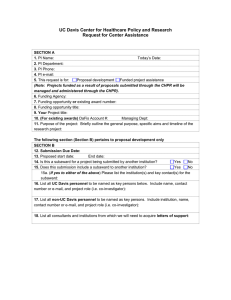
Inter-institutional agreements: Why? When? And how? February 21, 2014 Overview 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. RAN updates Introduction to Research Collaboration Preparing an inter-institutional application Managing an inter-institutional project Managing inter-institutional agreements issued to McGill Conclusion RAN Updates - Budget 2014 Budget 2014 presented February 11, 2014. Highlights include: • Funding increases for Tri-Agencies • CIHR: $15 M • NSERC: $15M • Industrial R&D fellowships will be phased out. Mitacs will now run all industrial-sponsored internships • SSHRC: $7M • Additional $10M over two years in targeted funding for a Social Innovation and Community Colleges Fund • Indirect Costs Program $9M • Mitacs • $8M over two years to expand the Elevate Postdoctoral Fellowships Program • Funding is now available to not-for-profit organizations with an economic focus RAN updates • FRQ – Request for Instalments Process 1. Request for instalment (portal open now) must be submitted online for OSR review and approval • All leaves must be indicated in the request for instalment. Contact Amy for more details. 2. 3. FRQ considers the requests & confirms instalments for 2014-15 fiscal year Grant holder must go back into electronic system to “Accept” the instalment • CIHR – Foundation Scheme Live Pilot - Update • Funding start date has been changed from October 1, 2015 to July 1, 2015 • PI departures, leaves, as well as new recruits • Will be discussed at next meeting, but contact Amy for more details RESEARCH COLLABORATION – INTRODUCTION Key terms I • Inter-institutional agreements: also known as subaward/subgrant agreement, transfer of funds, subcontracts • Originating Sponsor: ultimate source of the funding • Prime Institution (“Prime”): the institution awarded funding from the originating sponsor • Collaborating Institution: the institution receiving the funding via subaward agreement (also referred to as subrecipient) Research Collaboration • Increasingly common that researchers are working in teams • Sponsors are encouraging more collaboration among researchers, because: • Adds a new perspective to research problems • Maximizes research investment and avoids duplication of funding for similar research objectives • Increases international profile of institutions and sponsors • Canada's S&T Strategy: Mobilizing Science and Technology to Canada's Advantage (published in 2007) • Highlighted that Canada did not have enough collaboration and partnerships, particularly in STEM fields • Outlined strategic goal of fostering collaboration to improve Canada’s economy Types of Collaboration Disciplinary research • a team of researchers from one academic field working to advance a common, shared program of research. Interdisciplinary research • a mode of research by teams or individuals that integrates information, data, techniques, tools, perspectives, concepts, and/or theories from two or more disciplines or bodies of specialized knowledge to advance fundamental understanding or to solve problems whose solutions are beyond the scope of a single discipline or area of research practice.* Partnership • a multi-directional flow of knowledge, often incorporating perspectives from non-academic sectors to develop new knowledge and expertise. *See Interdisciplinary Research, National Science Foundation Types of Funding Programs Standard Grant Partnership Joint Initiative Co-Funding • All funds are paid to the administering organization who then disperses the funds via subaward agreement as required. • Grant funds paid to one administering (lead) institution • Cash and/or in-kind support often required from lead and partnering organizations which must be managed at institutional level • Program is supported via several funders but all support is collected by the primary sponsor who then issues one payment to the lead institution (managed like a standard grant) • One project is being supported but payments may be made via several organizations. • Either paid to one institution or can be paid to each institution directly • Example: Digging into Data Reality of Research Collaboration • Although grant is awarded to McGill as lead applicant institution, it is codirected by researchers located at different collaborating institutions or organizations. • Each co-director will be incurring project-related expenses at their institution. U of T Harvard Cambridge • Anticipated Project Costs: • Student • Travel • Participant costs • Anticipated Project Costs: • Student • Conference Organization • Anticipated Project Costs: • Research Associate • Participant Costs So, how does this work? Total grant is awarded to McGill. McGill is responsible for reporting to the sponsor. For the sponsor, the relationship is uniquely between them and McGill. Sponsor McGill U of T Harvard Cambridge McGill can prepare subaward agreements which flow down portions of the funds, along with agency terms and conditions, to the collaborating institutions. I’m sorry, but I’m still confused. How does this work? Grant awarded to lead institution Award approval and Fund creation for full award Principal Investigator requests, in writing, subaward(s) noting the investigator(s), the institution(s) and the amount(s) McGill (OSR/RFMS) prepares and issues the subaward agreement Collaborating Institution agrees to a legal relationship to manage the grant according to outlined terms and conditions. Award approval process begins at the Collaborating Institution PREPARING AN INTER-INSTITUTIONAL GRANT APPLICATION Start early!! Review objectives and requirements of the opportunity OSR Grants Officer can provide additional expertise on the agency requirements, strategies for success, as well as the internal deadlines. Important to contact OSR as early as possible in the process. Proposal submitted to OSR for review Contact OSR Grants Officer Gather application requirements Draft proposal and other application requirements Make a list of what is needed for the application. CVs, biosketches for research team members, letters of support, institutional signatures for team members, etc. Considerations: Application Phase Are institutional signatures required for participating institutions? If so, have the research team members advised their Research Offices? If funds will be used at an Eligibility requirements affiliated hospital, a subaward agreement will be required. Who can incur research expenses? Are subawards allowable? Does the role assigned in the application (e.g., coapplicant/collaborator) reflect the activities that they will undertake? Research plans Is it possible to issue funds to organizations located elsewhere in Canada or abroad? Is there any required matching contributions? With most partnership programs, there is a required matching. Have the sources been confirmed? Roles within a project Co-Applicant • Involved in intellectual direction of the project • Expected to incur research expenses • AKA: Co-investigator Collaborator • Advisory role within the project • May incur project-related expenses but not intended to be involved in the conduct of research Consultant • Providing a service to the project • Fee for service arrangement • Does not contribute to intellectual direction of the project Vendor • Enterprise selling goods on the public market Considerations: Foreign Organizations • Currency: subawards are issued in Canadian Dollars (with the exception of awards issued to McGill in USD, which can be issued in USD). • Recipient institution may convert to domestic currency for internal grant management, but all reporting must be done in Canadian Dollars (except in cases of subawards issued in USD, which are reported in USD). • Financial Management: when issuing to foreign not-for-profit organizations, OSR assesses the capacity of the organization to adhere to financial management requirements. • The Federal Agencies' Grant and Award Management Questionnaire (used by the Tri-Agencies) is a useful tool in assessing expected grant management mechanisms. • If McGill has concerns of the mechanisms in place, it may propose other options to mitigate that risk Considerations: Budget Rates of pay for research personnel Keep in mind rates of Per diem rates for travel pay are significantly higher elsewhere in Taxes Canada. HR policies Institutional agreements with certain agencies Risk Management (insurance) Audit Requirements (for ex., record retention, audit costs, etc.) In cases where subawards/subcontracts are anticipated, the institutional requirements of each collaborating institution should be taken into consideration when building the budget. Considerations: Indirect Costs (IDC) • It is expected that the indirect costs are shared, if allowed by sponsor. In those cases, subaward would be inclusive of any indirect costs. • If no sponsor rate exists, the institutional policy for IDC is applied. Each subaward agreement will be inclusive of the institutional rate of the subrecipient institution. • If indirect costs are not allowable, all recipient institutions must waive indirect costs. U of T portion (incl. institutional IDC rate of 10%) Harvard portion (incl. institutional IDC rate of 30%) McGill portion (incl. institutional IDC rate of 15%) Cambridge portion (incl. institutional IDC rate of 20%) IDC rates of all Collaborating Institutions must be factored into the application budget, if subawards expected. Results Announced Application was awarded funding. Now, the implementation for the multi-site project begins. MANAGING AN INTER-INSTITUTIONAL PROJECT Roles and Responsibilities – Subaward agreements Principal Investigator • Determines the intellectual direction of the research project • Determines and monitors project activities in collaboration with team members • Requests the Subaward, amendments • Advises central offices about any necessary changes to agreement McGill – Central Offices (OSR, RFMS) • Prepares and executes Subaward agreements & amendments on behalf of McGill • Liaises with sponsor • Clarifies terms and conditions for recipient institution • Follows up with recipient institutions if audited Subrecipient Institution • Negotiates and signs the agreement on behalf of the institution • Ensures compliance with terms and conditions • Liaises with McGill • Notifies McGill of required changes to the terms of the agreement • Provides supporting documentation to McGill, as required PI/Research Team responsibilities in inter-institutional projects When a inter-institutional/team project is awarded the PI should: • meet with the research team to discuss expectations regarding: Research plans (including roles and responsibilities for team members) Intellectual Property Data ownership Equipment ownership Publication (including co-authorship) • Involve research offices and research administrators from all the institutions as soon as possible following award results Scopes of Work • In consultation with research team, PI should develop Scopes of Work for each anticipated subaward agreement. • As a best practice, a Scope of Work should describe the expectations and requirements of the Prime Institution from the subrecipient, including: Anticipated activities and outcomes Timelines for the achievement of deliverables Expected method to meet the deliverables Budget breakdown by cost categories Reporting schedule to the PI/team Scopes of work are to the PI’s advantage as they outline the expected activities and can be used to resolve disputes between parties. Other considerations: research compliance • Inter-institutional projects may require approval from several Research Ethics Boards (REB) and/or Animal Compliance offices • Considerations for the Prime Institution: • If any activity to be conducted under the project will involve human subjects and/or animal subjects, regardless of the research site, an approval from the Prime’s REB or Animal Care Committee is required. • Considerations for the subrecipient(s): • If the research being conducted at the research site will involve human subjects and/or animal subjects, an approval from the applicable office at the recipient institution will be required prior to account authorization there. Why issue subawards ? • Binds all parties to the originating sponsor’s requirements • Creates a legal relationship between institutions to ensure compliance with regulations, including: • Financial Administration (account management, record keeping, use of research funds, etc.) • Financial reporting • Responsible conduct of research (ethics, research integrity, etc.) • Provides opportunity for research team to include language on reporting, intellectual property, governance, etc. • Subrecipient is usually required to submit financial and technical reports earlier than the sponsor deadline for the prime institution. Why issue subawards? (continued) • Required in all cases where research funding is being issued to another institution • McGill will not pay or issue an invoice without a subaward agreement in place. • Mitigates the risk for the prime institution by ensuring compliance with governing terms and conditions. Note: Prime institution continues to be accountable to the sponsor for the entire awarded amount. • Mitigates the risk for the subrecipient institution as it ensures a legally binding obligation to pay for research costs incurred. • Signed agreement allows the institution to authorize Fund opening. It is not the receipt of the payment, but rather the execution of the agreement, guaranteeing payment, that allows spending power. Who to contact? RFMS OSR • Issuance of agreement to eligible institutions • Agencies: SSHRC, NSERC, CIHR, FRQSC, FRQNT, and FRQS. • Issuance of agreements to ineligible institutions on TriAgency grants • Issuance of agreements on other research funds Template sub issued by RFMS Template sub issued by OSR Key terms Take 2 • Originating Sponsor: ultimate source of the funding. • Prime Institution (“Prime”): the institution awarded funding from the originating sponsor • Listed as the “Sponsor” in InfoEd for any inter-institutional agreements issued to McGill • Collaborating Institution: the institution receiving the funding via Subaward agreement (also referred to as subrecipient) • Period of Performance: the full period of collaboration (e.g., April 1, 2012 to March 31, 2017) • Budget period/instalment period: the period for each budget instalment (e.g, April 1, 2012 to March 31, 2013). It is common that the period of performance is indicated but each budget year amount confirmed annually. • Although project period confirms the duration of the researcher’s involvement in the project, carryover is clarified in the governing terms and conditions. • Amendment: • OSR: amends the terms of the original agreement (for ex., a new budget year, additional funding, changes in scope of work, etc.) • RFMS: amends the terms of the annual transfer of funds (for ex., increase in funding for a budget year where a transfer has already been issued) Payment Mechanisms Accountable Advance Payment Cost-reimbursement • Money is issued in advance of expenditures (usually upon signature of the agreement) • Collaborating institution provides financial statements, reconciling expenses against the funding provided • Unspent funds at the end of the Period of Performance must be returned • Common for Tri-Agency & FRQ grants • Collaborating institution advances uses of funds (like a line of credit) to PI there with the understanding that the payments will be received at a later date • Collaborating institution incurs expenses in advance of payment • Claims sent to prime institution reporting on actual expenditures incurred • Prime institution issues payments based on real costs incurred • Common for non-Tri-Agency funding (US Federal, etc.) Generally, the method of payment from the Originating Sponsor dictates the method of payment on subawards. Subaward – Options Annual (Issued by RFMS and OSR) • Instalments are confirmed via an agreement issued annually • PI must contact OSR/RFMS each year to request amendment/agreement • OSR/RFMS must issue and execute an amendment/agreement each year confirming the next instalment • Total Project Period can be noted on the face page of the subaward (confirms end date for use of funds) but allocates budget one year at a time Multi-year (Issued by OSR only) • One agreement is executed, covering all years of the project • If paid via accountable advances, PI must notify RFMS Financial Administrator each year to prompt issuance of the next payment • Amendments may be issued to modify award parameters as required OSR issued subawards Fund created for prime award McGill researcher must contact OSR requesting the subaward Awards OSR assesses the request and follows up with PI Subaward negotiation phase Draft Subaward agreement sent to PI then to collaborating institution for review Awards OSR begins preparing Subaward agreement Subaward executed Agreement uploaded into Agreements tab of InfoEd and sent to RFMS for action RFMS either issues payment (for advances); OR, encumbers the amount subawarded (for cost reimbursement) RFMS issued subawards PI requests Subaward via email to financial administrator Financial Administrator assesses eligibility of institution and availability of funds Letter of Transfer prepared by RFMS Payment issued following receipt of signed copy Fully signed letter uploaded into InfoEd Letter of Transfer issued to recipient institution PI notified when payment is issued RFMS sends reminders to recipient institution for annual financial statement RFMS issues Letter of Transfer for each instalment upon request from PI When can Tri-Agency funds be Subawarded? Desired Action Transfer of funds to Co-investigator Transfer of funds to Collaborator Transfer of funds to eligible team member but ineligible organization (including NGOs, international universities, etc.) Transfer of funds to ineligible organization (including NGOs, international universities, etc.) with no eligible team member Cost reimbursable agreement with ineligible Canadian organization (including affiliated hospitals) Cost reimbursable agreement with ineligible non-Canadian organization Agency Office NSERC SSHRC CIHR RFMS OSR RFMS issues to: NSERC Eligible Institutions SSHRC Eligible Institutions CIHR Eligible Institutions OSR issues to: All other institutions MANAGING INTER-INSTITUTIONAL AGREEMENTS ISSUED TO MCGILL Subawards to McGill Grant awarded to Prime Institution OSR approves the creation of the Fund per subaward parameters and notifies RFMS (see Life Cycle Presentation of Feb. 2013) Any changes to subaward parameters requires an amendment Lead PI requests subaward from their research office Subaward received at McGill Awards OSR negotiates and executes agreement Awards OSR contacts McGill researcher for required docs as may be needed (checklist, proposal, certificate) **Project Period noted on subaward dictates Fund end date** IN CONCLUSION Common delays • Research Office is not aware of the subaward. PI has not requested that the subaward be issued. • Often PIs assume that OSR/RFMS will automatically issue the subaward. We cannot proceed without written authorization from the PI. • Details are missing to complete the subaward • Recipient institution is not aware of the grant and must start building the file from scratch • Discrepancies between the expectations of the research team members (amount issued, reductions in budget, grant period, expected activities, etc.) • Activities described in the research proposal are not in line with the use of funds guidelines of the agency. Common subaward terms and conditions • Payment mechanism: Accountable Advance Cost Reimbursement • Period of Performance Single year (is it really a one year collaboration?) Multi year • Budget period confirmed (Y/N) • Carry forward from one instalment year to the next (Y/N) • Reporting deadlines • Reporting of co-investigator to PI • Financial statements/invoices/deliverables required • Flexibility of budget line items (Y/N) • Ownership of equipment confirmed Collaborating institution Prime institution • Audit requirements • Record retention guidelines • Audit required Thank you! Questions?


![[Date] Tolif Hunt Grants and Contracts Administrator](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010776578_1-d1d361bf891a4262d8230dfa37d005e7-300x300.png)