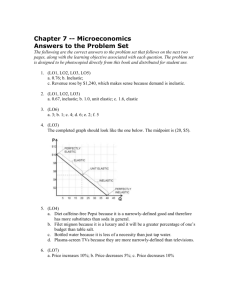
SYLLABUS AUTUMN
advertisement

SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 SYLLABUS Against each content of the syllabus, the given number shows the level of understanding expected by the Institute. The levels are explained as under: Level 1 The competency of this level requires understanding and awareness of the subject matter and related concepts. The persons will be expected to have ability to understand the nature of basic concepts. Level 2 The competency of this level requires good understanding and detailed evaluation of the subject matter and related concepts, along with the ability to apply concepts and skills in simple professional scenario. The persons will be expected to have ability to provide reasonable justification and logical explanation to support their professional judgment and decision making. Level 3 The competency of this level requires in-depth understanding of the subject matter and related concepts. The person will be expected to have ability to critically examine and evaluate all concepts and available information to make firm professional judgments and make decisions. TABLE OF CONTENTS Syllabus Page No. ASSESSMENT OF FUNDAMENTAL COMPETENCIES AFC-1 FUNCTIONAL ENGLISH 1 AFC-2 BUSINESS COMMUNICATION 3 AFC-3 QUANTITATIVE METHODS 6 AFC-4 INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY 13 CERTIFICATE IN ACCOUTNING AND FINANCE CAF-1 INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTING 18 CAF-2 INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS AND FINANCE 24 CAF-3 BUSINESS LAW 29 CAF-4 BUSINESS MANAGEMENT AND BEHAVIORAL STUDIES 37 CAF-5 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING AND REPORTING I 44 CAF-6 PRINCIPLES OF TAXATION 48 CAF-7 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING AND REPORTING II 53 CAF-8 COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING 58 CAF-9 AUDIT AND ASSURANCE 64 PCSC-01 PRESENTATION AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS COURSE - I 75 PCSC-02 PRESENTATION AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS COURSE - II 76 AFC-1 ASSESSMENT OF FUNDAMENTAL COMPETENCIES *FUNCTIONAL ENGLISH Objective To ensure that candidates can communicate effectively in the English language. Learning Outcome On the successful completion of this paper candidates will be able to: 1 use a range of vocabulary correctly 2 construct sentences using correct grammar 3 demonstrate the ability of speed reading and comprehension. Grid Weighting Vocabulary 15-20 Practical use of Grammar 20-25 Comprehension and Speed reading (General) 10-15 Total Syllabus Ref A Contents Level 50 Learning Outcome English Vocabulary 1 B Meanings and application of vocabulary listed on: a: “The Oxford 3000- Seventh Edition”, and b: Any other list as the Institute may provide at any time before the conduct of Examination. 3 LO1.1.1: Comprehend the role that language plays in different contexts LO1.1.2: Identify the correct meaning of the word and use synonyms or antonyms for the given words in a sentence LO1.1.3: Construct meaningful sentences using the prescribed word list. Practical use of Grammar 1 Parts of speech 3 LO2.1.1: Suggest the use of verb, adverb, noun, pronoun, adjective, preposition, conjunction and interjection in constructing sentences. 2 Rules of sentences 3 LO2.2.1: Understand and determine declarative, interrogative, imperative, exclamatory and optative sentences LO2.2.2: Understand and identify simple, compound, complex, multiple and conditional sentences. 3 Phrases and idioms SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 3 LO2.3.1: Construct meaningful sentences using commonly used phrases and idioms. 1 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome 4 Tenses 3 LO2.4.1: Understand and apply rules of tenses in sentences. 5 Direct and indirect speech 3 LO2.5.1: Understand the difference between direct and indirect speech. LO2.5.2: Use direct speech with the correct punctuations and various reporting verbs LO2.5.3: Identify the changes incidental to the transformation of direct speech to indirect speech. 6 Active and passive voice 3 LO2.6.1: Change the active voice to passive voice and passive voice to active voice. 7 Punctuation 3 LO2.7.1: Determine the appropriate use of capital letter, question mark, exclamation mark, full stop, semi-colon, comma, colon, apostrophe, quotation marks, brackets, dash, hyphen, ellipsis. Comprehension and Speed reading (General) C 1 Comprehension 3 LO3.1.1: Comprehend a brief write up and answer questions based on that write up 2 Speed reading 3 LO3.2.2: Assimilate the key contents of a lengthy write up and answer questions based on that write up. Note: *Syllabus has been revised in 264th meeting of the Council held on May 8th and 9th, 2015. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 AFC-2 ASSESSMENT OF FUNDAMENTAL COMPETENCIES *BUSINESS COMMUNICATION Objective To ensure that candidates can communicate effectively while performing their professional responsibilities. Learning Outcome On the successful completion of this paper candidates will be able to: 1 comprehend concepts of business communication 2 demonstrate awareness of intra-personal and interpersonal skills 3 understand formats of basic business messages and message-writing etiquette 4 understand the utility of the internet with respect to business communication. Grid Weighting Concepts 10-15 Intra-personal and Interpersonal skills 20-25 Communication via the internet 10-15 Total Syllabus Ref A 1 2 Contents Business Communication Concepts Introduction to business communication Communication process Level 3 2 50 Learning Outcome LO1.1.1: Define business communication LO1.1.2: Describe with simple examples the goals, patterns (formal and informal), and channels of business communication. LO1.2.1: Define “communication process” LO1.2.2: Explain and illustrate the components of the communication process, namely: context, sender, message, medium, recipient and feedback LO1.2.3: Identify the information needs of the organization and its sources, levels and usefulness for effective communication LO1.2.4: Explain with simple examples the barriers to effective communication LO1.2.5: Describe different methods of communication and also state its appropriate medium SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 3 Syllabus Ref 3 B 1 2 Contents Seven C’s of effective communication Intra-personal and inter-personal skills Nature of Intra-personal communication Nature of Interpersonal communication Level 3 Learning Outcome LO1.2.6: Classify different types of communication networks and describe their influence on the communication process within an organization. LO1.3.1: Describe with simple examples the seven C’s of effective communication LO1.3.2: Identify weaknesses in a given simple communication process applying the Seven C’s concept and suggest corrections. 3 3 LO2.1.1: Develop an awareness and appreciation of the importance of intrapersonal communication LO2.1.2: Identify the basic aspects of intra-personal communication including self-concept, perception and expectation. LO2.2.1: Identify the axioms of interpersonal communication LO2.2.2: Specify the purposes of interpersonal communication LO2.2.3: Determine the role of stereotypes in the communication process LO2.2.4: Identify the role of communication conflict in intercultural relationships LO2.2.5: Explain the key ways to improve interpersonal skills 3 4 5 Critical Thinking Non-verbal communication Verbal communication 3 3 3 LO2.2.6: Identify the elements and traits of ethics in interpersonal communication. LO2.3.1: Explain the difference between creative thinking and critical thinking LO2.3.2: Assess the effect of critical thinking over communication. LO2.4.1: Identify forms of non-verbal communication including facial expressions, posture, gestures, eye contact, voice and touch LO2.4.2: Explain the uses of non-verbal messages. LO2.5.1: Contrast between oral and written communication LO2.5.2: Explain and account for the basic forms of oral communication including; face to face communications, interviews, telephone conversations, grapevine, negotiations, meetings, lecture/speech. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 4 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO2.5.3: Contrast between speaking and listening skills LO2.5.4: Develop a personal, constructive approach to dealing with conflict situations though speech communication strategies of conflict resolution LO2.5.5: Explain the principles of preparing and delivering an effective public speech LO2.5.6: Explain the importance of listening in effective business communication 6 Visual communication 2 7 Written Communication 3 LO2.5.7: Describe types and barriers to listening. LO2.6.1: Assess the role of visual communication in simplifying and comparing information and illustrating trends and ideas. LO2.7.1: Classify the types of business letters and circulars LO2.7.2: Determine the qualities of an effective letter and circular LO2.7.3: Describe the different components of business letter LO2.7.4: Explain the salient features of the persuasive letters and circulars LO2.7.5: State the meaning and purpose of a short business report LO2.7.6: Describe the contents of a business report LO2.7.7: Differentiate between different types of reports C LO2.7.8: Explain the contents of different types of reports. 1 Communication via the internet Website hosting (types and services) 1 2 Types of electronic communication 2 LO3.1.1: State meaning, types and services of web hosting. LO3.2.1: Explain the main features and practical use of social networking forums, blogs, podcasting, discussion boards, messaging, video conferencing and email LO3.2.2: Discuss the benefits and limitations of various types of electronic communication. Note: *Syllabus has been revised in 264th meeting of the Council held on May 8th and 9th, 2015. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 5 AFC-3 ASSESSMENT OF FUNDAMENTAL COMPETENCIES QUANTITATIVE METHODS Objective To develop the ability to apply quantitative methods and statistics to business problems. Learning Outcome On completion of this paper the candidate will be able to: 1 understand basic mathematics to build a base for financial analysis and transform business problems into mathematical equations 2 apply financial mathematics to solve business problems 3 analyse business solutions and identify feasible, alternative optimum and unbounded solutions using graphical methods 4 evaluate maximised profit, minimised cost and feasible manufacturing quantity by using calculus 5 analyse production planning cases and formulate solutions using matrices 6 present collected data using diagrams, charts and graphs and evaluate common measures of dispersion and central tendencies 7 evaluate the impact of inflation and rebase numbers using indices 8 use statistical methods in analyzing historical data for decision making and estimating future outcomes 9 explain and apply probability theory 10 explain sampling and explain and carry out tests of significance. Grid Weighting Mathematics Basic mathematics 10-15 Financial mathematics 15-25 Calculus 10-15 Matrices and determinants 10-15 Statistics Statistical methods 20-25 Methods of least square and regression 5-10 Probability and probability distribution 5-10 Sampling and decision making 5-10 Total SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 100 6 Syllabus Ref Contents A Mathematics a Basic mathematics 1 Exponential and logarithmic functions Level 2 Learning Outcome LO1.1.1: Demonstrate adequate knowledge of laws of logarithm LO1.1.2: Make use of logarithms in solving business problems LO1.1.3: Perform calculations involving exponential and logarithmic functions LO1.1.4: Analyse the behaviour of business problems involving exponential and logarithmic functions. 2 Equation of straight line 2 LO1.2.1: Demonstrate adequate understanding of various forms of the equation of a straight line. 3 Application of straight line in business and economics 2 LO1.3.1: Identify business situations where the equation of a straight line could be used LO1.3.2: Use the equation of a straight line in relevant business problems. 4 Simultaneous equation- linear and quadratic 2 LO1.4.1: Demonstrate adequate command of solving simple equations, including two variable simultaneous equations and quadratic equations. 5 Coordinate system 2 LO1.5.1: Demonstrate understanding of the coordinate system and be able to prepare graphs of linear equations. 6 System of linear inequalities and their graphical presentation 2 LO1.6.1: Demonstrate an understanding of linear inequalities LO1.6.2: Demonstrate the graphical presentation of linear inequalities. 7 Factorisation of equations including factorisation by completion of squares 2 LO1.7.1: Perform multiplication and division operations on linear and quadratic equations LO1.7.2: Solve quadratic equations by factoring and by completing the square method. 8 Arithmetic progression 2 LO1.8.1: Identify situations where data is in arithmetic progression LO1.8.2: Use arithmetic progression in business problems to calculate monthly instalments, first instalment, total amount paid and total time required for settlement of a loan etc. 9 Geometric progression SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO1.9.1: Use geometric progression in relevant situations. 7 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome b Financial mathematics 1 Simple interest 2 LO2.1.1: Calculate interest value using simple interest. 2 Compound interest 2 LO2.2.1: Calculate interest value using compound interest. 3 Present value 2 LO2.3.1: Calculate the present value of a future cash sum using both a formula and tables LO2.3.2: Calculate the net present value (NPV) of a project LO2.3.3: Use NPVs to choose between mutually exclusive projects.. 4 Future values 2 LO2.4.1: Calculate future values using both simple and compound interest. 5 Annuities 2 LO2.5.1: Calculate the present value of an annuity using both a formula and tables. 6 Internal rate of return 2 LO2.6.1: Explain with examples the use of the internal rate of return of a project. 7 Interpolation and perpetuities 2 LO2.7.1: Calculate the present value of perpetuity. c Linear programming 1 Graphical solution to linear programming problems involving redundant constraints, bounded and unbounded feasible regions, no feasible solution and alternative optimum solution 2 LO3.1.1: Demonstrate adequate expertise in transforming a business problem into a system of linear programming LO3.1.2: Identify constraints and cost minimization or profit maximization functions LO3.1.3: Identify the redundant constraint LO3.1.4: Use the Corner Point Theorem LO3.1.5: Prepare a graphical solution of a linear programming problem LO3.1.6: Analyse a graphical solution and identify whether it has a bounded or an unbounded feasible region or no feasible solution at all LO3.1.7: Analyse the solution of a linear programming problem and identify alternative and optimum solutions, if any exist. d Calculus 1 Rules for differentiation- Sum, difference, product and quotient rules of differentiation 2 LO4.1.1: Demonstrate an adequate understanding of rules of differentiation. 2 Marginal function, calculation of revenue, cost and profit of marginal unit 2 LO4.2.1: Make use of differentiation techniques in determining marginal functions SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 8 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO4.2.2: Calculate revenue, cost and profit of a marginal unit using differentiation techniques. 3 Use of second order derivatives; maxima, minima and point of inflexion. e Matrices and determinants 1 Fundamentals of matrices, addition, subtraction, multiplication, inverse of matrices 2 LO4.3.1: Demonstrate the application of second order derivatives in calculating maxima, minima and the point of inflexion. 2 LO5.1.1: Demonstrate an adequate knowledge of matrix algebra (addition, subtraction and multiplication) LO5.1.2: Calculate the determinant, adjoint and inverse of a matrix LO5.1.3: Make use of the properties of determinants while calculating determinants. 2 B Solution of simultaneous linear equations using Cramer’s Rule and Matrix Inverse Method 2 LO5.2.1: Represent simultaneous linear equations in matrix form LO5.2.1: Solve simultaneous linear equations using Cramer’s Rule and Matrix Inverse Method. Statistics a Presentation and use of data 1 Collection and tabulation of data 2 LO6.1.1: Classify different types of data LO6.1.2: Perform data collection through various methods LO6.1.3: Organise and summarise data and present it as a frequency distribution. 2 Presentation through graphs, charts and diagrams, including stem and leaf display, box and whisker plot 2 LO6.2.1: Present data using a simple bar chart, a multiple bar chart and a component bar chart LO6.2.2: Construct pie charts, histograms, frequency polygons, ogives, stem and leaf displays and box and whisker plots LO6.2.3: Analyse graphical representations of data. 3 Measures of central tendencies and measures of dispersions 2 LO6.3.1: Calculate various measures of central tendency such as mode, median, arithmetic, geometric and harmonic means LO6.3.2: Analyse the advantages and disadvantages of various central tendency measures LO6.3.3: Identify the characteristics and measures of dispersion SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 9 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO6.3.4: Use measures of dispersion, such as standard deviation or variance, to ascertain the degree of variation or variability in a distribution. b Index numbers 1 Index numbers, weighted index numbers, concept of purchasing power and deflation of income 2 LO7.1.1: Define the index number and its types LO7.1.2: Use different formulae/methods to calculate various types of index number LO7.1.3: Analyse the uses and limitations of index numbers. For example, use index numbers to deflate or inflate a series and explain the result. c Methods of least square and regression 1 Scatter diagram, linear relationship, simple linear regression lines by method of least square 2 LO8.1.1: Demonstrate an understanding of scatter diagrams, including their construction, uses and limitations LO8.1.2: Demonstrate an understanding of the basic concept of regression lines and how they are used LO8.1.3: Use least squares linear regression to construct a regression line (line of best fit) LO8.1.4: Analyse regression lines LO8.1.5: Use a regression line to calculate a forecast of the value of a dependent variable where given the value of an independent variable. 2 Simple linear correlation 2 LO8.2.1: Demonstrate an understanding of the basic concept of correlation coefficient analysis. 3 Coefficient of correlation and determination 2 LO8.3.1: Calculate and analyse coefficients of correlation and determination. 4 Rank correlation 2 LO8.4.1: Define rank correlation LO8.4.2: Calculate the rank correlation coefficient between two sets of data and explain the value. d Probability and probability distribution 1 Counting techniques 2 LO9.1.1: Use counting techniques, like the mn counting rule and factorials for calculating, for example, a total number of outcomes LO9.1.2: Use permutations and combination to calculate the total number of possible selections from a set of data. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 10 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome 2 Probability 2 LO9.2.1: Understand the definition of probability and other basic terms as well as their applications. 3 Addition law for mutually exclusive and not mutually exclusive events 2 LO9.3.1: Use the addition rule while calculating probabilities LO9.3.2: Identify the difference between mutually exclusive and non-mutually exclusive events. 4 Multiplicative laws for dependent and independent events 2 LO9.4.1: Identify the difference between dependent and independent events LO9.4.2: The use of multiplication rule while calculating conditional probabilities. 5 Binomial distribution 2 LO9.5.1: Account for the assumptions that underlie the Binomial distribution LO9.5.2: Demonstrate the use of Binomial distribution to calculate probabilities. 6 Poisson distribution 2 LO9.6.1: Account for the properties of the Poisson distribution LO9.6.2: Demonstrate the use of the Poisson distribution to calculate probabilities. 7 Hyper-geometric distribution 2 LO9.7.1: Identify situations where Hypergeometric distribution could be used LO9.7.2: Demonstrate the use of Hypergeometric distribution to calculate probabilities. 8 Normal distribution 2 LO9.8.1: Demonstrate the use of normal distribution including the use of tables LO9.8.2: Demonstrate the application of the normal distribution to calculate probabilities. e Sampling and decision making 1 Simple random sampling 2 LO10.1.1: Understand the terms, population and sample LO10.1.2: Explain methods for selecting a simple random sample. 2 Sampling distribution of mean 2 LO10.2.1: Define and construct a sampling distribution of the sample means LO10.2.2: Calculate the mean and standard deviation of a sampling distribution of sampling means. 3 Standard error of mean 2 LO10.3.1: Calculate standard error of mean. 4 Sampling with and without replacement 2 LO10.4.1: Select an appropriate sampling technique for calculating the probabilities of sample means. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 11 Syllabus Ref 5 Contents Testing of hypothesis for population means, difference between population means and population proportion and difference between two population proportions Level 2 Learning Outcome LO10.5.1: Demonstrate the use of hypothesis testing, significance testing and testing a hypothesis LO10.5.2: Perform hypothesis test of populations means based on small and large samples LO10.5.3: Perform hypothesis tests of the difference between two population means based on small and large samples LO10.5.4: Perform hypothesis tests of the difference between two population proportions LO10.5.5: Select appropriate distributions i.e., z or t for constructing a confidence interval for a population mean. 6 Single population variance based on test of Chi-square. 2 LO10.6.1: Use the Chi-square distribution to perform tests of goodness of fit and independence. 7 Confidence interval for estimating population means, proportions and variance, and differences between proportions means, proportions and variance. 2 LO10.7.1: Construct the confidence interval for population means and difference of means Problems of determination of sample size for the study of population mean and proportion. 2 8 SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 LO10.7.2: Construct the confidence interval for population means and difference of proportion and variance. LO10.8.1: Calculate a sample size for an interval estimate of a population mean LO10.8.2: Calculate a sample size for an interval estimate of a population proportion. 12 AFC-4 ASSESSMENT OF FUNDAMENTAL COMPETENCIES INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Objective To enable candidates to equip themselves with the fundamental skills and proficiency required to cope with today’s highly challenging IT oriented business environment. Learning Outcome The candidates will be able to: 1 describe and classify different elements of a computer system 2 describe the basic operations in commonly used operating systems 3 demonstrate performance level knowledge in Microsoft Excel 4 demonstrate performance level knowledge in Microsoft Word 5 demonstrate performance level knowledge in Microsoft PowerPoint. Grid Weighting Computer hardware and types of operating system 3-6 Microsoft Excel 18-22 Microsoft Word 12-18 Microsoft PowerPoint 8-12 Total Syllabus Ref Contents A Computer hardware and operating systems Level Learning Outcome 50 1 Central processing units (CPUs) – processor, hard disk, random access memory, read-only memory 1 LO1.1.1: Explain the role and importance of basic components of a CPU. 2 Input devices – Key board, mouse, touch pads, magnetic ink character reader, optical mark reader, optical character reader, barcode reader and electronic point of sale. 1 LO1.2.1: State the uses/benefits and limitations of common input devices. 3 Output devices – monitor, printer 1 LO1.3.1: State the differences between CRT and LCD/LED monitors LO1.3.2: Classify different types of printers and state their relative advantages and limitations. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 13 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome 4 Operating systems – DOS, Windows, Linux 1 LO1.4.1: State key operating system commands used for efficient searches, formatting disks, viewing IP configurations, testing network connections and exploring the network. 5 Core Windows tasks – customize desktop and start menus, work with files and folders, log-on and log-off, search for information, lock the computer, use a screen-saver password, reset a password 1 LO1.5.1: State methods for customizing desktop presentation and the start menu LO1.5.2: Define techniques to work efficiently with files and folders LO1.5.3: State efficient ways to search for required information from active and archive files LO1.5.4: State the important information that could be recorded whilst a user is logged-in LO1.5.5: Define basic controls and practices that should be adopted by users for safeguarding data stored in computers. B Microsoft Excel 1 Construction of formulae and application of constructed and built-in functions and formulae 2 LO2.1.1: Show clear understanding of options in the menu bar like File, Home, Insert, Page layout, Formulas, Data, Review and View LO2.1.2: Demonstrate how to construct formulae using functions, cell references, constants and operators LO2.1.3: Demonstrate how to construct nested formulae LO2.1.4: Demonstrate adequate command and ability to use the functions like Sum, Sumif, Trunc, Subtotal, Round, Floor, Ceiling, int, Mod, Abs, Average, Count, CountA, Countif, Max, Min, Median, Stdev.S,Percentile, Rank, IRR, Rate, Effect, PV, NPV, SLN, Yield, PMT, ACCRINT, ACCRINTM, COUPDAYS, CUMPRINC, Vlookup, Hlookup, IF, IFERROR, NOT, AND, OR, ISBLANK, ISERR, ISERROR, ISLOGICAL, ISNA, ISNUMBER, ISTEXT, ISNONTEXT, ISREF, Exact, Trim, Left, Right, Len, Lower, Upper, Mid, Proper, Text, Today, Now, Weekday and Weeknum. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 14 Syllabus Ref 2 Contents Creating and modifying customized data formats Level Learning Outcome 2 LO2.2.1: Show how to use multiple worksheets, and navigate, select, rename, insert, delete, move, copy and print worksheets LO2.2.2: Demonstrate how to move and copy data between worksheets and sort, filter, find, replace data and its formatting as required LO2.2.3: Use appropriate Excel features to create customized data formats LO2.2.4: Modify existing data formats to enhance readability. 3 Using conditional formatting 2 LO2.3.1: Use the conditional formatting feature to highlight exceptions LO2.3.2: Demonstrate the use of Conditional Formatting Rules Manager. 4 Protecting cells, worksheets and workbook 2 LO2.4.1: Perform the steps to protect certain cells, individual worksheets and an entire workbook LO2.4.2: Demonstrate the use of Digital Signature. 5 Merging workbooks 2 LO2.5.1: Perform the steps to share a workbook LO2.5.2: Perform the steps to merge multiple copies of a shared workbook. 6 Importing and exporting data to and from Excel 2 LO2.6.1: Demonstrate ability to store data directly in an Excel workbook or in an external data source LO2.6.2: Demonstrate basic understanding of creating, editing, refreshing and finding data connections in Excel LO2.6.3: Demonstrate adequate command on importing data to Excel from other applications and data sources LO2.6.4: Demonstrate adequate command on exporting data from Excel to other applications and data sources. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 15 Syllabus Ref 7 Contents Creating and editing charts and templates Level 2 Learning Outcome LO2.7.1: Show how to insert/create, move and resize charts LO2.7.2: Demonstrate command on formatting and changing chart types LO2.7.3: Demonstrate adequate knowledge in creating and editing Excel templates. C Microsoft Word 2010 1 Creating custom style for text, tables and lists 2 LO3.1.1: Show clear understanding of options in the menu bars like File, Home, Insert, Page Layout, References, Mailings, Review and View LO3.1.2: Use various Word features to present letters, reports and other documents in a presentable custom style LO3.1.3: Demonstrate adequate command on using Mail Merge feature to create letters, envelopes, directory etc. 2 Creating and modifying tables 2 LO3.2.1: Demonstrate command on inserting/creating tables and making use of pre-defined table style for improved presentation LO3.2.2: Demonstrate command on editing tables and use of formatting tools to improve readability of data in tables LO3.2.3: Demonstrate the use of formulas in tables LO3.2.4: Use Word’s built-in features to sort contents saved in tables. 3 Creating and modifying a table of contents 2 LO3.3.1: Identify the basic formatting requirements to insert a table of contents LO3.3.2: Demonstrate performance level knowledge to insert and modify a table of contents. 4 Use of Review and Reference tab commands 2 LO3.4.1: Demonstrate the ability to make effective use of Track Changes command LO3.4.2: Demonstrate performance level knowledge to insert and modify bibliography, endnotes, footnotes, captions, comments & cross references. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 16 Syllabus Ref Contents D Microsoft PowerPoint 1 Creating new presentations from templates Level 2 Learning Outcome LO4.1.1: Select a template from PowerPoint’s sample templates to construct simple presentations LO4.1.2: Demonstrate performance-level knowledge of working with Slide Masters and Layouts. 2 Inserting and editing text-based content 2 LO4.2.1: Perform inserting and editing of text based content. 3 Inserting, and editing tables, charts, diagrams, pictures, shapes, graphs and objects 2 LO4.3.1: Demonstrate performancelevel knowledge of inserting and editing tables, charts and other objects in the presentation LO4.3.2: Use appropriate PowerPoint features to insert and edit pictures, videos, charts/graphs and other objects in the presentation. 4 Running and printing presentations 2 LO4.4.1: Demonstrate performance-level knowledge whilst applying meaningful slide transitions LO4.4.2: Demonstrate performance-level knowledge whilst setting up slide shows, recording slide shows, starting slide show from beginning or from current slide, broadcasting slide show and creating custom slide shows LO4.4.3: Demonstrate performance-level knowledge whilst printing Notes Pages, Hand outs and Slides. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 17 CAF-1 Certificate in Accoutning and Finance INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTING Objective To enable candidates to equip themselves with the fundamental concepts of accounts needed as a foundation for higher studies of accounting. Learning Outcome On the successful completion of this paper candidates will be able to: 1 understand the nature of accounting, elements of accounts and double entry rules 2 identify financial transactions and make journal entries 3 prepare general ledger accounts and a trial balance 4 make period end adjustments prior to the completion of financial statements 5 prepare basic financial statements 6 prepare partnership accounts and account for transactions of admission, retirement etc. Grid Weighting Introduction to accounting and book keeping 35-40 Adjustments prior to completion of financial statements 15-25 Preparation of final accounts of sole traders 15-25 Accounting for partnerships 15-25 Total Syllabus Ref Contents A Introduction to accounting and book keeping a Introduction to accounting 1 Meaning of business Level 1 100 Learning Outcome LO1.1.1: Explain the characteristics of a business LO1.1.2: Classify transactions that fall under the definition of business transactions. 2 Mode of business organization (meaning) - sole proprietorship; partnership; limited company 1 LO1.2.1: Describe the key features of sole proprietorship, partnership and limited company LO1.2.2: Differentiate amongst the features of sole proprietorship, partnership and limited company. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 18 Syllabus Ref 3 Contents Fundamental accounting concepts accrual, consistency, true and fair view, materiality, prudence, completeness, going concern, substance over form Level 2 Learning Outcome LO1.3.1: Explain the difference between book-keeping and accounting LO1.3.2: Describe and illustrate the main accounting concepts, namely, accrual, consistency, and completeness LO1.3.3: Demonstrate familiarity with the concepts of true and fair view, materiality, prudence, going concern and substance over form LO1.3.4: Apply the concepts of accrual, consistency and completeness to simple and well explained circumstances. 4 Financial statements- components, responsibility, presentation, users 1 LO1.4.1: List the components of a set of financial statements LO1.4.2: Explain the characteristics and purpose of the statement of financial position and the statement of comprehensive income LO1.4.3: Identify the responsibility to prepare and present financial statements LO1.4.4: Describe the basic presentation layout of statements of financial position and statements of comprehensive income LO1.4.5: Identify users of financial information and describe how the information is useful to them. b Bookkeeping 1 Elements of financial statements (meaning) - Assets, liabilities, equity, income, expense 2 LO2.1.1: Define and give examples of assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses LO2.1.2: Apply the underlying concepts of assets, liabilities, income and expenses in simple and well explained circumstances. 2 Chart of accounts 1 LO2.2.1: Understand the meaning of a chart of accounts LO2.2.2: Explain the purpose of establishing a chart of accounts LO2.2.3: Construct a chart of accounts using given data. 3 Double entry system, accounting equation and rules of debit and credit 2 LO2.3.1: Understand and apply, the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) in simple practical and common scenarios LO2.3.2: Identify financial and nonfinancial transactions in a well-defined scenario SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 19 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO2.3.3: Understand and apply the concept of double entry accounting to simple and common business transactions. 4 General journal 2 LO2.4.1: List and describe the basic contents of the general journal LO2.4.2: Prepare and use the general journal to record journal entries. 5 Sales journal and the sales ledger 2 LO2.5.1: Understand the use of business documents as source of information LO2.5.2: Describe the basic contents of the sales day book and the customer/ debtors ledger LO2.5.3: Record entries in the sales day book and the customer/debtors ledger. 6 Purchase journal and the purchase ledger 2 LO2.6.1: Describe the basic contents of the purchase journal and purchase ledger/creditors ledger LO2.6.2: Record entries in the purchase journal and purchase ledger/creditors ledger. c General ledger and trial balance 1 General ledger 2 LO3.1.1: Describe the main features of the general ledger LO3.1.2: Post entries in the general ledger LO3.1.3: Balance the ledger accounts as required, make transfers to the final accounts. 2 Trial balance 2 LO3.2.1: Understand the purpose of the trial balance LO3.2.2: Understand and demonstrate mapping between general ledger balances and the trial balance LO3.2.3: Identify the limitations of a trial balance. B Adjustments before final accounts 1 Straight line, diminution balance, sumof-years-digit, number of units produced methods and recording of depreciation on fixed Assets 2 LO4.1.1: Explain nature of depreciation expense and accumulated depreciation LO4.1.2: Calculate depreciation expense using straight line, diminution balance, sum-of-digits and number of units produced methods LO4.1.3: Post journal entry to record depreciation expense. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 20 Syllabus Ref 2 Contents Allowance for bad debts and write off Level 2 Learning Outcome LO4.2.1: Estimate allowance for bad debts based on a given policy LO4.2.2: Post journal entry to record bad debt expense LO4.2.3: Compute and record write off and understand its impact on allowance for bad debts. 3 Prepayments and accruals 2 LO4.3.1: Understand the matching concept that applies to prepayments and accruals LO4.3.2: Post journal entries and ledger entries for prepayments and accruals LO4.3.3: Post adjusting entries to recognize revenues or expenses. 4 Closing entries of inventory 2 LO4.4.1: Understand the concepts of periodic and perpetual inventory system LO4.4.2: Identify the need to post the adjustment entries of inventory at the end of the period in case of periodic inventory system LO4.4.3: Pass the adjusting entries and ledger entries at the end of the period. 5 Bank reconciliation and related adjustments 2 LO4.5.1: Understand the need for a bank reconciliation LO4.5.2: Identify the main reasons for differences between the cash book and bank statements LO4.5.3: Prepare a bank reconciliation statement in the circumstances of simple and well explained transactions LO4.5.4: Correct cash book errors and post journal entries after identifying the same in bank reconciliation statement. 6 Control accounts - reconciliation and adjustments 2 LO4.6.1: Understand the mapping between control accounts and subsidiary ledger for accounts receivable and accounts payable LO4.6.2: Prepare control accounts and subsidiary ledger from well explained information provided LO4.6.3: Perform control accounts reconciliation for accounts receivable and accounts payable LO4.6.4: Identify errors after performing reconciliation LO4.6.5: Identify and correct errors in control account and subsidiary ledgers. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 21 Syllabus Ref 7 Contents Correction of errors in record keeping Level Learning Outcome 2 LO4.7.1: Identify the types of error which may occur in a record keeping system LO4.7.2: Calculate and understand the impact of errors on the financial statements within a reporting period LO4.7.3: Prepare journal entries to correct errors that have occurred within a reporting period. C Preparation of final accounts of a sole trader 1 Statement of financial position 2 LO5.1.1: Explain the difference between a trading and a service business LO5.1.2: Understand the purpose of the statement of financial position LO5.1.3: Prepare simple statements of financial position from information provided. 2 Statement of comprehensive income 2 LO5.2.1: Understand the purpose of the statement of comprehensive income LO5.2.2: Prepare simple statements of comprehensive income from information provided. 3 Receipt and payment accounts 2 LO5.3.1: Understand the purpose of a receipts and payments account LO5.3.2: Prepare a simple receipts and payments account from information provided. D Accounting for partnerships 1 Preparation of partnership accounts 2 LO6.1.1: Define a partnership and state its essential elements LO6.1.2: Understand goodwill LO6.1.3: Prepare • Capital account • Current account LO6.1.4: Prepare a profit and loss account and a statement of financial position of a partnership. 2 Admission and amalgamation SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO6.2.1: Process the necessary adjustments on the admission of a new partner, namely: • Revaluation of assets and liabilities of the firm • Treatment of goodwill • Application of new profit sharing ratio 22 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO6.2.2: Prepare the nominal accounts, profit and loss account and statement of financial position upon amalgamation of two partnerships. 3 Retirement, death, dissolution, liquidation 2 LO6.3.1: Make journal entries in the case of the dissolution of a partnership to record: • transfer and sale of assets and liabilities to third parties and partners • payment of realization expenses • closing of the realization account and • settlement of partners’ capital account. LO6.3.2: Process the necessary adjustments on the death or retirement of a partner: SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 • adjustments relating to goodwill, accumulated reserves and undistributed profits • revaluation account • adjustment and treatment of partners’ capital • application of new profit sharing ratio 23 CAF-2 Certificate in Accoutning and Finance INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS AND FINANCE Objective To enable candidates to equip themselves with the fundamental concepts of economics and finance needed as foundation for higher studies of finance. Learning Outcome The candidate will be able to: 1 understand the nature of micro-economics and its basic concepts. 2 understand the nature of macro-economics and its relation with the measurement of economic growth. 3 understand how the balance of payments of a country is worked out. 4 understand the nature of banking systems 5 understand the basic function of financial markets. Grid Weighting Concepts of economics 5-10 Microeconomics 25-35 Macroeconomics 25-35 Introduction to banking system, financial markets and international trade 25-35 Total Syllabus Ref A Contents Level 100 Learning Outcome Concepts of economics 1 The economic problem - wants, resources, scarcity 1 LO1.1.1: Understand the fundamental nature of economics LO1.1.2: Describe the scope and objectives of economics LO1.1.3: Describe, with examples, the concept of economic problem and its implications for an economy LO1.1.4: Explain with examples the four factors of production LO1.1.5: Discuss the production possibility curve and its relevance to the concept of opportunity cost. 2 Economic systems - planned, market and mixed economies 1 LO1.2.1: Describe the major functions of an economic system LO1.2.2: Explain the salient features of planned, mixed and market economies SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 24 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO1.2.3: Provide examples of ,mixed, planned and market economies LO1.2.4: Describe the shortfalls of a market economy. 3 Islamic economic system 1 LO1.3.1: Describe the main features of the Islamic economic system LO1.3.2: Compare the Islamic economic system with other economic systems. B Microeconomics 1 Microeconomics – nature 2 LO2.1.1: Define micro economics and discuss its scope and limitations. 2 Demand and supply 2 LO2.2.1: Define law of demand and explain its assumptions, limitations and exceptions LO2.2.2: Define law of supply and explain its assumptions. 3 Equilibrium of demand and supply 2 LO2.3.1: Explain the determination of price by equilibrium of demand and supply LO2.3.2: Explain the effect of changes in demand and supply LO2.3.3: Discuss the determination of price of perishable and durable goods. 4 Elasticity of demand and supply 2 LO2.4.1: Describe the concept of elasticity of demand and its practical application LO2.4.2: Explain the determinants of the elasticity of demand LO2.4.3: Demonstrate the measurement of price, income, point, arc and cross elasticity of demand LO2.4.4: Describe the concept of elasticity of supply and explain the percentage and graphical methods of measurement of elasticity of supply LO2.4.5: Describe the determinants of supply elasticity. 5 Utility analysis and indifference curve 2 LO2.5.1: Explain the law of diminishing marginal utility and discuss its assumptions and limitations LO2.5.2: Explain the law of equi-marginal utility LO2.5.3: Discuss the meaning and characteristics of indifference curves LO2.5.4: Explain consumers’ equilibrium through indifference curve analysis. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 25 Syllabus Ref 6 Contents Cost and revenue curves Level Learning Outcome 2 LO2.6.1: Discuss short run curves of total cost, total fixed cost, total variable cost, average cost and marginal cost LO2.6.2: Derive a long run average cost curve from a short run average cost curve LO2.6.3: Derive a long run marginal cost curve LO2.6.4: Discuss revenue curves under perfect and imperfect competition LO2.6.5: Discuss the concept of economies and diseconomies of scale. 7 8 Equilibrium of firm short and long term under perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly and monopolistic conditions 2 Laws of increasing and diminishing returns 2 LO2.7.1: State the features of perfect and imperfect competition LO2.7.2: Discuss the short and long run equilibrium of firms under perfect and imperfect competition. LO2.8.1: Explain the law of increasing returns and its application and assumptions LO2.8.2: Explain the law of diminishing returns and its application and assumptions. C Macroeconomics 1 Measurement of national income including knowledge of basic concepts like GDP, GNP, NNP; 2 LO3.1.1: Define macro- economics and discuss its scope and limitations LO3.1.2: Define gross national product, gross domestic product and net national product LO3.1.3: Explain the product approach, income approach and expenditure approach to the measurement of national income LO3.1.4: Explain Circular flow of Income LO3.1.5: State the difficulties usually faced in measuring National Income. 2 Consumption, saving and investment functions; 2 LO3.2.1: Understand the meaning of consumption and saving and its relationship with the income LO3.2.2: Identify how Keynes’ Psychological law of consumption explains the relationship between consumption and income with the help of average propensity to consume and marginal propensity to consume curves LO3.2.3: Understand the determinants of the consumption function SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 26 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO3.2.4: Understand the stability of consumption and saving functions in the short run and discuss the reasons thereof LO3.2.5: Understand the meaning of investment, induced investment and autonomous investment LO3.2.6: Explain the relationship of investment with marginal efficiency of capital and interest rate. 3 Marginal propensity to consume and save 2 LO3.3.1: Discuss the marginal propensity to consume and save. 4 Multiplier and accelerator; 2 LO3.4.1: Comprehend the effect of the multiplier on the level of national income LO3.4.2: Understand the assumptions and limitations of the multiplier concepts LO3.4.3: Comprehend the principle of acceleration of derived demand LO3.4.4: Understand how the multiplier and accelerator interact. 5 Money and its value 2 LO3.5.1: Understand the main functions of money LO3.5.2: Understand credit money and its advantages and disadvantages LO3.5.3: Understand sources of the money supply LO3.5.4: Understand the quantity theory of money LO3.5.5: Understand the measurement of the value of money LO3.5.6: Understand inflation, its kinds and impacts LO3.5.7: Understand the causes of inflation and measures for overcoming inflation LO3.5.8: Understand the unemployment and its types and Phillips Curve. 6 Growth and recession 2 LO3.6.1: Understand different phases of the business cycle LO3.6.2: Understand the indicators of growth and recession. 7 Fiscal budget 2 LO3.7.1: Explain the fiscal policy and its objectives and how they are achieved through fiscal budgets LO3.7.2: Discuss the limitations of fiscal policy. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 27 Syllabus Ref 8 Contents Direct and indirect taxation Level 2 Learning Outcome LO3.8.1: Define direct and indirect taxation LO3.8.2: Understand functions of taxation, types of taxes and characteristics of good tax policy LO3.8.3: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of direct taxation LO3.8.4: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of indirect Taxation. D Introduction to banking system, financial markets and international trade a Banking system 1 Credit formation by banks 1 LO4.1.1: Explain the process of creation of credit money by the banks LO4.1.2: Discuss the limitations on the creation of credit. 2 Role of Central Bank; 1 LO4.2.1: Describe the functions of a central bank. 3 Monetary policy 1 LO4.3.1: Understand the meaning of monetary policy LO4.3.2: Understand the objectives of monetary policy and the mutual conflict of the objectives. 1 LO4.4.1: Define a bank and describe its kinds. Money market 1 LO5.1.1: Describe the main features and objectives of money markets. 2 Capital markets. 1 LO5.2.1: Describe the main features and objectives of capital markets. 3 Derivative market 1 LO5.3.1: Describe the main features and objectives of derivatives and derivative markets. c International trade 1 Balance of trade and payment 2 LO6.1.1: Discuss the concept of exchange rate, its determination and government’s policy to influence it 4 Types of banks and financial institution b Financial market-Meaning 1 LO6.1.2: Understand the nature of items that are accounted for the concept of balance of trade and payment LO6.1.3: Understand the different parts of balance of payment. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 28 CAF-3 Certificate in Accoutning and Finance BUSINESS LAW Objective To give students an understanding of the legal system and commercial laws; and build a knowledge base of corporate laws. Learning Outcome The candidate will be able to demonstrate: 1 basic knowledge of the legal environment 2 comprehension of laws governing contracts, partnership and negotiable instruments 3 knowledge of the legal terminology of company law and the basics of company incorporation 4 familiarity with the provisions governing the issuance of shares 5 knowledge of the management of companies 6 familiarity with investment by companies, financial accounts and distribution of profit 7 knowledge of the appointment of auditors and their responsibilities and duties. Grid Weighting Introduction to legal system 5-10 Mercantile law Contract Act 1872 20-30 Partnership Act 1932 10-15 Negotiable Instrument Act 1881 10-15 50 Companies Ordinance 1984 Sections 1 to 51 of the Companies Ordinance, 1984 8-15 Sections 52 to 136 of the Companies Ordinance, 1984 8-15 Sections 142 to 204A of the Companies Ordinance, 1984 8-15 Sections 208 to 251 of the Companies Ordinance, 1984 8-15 Sections 252 to 257 of the Companies Ordinance, 1984 8-15 Total SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 50 29 Syllabus Ref A Contents Level Learning Outcome Introduction to the Legal System Sources and process of legislation 1 Sources of law and an introduction to the Constitution of Pakistan 1 LO1.1.1: Briefly describe sources of law in Pakistan LO1.1.2: Describe the basic structure of the constitution of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. 2 Process of legislation and legal system in Pakistan 1 LO1.2.1: Define legislation and describe its forms LO1.2.2: Briefly describe the process of legislation as per the Constitution LO1.2.3: Identify and briefly explain the structure of the courts in Pakistan. B Mercantile law a Contract Act 1872 1 All sections 2 LO2.1.1: Discuss the provisions of the act with respect to the following and demonstrate comprehension in simple scenario based problems: • communication, acceptance and revocation of proposals • contracts, voidable contracts and void agreements • contingent contracts • performance of contracts • certain relations resembling those created by contracts • breach of contract/consequences • indemnity and guarantee • bailment and pledge • contract of agency b Partnership Act 1932 1 Chapter I – Preliminary 2 LO2.2.1: Define the terms. 2 Chapter II - The nature of partnership 2 LO2.3.1: Understand and describe the partnership relationship, its creation and identify and explain the types of partnership and the mode of determining existence of a partnership. 3 Chapter III - Relations of partners to one another 2 LO2.4.1: Determine and explain the rights and duties of partners of the firm under various circumstances SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 30 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO2.4.2: Explain the provisions of the law relating to conduct of the business, property of the firm and personal profits earned by partners. 4 Chapter IV - Relations of partners to third parties 2 LO2.5.1: Describe the relationship of partners with third parties LO2.5.2: Identify and explain the concepts of implied authority of the partner in relation to third parties, partner’s authority in an emergency, mode of doing act to bind the firm, effect of admissions by a partner, effect of notice to acting partner, liability of a partner for acts of the firm and liability of the firm for wrongful acts of a partner or misapplication by partners, principle of holding out in given situations LO2.5.3: Identify and explain the rights of transferee of a partner’s interest and the rights and liabilities of a minor admitted to the benefits of partnership: c Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 1 Definitions and meanings (Section 1 to 25) 1 2 Discharge of liability (Section 82 to 90) 2 LO2.7.1: Identify and explain how the maker of a negotiable instrument is discharged from his liability under given scenarios. 3 Provisions relating to cheques (Section 122A to 131C) 2 LO2.8.1: Describe provisions relating to crossing of cheques LO2.6.1: Define and explain terms LO2.6.2: Explain provisions relating to types of negotiable instruments and their maturity. LO2.8.2: Briefly describe and differentiate between a cheque crossed generally and a cheque crossed specially and their payment modes. C Companies Ordinance 1984 a Preliminary and incorporation (Sections 1 to 51) 1 Definitions (Section 2) 1 LO3.1.1: Define the terms which are relevant to the areas covered in the syllabus. 2 Meaning of «subsidiary» and «holding company» (Section 3) 2 LO3.2.1: Explain subsidiary and holding company and when a company becomes a subsidiary or holding company of another company. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 31 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO3.2.2: Apply the concept of subsidiary in simple scenarios. 3 Powers and functions of the Commission (Section 12) 1 LO3.3.1: Demonstrate familiarity with the powers and functions of the Commission. 4 Memorandum of association (Section 15 to 25) 2 LO3.4.1: Describe the memorandum of association and state its purpose LO3.4.2: List/explain the clauses of memorandums of association of various types of companies LO3.4.3: Describe the purpose and procedure of alteration to different clauses of a memorandum of association. 5 Articles of association (Section 26) 2 LO3.5.1: Define the articles of association and state its purpose LO3.5.2: State the information which should be contained in the articles of various companies. 6 Registration of memorandum and articles of association (Section 30 to 36) 2 LO3.6.1: Describe the procedure of registration of the memorandum and articles of association LO3.6.2: Describe the effects of registration of the memorandum and articles of association. 7 Provisions with respect to names of companies (Section 37 to 41) 2 LO3.7.1: Describe with examples the procedure / prohibitions with regard to the selection of the name of a company LO3.7.2: Identify/explain the actions and procedures needed to be taken by company and registrar, if a company is registered by a prohibited name. 8 Association not for profit (Section 42) 1 LO3.8.1: Comprehend the nature of association not for profit. 9 Companies limited by guarantee (Section 43) 1 LO3.9.1: Understand the provisions regarding divisible profit and dividing the undertaking into shares or interest. b Allotment of shares, registration of charge etc. (Sections 52 to 136) 1 Prospectus, allotment, issue and transfer of shares and debentures, deposits, etc. (Section 52 to 57) 1 LO4.1.1: Define a prospectus and explain its purpose SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 LO4.1.2: Understand the requirements relating to a prospectus as laid down in Section 52, 53 (1), (5) and (8) 32 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO4.1.3 Describe the matters that are to be specified in a prospectus as required under clause 1 to 7 and 17, 18 19, 24, 26 and 27 of Section 1 of Part I of Second Schedule LO4.1.4: Describe the reports that are to be included in a prospectus as required under Section 2 of Part I of Second Schedule LO4.1.5: Understand/explain the provisions regarding statement and consent of expert. 2 Share capital and debentures (Section 89 to 95 and 108) 1 LO4.2.1: Describe the nature of shares and share certificates LO4.2.2: Describe the classes and kinds of shares LO4.2.3: Describe with simple example the condition of fully paid shares LO4.2.4: State with simple examples the kinds of alterations that can be made to the share capital. LO4.2.5: State the rules on prohibition of purchase of a company’s own or its holding company’s shares LO4.2.6: Understand the meaning of variation of shareholders’ rights LO4.2.7: Demonstrate familiarity with the procedure for cancellation of variation of shareholders’ rights. 3 Registration of mortgages, charges etc. (Section 121, 129, 132 and 136) 1 LO4.3.1: Discuss the meaning of mortgage/charge with simple examples, and the duty of company and the procedure for registration of charges LO4.3.2: State the right of an interested party in respect of a registration of mortgage/charge LO4.3.3: State the duty and procedure of payment or satisfaction of mortgage/ charge LO4.3.4: Demonstrate familiarity with the right to inspect the instrument creating a mortgage/charge LO4.3.5: Discuss the consequences of registered and unregistered mortgages/ charges. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 33 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome c Management and administration (Sections 142 to 204A) 1 Registered office, publication of names etc. (Section 142 to 145) 2 LO5.1.1: Discuss with simple examples the provisions with regard to having a registered office, publication of name and publication of paid-up capital. 2 Commencement of business by a public company (Section 146) 1 LO5.2.1: State the conditions to be fulfilled before commencement of business by a company LO5.2.2: State the applicability and nonapplicability of the conditions on different kinds of company. 3 Meeting and proceedings (Section 157 to 173) 1 LO5.3.1: State the timing, matters and reports relating to statutory meetings LO5.3.2: State the timing, matters and reports relating to an annual general meeting using simple examples LO5.3.3: State who can call an annual general meeting LO5.3.4: State the timing, matters and reports relating to an extraordinary general meeting LO5.3.5: State who can call an extraordinary general meeting LO5.3.6: State the quorum for a general meeting LO5.3.7: State the entitlement of a member in respect of appointment of proxy and conditions applicable thereon LO5.3.8: Describe the provisions relating to Agenda/ minutes of meetings. 4 Directors (Section 174 to 197A) 1 LO5.4.1: Explain and apply in given scenarios, the legal provision with respect to directors’: • Eligibility/Ineligibility • Number • Elections • Removal/Vacation of office • Remuneration • Powers, duties, rights and liabilities • Assignment of office • proceedings SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 34 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO5.4.2: State the legal provisions relating to loans to directors. 5 Chief executive (Section 198 to 204A) 1 LO5.5.1: Explain the appointment of first chief executive and subsequent chief executives using simple examples LO5.5.2: State the provisions/ conditions applicable on appointment, removal, engagement in any business LO5.5.3: State the provisions relating to appointment of a secretary. d Investments, accounts etc. (Sections 208 to 251) 1 Investment in associated companies and undertakings (Section 208) 2 LO6.1.1: Describe the conditions applicable to a company for making investment in associated companies and undertakings. 2 Investment of companies to be held in its own name (Section 209) 1 LO6.2.1: Discuss with simple examples as to how a company can hold its investment in names other than its own name. 3 Disclosure of interest by directors (Section 214) 1 LO6.3.1: Explain the requirements of disclosure of interest by director in contract / arrangement entered into by or on behalf of the company. 4 Interest of other officers etc. (Section 215) 1 LO6.4.1: Explain the requirements of disclosure of interest by officers in contract / arrangement entered into by or on behalf of the company. 5 Interested director not to participate or vote in proceedings of directors (Section 216) 1 LO6.5.1: Describe the provisions relating to participation of interested director in the proceedings of directors in contract / arrangement entered into by or on behalf of the company. 6 Accounts (Section 230, 233, 236, 241 and 242 ) 1 LO6.6.1: Describe the provisions relating to / List the books of accounts to be kept by company LO6.6.2: Explain the requirements with respect to the annual accounts and the balance sheet LO6.6.3: Describe directors’ report LO6.6.4: Describe the authentication of balance sheet and profit and loss account LO6.6.5: Discuss requirements of filing of balance sheets and profit and loss accounts with the registrar. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 35 Syllabus Ref 7 Contents Dividend (Section 248 to 251) Level 1 Learning Outcome LO6.7.1: Explain the requirements relating to declaration of dividend and identify/explain certain restrictions on declaration of dividend LO6.7.2: Describe the provisions applicable to payment of dividend. e Audit (Sections 252 to 257) 1 Audit (Section 252 to 257) 2 LO7.1.1: Explain the provisions applicable to • Appointment, removal and remuneration of auditors • Qualification and disqualification of auditors • Powers/ duties of auditors and an auditor’s right to access the record and information • An auditor’s duty to report and contents thereof • Signature on an audit report SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 36 CAF-4 Certificate in Accoutning and Finance BUSINESS MANAGEMENT AND BEHAVIORAL STUDIES Objective To equip candidates with the fundamentals of management and behavioral studies. Learning Outcome On the successful completion of this paper candidates will be able to: 1 demonstrate an understanding of the nature of management concepts and approaches 2 show familiarity with the structure of business organizations, their culture and the change process 3 demonstrate an understanding of human behavior 4 demonstrate an understanding of the concepts of motivation 5 show familiarity with the nature and kinds of leadership 6 show familiarity with the nature and importance of negotiation and conflict resolution 7 demonstrate a basic understanding of IT based management information systems. Grid Weighting Management concepts 20-30 Organizational process 18-22 Individual behavior and motivation 18-22 Leadership, negotiation and conflicts 18-22 Management information system 12-18 Total Syllabus Ref A Contents 100 Level Learning Outcome 2 LO1.1.1: Define the terms leadership and management their nature and purpose Management concepts 1 Meaning LO1.1.2: State the difference between Managers and Leaders using examples LO1.1.3: Describe the classification of management rolls enunciated by Henry Mintzberg. 2 Functions 2 LO1.2.1: Illustrate management model and explain the functions of management LO1.2.2: Describe the roles and skills of management. 3 Classical approach SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO1.3.1: Describe the principles of Scientific management stated by Fredrick Taylor 37 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO1.3.2: Explain the key principles of management by Fayol and Urwick LO1.3.3: Explain theories of management by Weber, Rosemary Stewart and Elton Mayo LO1.3.4: Discuss the criticism on scientific management and classical approach to management LO1.3.5: List the characteristics of bureaucratic organizations and discuss criticism on this form of management LO1.3.6: Discuss theories of management presented by Peter Drucker, Moss Kanter and Mintzberg. 4 Behavioral approach 2 LO1.4.1: Discuss the Hawthorne experiments on human relation approach, their significance and implications LO1.4.2: Discuss critically the relevance of these experiments for management and organizational behaviour LO1.4.3: Discuss Theory X, Theory Y and Theory Z including their implications and differences. 5 Management science approach 2 LO1.5.1: Explain the effects of operations research in business sciences LO1.5.2: Discuss management skills involving time and stress management, innovations and creativity, communications, mentoring and leadership. 6 External factors – Competitors, suppliers, labour, customers 2 LO1.6.1: Describe the direct and indirect interactive forces including political ,legal health and safety and consumer protection forces may affect the organizational environment. 7 General environment - Political, legal, technological, economic, social 2 LO1.7.1: Explain how the external forces affect the organizational environment using examples LO1.7.2: Explain how social, demographic, ecological and competitive factors would impact business environment. B Organizational process 1 Organizational structure - principles of organization, different ways of structuring organization SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO2.1.1: Explain the meaning and nature of organizational structure LO2.1.2: Describe the different types of organisations and their distinguishing features 38 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO2.1.3: Identify the different stakeholders who have interests in business firms LO2.1.4: Explain the importance of a good structure and consequences of a deficient structure. LO2.1.5: Describe the features of matrix functional, divisional and virtual organisations and their salient features LO2.1.6: Describe how the elements of organizational structure can be combined to create mechanistic and organic structures LO2.1.7: Describe the advantages and disadvantages of mechanistic and organic structure of organization. 2 Organizational change - nature of change process, resistance to change 2 LO2.2.1: Identify and explain the external forces creating changes in the performances of organizations LO2.2.2: Describe the process of organizational change LO2.2.3: Explain the forms of reactions to change. 3 Organizational culture - concept, dysfunctional aspect of culture 2 LO2.3.1: Describe organizational culture using examples LO2.3.2: Discuss using examples the different levels of organizational culture LO2.3.3: Descibe the types of cultures and their efficacies in the context of performances of organisations. C Individual behavior and motivation 1 Perception 2 LO3.1.1: Explain perception and perception process and their effects LO3.1.2: Discuss using examples the difference between sensation and perception LO3.1.3: Discuss using examples the internal and external factors that affect perceptual selectivity LO3.1.4: Describe the characteristics of Perceiver and Perceived LO3.1.5: Analyse the perceptual problems/distortions in dealing with other people like stereotyping and halo effect, etc. 2 Attitude SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO 3.2.1: Define attitude and its components with reference to organizational cultures 39 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO3.2.2: Discuss the differences between cognitively based attitudes and affectively based attitudes LO3.2.3: Describe the difference between implicit and explicit attitudes LO3.2.4: Discuss cross-cultural differences in the bases for attitudes LO3.2.5: Explain the relationship between attitude and behaviour. 3 Job satisfaction and stress 2 LO3.3.1: Explain by offering examples meaning and outcomes of job satisfaction LO3.3.2: Identify the measures to enhance satisfaction LO3.3.3: Describe stress and identify the causes of job stress LO3.3.4: Explain using examples the general categories of stressors that can affect performance LO3.3.5: Identify consequences of stress and strategies in order to cope up with stress. 4 Maslow need hierarchy Model 2 LO3.4.1: Describe using examples motivation LO3.4.2: Explain Maslow’s need hierarchy theory LO3.4.3: Explain strengths and problems in the application of Maslow’s theory. 5 Herzberg’s two-factor Theory 2 LO3.5.1: Explain Herzberg’s two factor theory of motivation and major criticism thereon. 6 McClelland’s theory of needs 2 LO3.6.1: Explain the three motivational needs theory presented by McClelland LO3.6.2: State the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motives. 7 Goal setting 2 LO3.7.1: Explain the major dimensions of goal setting theory LO3.7.2: Explain why and how goals contribute to self-motivation LO3.7.3: Describe how to set effective goals and the problems encountered in setting goals. 8 Management by objective SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO3.8.1: Explain the basic steps of the overall performance system of MBO. 40 Syllabus Ref 9 Contents Self-efficacy Level 2 Learning Outcome LO3.9.1: Define the term self-efficacy LO3.9.2: Demonstrate understanding of the concepts of high self-efficacy and low self-efficacy. 10 Reinforcement 2 LO3.10.1: Describe law of effect using relevant examples LO3.10.2: Describe the concept of reinforcement as used in behavioural management LO3.10.3: Describe positive and negative reinforcers using examples. D 11 Equity/organizational justice 2 LO3.11.1: Explain organizational justice and three components of the same, namely, distributive, procedural and interactional. 12 Expectancy 2 LO3.12.1: Describe using simple examples Vroom’s Expectancy theory and its three elements, namely, expectancy, instrumentality and valence. Leadership, negotiation and conflicts 1 Type of leadership 2 LO4.1.1: Discuss different leadership styles, namely, free-rein, engaging, participative, task oriented and autocratic. 2 Theories of leadership 2 LO4.2.1: Discuss using simple examples different theories of leadership, namely, trait theories, Blake and Mouton theory, situational and contingency theories LO4.2.2: Discuss Tannenbaum and Schmidt’s continuum model of leadership styles LO4.2.3: Discuss the various Contigency theories of leadership LO4.2.4: Describe the principles and the need for adaptive change. 3 Roles, activities, skills of leaders 2 LO4.3.1: Discuss leadership roles and activities LO4.3.2: Identify Skills needed for effective leadership. 4 Group Dynamics and teamwork - types of groups, group formation, group structure, individual in groups, team work 2 LO4.4.1: Explain the differences between groups and teams LO4.4.2: Discuss individual and group behavior at work Discuss formal and informal group behavior in work settings LO4.4.3: Explain and illustrate balance theory of group formation SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 41 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO4.4.4: Describe the concept and stages of team formation, team roles and performances of effective and ineffective teams LO4.4.5: Identify and describe stages of group development LO4.4.6: List down the factors that increase and decrease group cohesiveness LO4.4.7: Explain the ways to make teams more effective. 5 Negotiation skills 2 LO4.5.1: Explain various stages of the negotiation process LO4.5.2: Describe the different skills of effective negotiators LO4.5.3: Describe the roles of mediators, arbitrators, concillators and consultants LO4.5.4: Explain the low risk techniques of negotiation LO4.5.5: Explain the high risk techniques of negotiation. 6 Conflict resolution 2 LO4.6.1: Discuss the conflict resolution process LO4.6.2: Discuss conflicts at the individual and inter-group levels LO4.6.3: Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of conflicts in organisations LO4.6.4: Explain intra-individual conflict with model of frustration LO4.6.5: List some of the physical, psychological and behavioural problems that occur due to conflict. E Management information systems 1 General system concepts of information technology 1 LO5.1.1: Demonstrate basic understanding of computer hardware i.e. input, output, storage of information and networking LO5.1.2: Understand the concepts of information technology and information systems LO5.1.3: Understand the role and types of information systems in business. 2 IT-based transaction processing systems SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 1 LO5.2.1: Understand data entry, batch processing, online processing and real time -online processing. 42 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome 3 IT-based financial reporting systems 1 LO5.3.1: Understand IT based financial reporting system. 4 IT-based order processing and inventory control systems 1 LO5.4.1: Understand IT based order processing and inventory control systems. 5 IT-based personnel systems 1 LO5.5.1: Understand IT based personnel systems. 6 Integrated IT systems 1 LO5.6.1: Briefly describe integrated systems, their advantages and disadvantages LO5.6.2: Understand main features of Enterprise Resource Planning. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 43 CAF-5 CERTIFICATE IN ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING AND REPORTING I Objective To provide candidates with an understanding of the fundamentals of accounting theory and basic financial accounting with particular reference to international pronouncements. Learning Outcomes On the successful completion of this paper candidates will be able to: 1 prepare financial statements in accordance with specified international pronouncements 2 account for simple transactions related to inventories and property, plant and equipment in accordance with international pronouncements 3 understand the nature of revenue and be able to account for the same in accordance with international pronouncements 4 prepare financial statements in accordance with specified international pronouncements 5 understand the fundamentals of accounting for cost of production. Grid Weighting Preparation of components of financial statements 18-22 Income and expenditure account and preparation of accounts from incomplete records 15-20 Accounting for inventories; and property, plant and equipment 25-35 Revenue accounting 12-18 Branch accounts 8-12 Introduction to cost of production 8-12 Total Syllabus Ref Contents A Preparation of components of financial statements with adjustments included in the syllabus Level 100 Learning Outcomes 1 Preparation of statement of financial position (IAS 1) 1 LO1.1.1: Prepare simple statement of financial position in accordance with the guidance in IAS 1 from data and information provided. 2 Preparation of statement of comprehensive income (IAS 1) 1 LO1.2.1: Prepare simple statement of comprehensive income in accordance with the guidance in IAS 1 from data and information provided. 3 Preparation of statement of cash flows (IAS 7) 1 LO 1.3.1: Demonstrate thorough understanding of cash and cash equivalents, operating, investing and financing activites SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 44 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcomes LO 1.3.2: Calculate changes in working capital to be included in the operating activites LO1.3.3: Compute items which are presented on the statement of cash flows LO1.3.4: Prepare a statement of cash flows of an entity in accordance with IAS 7 using the direct and the indirect method. 4 Income and expenditure account 2 LO1.4.1: Prepare simple income and expenditure account using data and information provided. 5 Preparation of accounts from incomplete records 2 LO1.5.1: Understand situations that might necessitate the preparation of accounts from incomplete records (stock or assets destroyed, cash misappropriation or lost, accounting record, destroyed etc.) LO1.5.2: Understand and apply the following techniques used in incomplete record situations: B • Use of the accounting equation • Use of opening and closing balances of ledger accounts • Use of a cash and / or bank summary • Use of markup on cost and gross and net profit percentage Accounting for inventories (IAS 2); and property, plant and equipment (IAS-16) 1 Application of cost formulas (FIFO/ weighted average cost) on perpetual and periodic inventory system 2 LO2.1.1: Understand and analyze the difference between perpetual and periodic inventory systems LO2.1.2: Understand and analyze the difference between FIFO and weighted average cost formulas and use them to estimate the cost of inventory LO2.1.3: Account for the application of cost formulas ( FIFO/ weighted average cost) on perpetual and periodic inventory system LO2.1.4: Identify the impact of inventory valuation methods on profit. 2 Cost of inventories (cost of purchase, cost of conversions, other costs) 2 LO2.2.1: Calculate cost of inventory in accordance with IAS-2 using data provided including cost of purchase, cost of conversions, and other costs LO2.2.2: Identify relevant and irrelevant cost from data provided. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 45 Syllabus Ref 3 Contents Measurement of inventories (lower of cost or net realizable value) Level 2 Learning Outcomes LO2.3.1: Describe net realizable value (NRV) LO2.3.2: Explain the situation when the cost of inventories may not be recoverable LO2.3.3: Demonstrate the steps in measuring inventory at lower of cost or NRV LO2.3.4: Post journal entries for adjustments in carrying value (excluding reversal of write downs). 4 Presentation of inventories in financial statements 2 LO2.4.1: Understand the disclosure requirements and prepare extracts of necessary disclosures (excluding pledged inventories and reversal of write downs). 5 Initial and subsequent measurement of property, plant & equipment (components of cost, exchange of assets) 1 LO2.5.1: Calculate the cost on initial recognition of property, plant and equipment in accordance with IAS-16 including different elements of cost and the measurement of cost LO2.5.2: Analyse subsequent expenditure that may be capitalised, distinguishing between capital and revenue items. 6 Measurement after recognition of property, plant and equipment 2 LO2.6.1: Present property, plant and equipment after recognition under cost model and revaluation model using data and information provided. 7 Depreciation - depreciable amount, depreciation period and depreciation method 2 LO2.7.1: Define depreciation, depreciable amount and depreciation period LO2.7.2: Calculate depreciation according to the following methods • straight-line, • diminishing balance • the units of production LO2.7.3: Compute depreciation for assets carried under the cost and revaluation models using information provided including impairment LO2.7.4: Prepare journal entries and ledger accounts. 8 De-recognition 2 LO2.8.1: Account for de-recognition of property, plant and equipment recognized earlier under cost and revaluation methods LO2.8.2: Post journal entries to account for de-recognition using data provided. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 46 Syllabus Ref Contents C Revenue accounting 1 Revenue (IAS-18) Level 2 Learning Outcomes LO3.1.1: Describe revenue LO3.1.2: Apply the principle of substance over form to the recognition of revenue LO3.1.3: Describe and demonstrate the accounting treatment (measurement and recognition) for revenue arising from the following transactions and events: • sale of goods; • rendering of services use by others of entity assets yielding interest, royalties and dividends. D Branch accounts 1 Branch accounts (excluding foreign branches) 2 LO4.1.1: Describe the special features of branch accounting including differences to routine accounting LO4.1.2: Understand and apply the treatment of branch inventory, branch mark-up, goods sent to branch and branch debtors; in the books of head office LO4.1.3: Prepare trading/income statement of branch. E Introduction to cost of production 1 Meaning and scope of cost accounting 2 LO5.1.1: Explain the scope of cost accounting and managerial accounting and compare them with financial accounting. 2 Analysis of fixed, variable and semi variable expenses 2 LO5.2.1: Explain using examples the nature and behaviour of costs LO5.2.2: Identify and apply the concept of fixed, variable, and semi variable costs in given scenarios. 3 Direct and indirect cost 2 LO5.3.1: Identify and apply the concept of direct and indirect cost in given scenarios. 4 Cost estimation using high-low points method and linear regression analysis 2 LO5.4.1: Apply high-low points’ method in cost estimation techniques LO5.4.2: Apply regression analysis for cost estimation. 5 Product cost and period cost SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO5.5.1: Compare and comment product cost and period cost in given scenarios. 47 CAF-6 CERTIFICATE IN ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE Principles of Taxation Objective To provide basic knowledge in the understanding of objectives of taxation and core areas of Income Tax Ordinance, 2001, Income Tax Rules 2002 and Sales Tax Act 1990 and Sales Tax Rules. Learning Outcome The candidate will be able to: 1 understand the objective of levy of taxation, and its basic concepts 2 understand the system of taxation in pakistan 3 understand the historical background of taxation in pakistan 4 understand constitutional provisions of taxation in pakistan 5 understand and explain the basic ethics of taxation 6 understand and explain provisions of income tax law mainly relevant to individuals and association of persons 7 understand and explain sales tax law relevant to operational level tasks. Grid Weighting Objective, system and historical background, constitutional provisions and ethics 8-12 Income tax 60-70 Sales tax 20-30 Total Syllabus Ref A Contents Level 100 Learning Outcome Objective, system and historical background, constitutional provisions and ethics a Basic concepts of taxation 1 Objectives 1 LO1.1.1: Comprehend the main objectives of taxation LO1.1.2: Justify Taxation as means of development. 2 Basic concepts 1 LO1.2.1: Understands the implication of direct and indirect taxation. 3 System of taxation in Pakistan (Income Tax, Sales Tax, Federal Excise Tax, Capital Value Tax, Customs) 1 LO1.3.1: Comprehend different kinds of taxes and their scope. 4 Historical background 1 LO1.4.1: State the history of taxation in the sub-continent. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 48 Syllabus Ref Contents b Constitutional provisions 1 Federal financial procedures (Article 78 to 88 of the Constitution of Pakistan) Level Learning Outcome 1 LO2.1.1: Demonstrate familiarity with the Federal Consolidated Fund and Public Account LO2.1.2: Demonstrate familiarity with the expenditure that can be charged upon Federal Consolidated Fund. 2 Provincial financial procedures (Article 118 to 127 of the Constitution of Pakistan) 1 LO2.2.1: Demonstrate familiarity with the Provincial Consolidated Fund and Public Account LO2.2.2: Demonstrate familiarity with the expenditure that can be charged upon Provincial Consolidated Fund. 3 Distribution of revenues between Federation and the Provinces (Article 160 to 165A of the Constitution of Pakistan) 1 LO2.3.1: Demonstrate familiarity with the formation of National Finance Commission and its main function LO2.3.2: Demonstrate familiarity with the taxes that can be raised under the authority of Parliament LO2.3.3: Demonstrate familiarity with the powers of provincial assemblies in respect of professional tax LO2.3.4: Demonstrate familiarity with the exemption available to federal and provincial governments LO2.3.5: Demonstrate familiarity with the tax on corporation owned by federal and provincial government. 4 Federal legislative lists relating to revenue generating measures (related part of Fourth Schedule to the Constitution of Pakistan) 1 LO2.4.1: Enlist the revenue collection as mentioned at S. No. 43 to 53 in Fourth Schedule attached to the Constitution c Ethics 1 Ethics for tax legislation 2 LO3.1.1: Describe how canons of taxation developed by economists are relevant for legislators while formulating tax policies. 2 Ethics for taxpayers 2 LO3.2.1: Understand the right and purpose of state to tax its citizen LO3.2.2: Understand morality behind compliance with tax laws. 3 Ethics for tax implementing authorities 2 LO3.3.1: Understand the powers Vs ethical responsibilities of tax implementation authorities LO3.3.2: Understand pillars of tax administration, namely, fairness, transparency, equity and accountability. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 49 Syllabus Ref 4 B Contents Tax evasion and avoidance Level Learning Outcome 2 LO3.4.1: Explain with simple examples the basic difference between evasion and avoidance of tax. 1 LO4.1.1: Describe the definitions given in section 2 sub-section 1, 5, 5A, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11A, 19, 19C, 20, 21, 22, 23, 29, 29A, 29C, 36, 37, 38, 41, 44A, 46, 47, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 68 Income Tax 1 Chapter I – Preliminary (concepts of terms defined section 2 sub-section 1, 5, 5A, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11A, 19, 19C, 20, 21, 22, 23, 29, 29A, 29C, 36, 37, 38, 41, 44A, 46, 47, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 68) LO4.1.2: Describe other definitions covered under relevant sections LO4.1.3: Apply definitions on simple scenarios. 2 Chapter II – Charge of tax (excluding section 7) 2 LO4.2.1: Explain the chargeability of tax with simple examples. 3 Chapter III – Tax on Taxable income (Excluding Section 29A, 30 and 31) 2 LO4.3.1: Compute taxable income and tax thereon relating to salary, income from property, income from business, capital gain, dividend, profit on debt, ground rent, rent from sub-lease, income from provision of amenities, utilities or any other services connected with rented building and consideration for vacating the possession of building. 4 Chapter IV – (Part I, II and III) – Common rules (Excluding Sections 78 and 79) 1 LO4.4.1: Understand and apply on simple scenarios provisions for income of joint owner, apportionment of deductions, fair market value and receipt of income LO4.4.2: Explain using simple examples the provisions relating to tax year LO4.4.3: Explain with simple examples the provisions relating to disposal and acquisition of assets, cost and consideration received. 5 Chapter V Part I – Central concepts 2 LO4.5.1: Describe with simple examples the meaning of persons, resident and non-resident persons and associates. 6 Chapter V Part II Div I and II – Individuals (Excluding Section 88A) 2 LO4.6.1: Describe with simple examples the principles of taxation of individuals. 7 Chapter V Part III – Association of persons 2 LO4.7.1: Describe with simple examples the principles of taxation of association of persons. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 50 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome 8 Chapter VII Part II – Taxation of foreignsource income of residents 2 LO4.8.1: Understand the applicability of tax on foreign salary income, credit against foreign tax and treatment of foreign loss of a resident on simple scenarios. 9 Chapter X Part I – Returns 2 LO4.9.1: Identify persons required to furnish a return of income LO4.9.2: Identify persons not required to furnish a return of income LO4.9.3: Identify persons required to furnish wealth statements LO4.9.4: List the contents of wealth statement. 10 Chapter X Part II – Assessments 1 LO4.10.1: Understand the meaning of assessment by Commissioner and power of Commissioner to conduct audit. 11 Chapter X Part III – Appeals 1 LO4.11.1: List the appellate bodies LO4.11.2: Explain using simple examples the circumstances when appeal to the Commissioner (Appeals) is made and the pre-conditions applicable LO4.11.3: Explain the provisions relating to decision of appeals by Commissioner (Appeals) using simple examples. 12 Chapter X Part VIII – Records, Information Collection and Audit (Section174 and 177) 2 LO4.12.1: Understand the provisions relating to records to be kept by the taxpayers LO4.12.2: Describe the provisions relating to audit by Commissioner. C 13 The Income Tax Rules related to the above chapters of the Income Tax Ordinance 2001 shall also be examined 1 LO4.13.1: Apply rules relevant to learning outcomes specified against each topic on well explained scenarios. 14 First and Second Schedule attached to the Income Tax Ordinance 2001 2 LO4.14.1: Apply clauses relevant to learning outcomes specified against each topic on well explained scenario. 2 LO5.1.1: Describe the definitions given in section 2 sub-section 3, 5AA, 9, 11, 14, 16, 17, 20, 21, 22A, 25, 27, 28, 29A, 33, 35, 39, 40, 41, 43, 44, 46 Sales Tax a Sales Tax Act 1990 1 Chapter I – Preliminary (concepts of terms defined Section 2 sub-sections 3, 5AA, 9, 11, 14, 16, 17, 20, 21, 22A, 25, 27, 28, 29A, 33, 35, 39, 40, 41, 43, 44, 46) LO5.1.2: Describe other definitions covered under relevant sections LO5.1.3: Apply definitions on simple scenarios. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 51 Syllabus Ref 2 Contents Chapter II – Scope and payment of tax Level Learning Outcome 2 LO5.2.1: Understand the application of sales tax law on taxable supplies including zero rated and exempt supplies LO5.2.2: State the determination, time and manner of sales tax liability and payment using simple examples. 3 Chapter III – Registration 2 LO5.3.1: State the requirement and procedure of registration. 4 Chapter IV – Book keeping and invoicing requirements 2 LO5.4.1: List the record to be kept by a registered person LO5.4.2: State the requirements of tax invoice LO5.4.3: Explain the retention period of record using simple examples. 2 LO5.5.1: Understand the various types of returns required to be filed by registered and un-registered persons. Chapter I – Registration, Compulsory registration and De-registration 2 LO6.1.1: Explain the requirement and procedure of registration, compulsory registration and deregistration using simple examples. 2 Chapter II – Filing of return 2 LO6.2.1: Explain the requirement and procedure of filing of return using simple examples. 3 Chapter III – Credit and Debit And Destruction of Goods 2 LO6.3.1: Explain the requirement and procedure of issuing debit and credit notes using simple examples 5 Chapter V – Returns b Sales Tax Rules, 2006 1 LO6.3.2: State the procedure for destruction of goods. 4 Chapter IV – Apportionment of Input Tax SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO6.4.1: Explain the requirement and procedure of apportionment of input tax using simple examples. 52 CAF-7 CERTIFICATE IN ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING AND REPORTING II Objective To broaden the knowledge base of basic accounting acquired in earlier modules with emphasis on International Financial Reporting Standards. Learning Outcome On the successful completion of this paper candidates will be able to: 1 prepare financial statements in accordance with the relevant law of the country and in compliance with the reporting requirements of the international pronouncements 2 account for transactions relating to tangible and intangible assets including transactions relating to their common financing matters 3 understand the implications of contingencies; changes in accounting policies and estimates; errors and events occurring after reporting period 4 account for transactions relating to taxation 5 demonstrate knowledge of basic ethical issues in preparation and reporting of financial information 6 apply financial analysis on given financial and non-financial information. Grid Weighting Final Accounts 8-12 Consolidation of single subsidiary 10-20 Accounting for tangible and intangible assets, leases and borrowing cost 25-35 Provisions and contingencies; changes in accounting policies and estimates; errors and events occurring after reporting period; and taxation 25-35 Ethics 5-10 Financial analysis 5-10 Total Syllabus Ref Contents A Preparation of financial statements – Final accounts 1 Preparation of financial statements of limited companies in line with the requirements of the Companies Ordinance, 1984 and International Financial Reporting Standards (IAS 1 and 7 and others included in the syllabus) excluding liquidations reconstructions and mergers SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 100 Level Learning Outcome 2 LO1.1.1: Prepare statements of financial position in accordance with the guidance in IAS 1 from data and information provided LO1.1.2: Identify the laws, regulations, reporting standards and other requirements applicable to statutory financial statements of a limited company 53 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO1.1.3: Prepare and present the following in accordance with the disclosure requirements of IAS1, Companies ordinance, fourth schedule / fifth schedule • Statement of financial position • Statement of comprehensive income • Statement of changes in equity • Notes to the financial statements LO1.1.4: Prepare statement of cash flows in accordance with the requirements of IAS 7. Preparation of financial statements – Consolidation of a single subsidiary B 1 Elimination of investment in subsidiary and parent’s equity 1 LO2.1.1: Describe the concept of a group as a single economic unit LO2.1.2: Define using simple examples subsidiary, parent and control LO2.1.3: Describe situations when control is presumed to exist LO2.1.4: Identify and describe the circumstances in which an entity is required to prepare and present consolidated financial statements LO2.1.5: Eliminate (by posting journal entries) the carrying amount of the parent’s investment in subsidiary against the parent’s portion of equity of subsidiary and recognize the difference between the two balances as either. 2 Identification of non-controlling interest 1 • goodwill; or • gain from bargain purchase LO2.2.1: Define and describe noncontrolling interest in the case of a partially owned subsidiary LO2.2.2: Identify the non-controlling interest in the following: 3 Profit and loss from intra-company transactions relating to assets and inventories without tax implications SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 1 • net assets of a consolidated subsidiary; and • profit or loss of the consolidated subsidiary for the reporting period LO2.3.1: Post adjusting entries to eliminate the effects of intergroup sale of inventory and depreciable assets. 54 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome 4 Preparation of consolidated statements of financial position 1 LO2.4.1: Prepare and present simple consolidated statements of financial position involving a single subsidiary in accordance with IFRS 10. 5 Preparation of consolidated statements of comprehensive income 1 LO2.5.1: Prepare and present a simple consolidated statement of comprehensive income involving a single subsidiary in accordance with IFRS 10. Recognition, de-recognition, measurement, depreciation / amortization and measurement after recognition of non-current assets (IAS 16 and IAS 38) 2 LO3.1.1: Explain and apply the accounting treatment of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets Leases (IAS 17) 2 C Accounting for tangible and intangible assets, leases and borrowing costs 1 2 LO3.1.2: Formulate accounting policies in respect of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets. LO3.2.1: Describe the method of determining a lease type i.e. an operating or finance lease LO3.2.2: Prepare journal entries and present extracts of financial statements in respect of lessee accounting, lessor accounting, and sale and lease back arrangements, after making necessary calculations LO3.2.3: Formulate accounting policies in respect of different lease transactions LO3.2.4: Analyze the effect of different leasing transactions on the presentation of financial statements. 3 Recognition of borrowing costs (IAS 23) 2 LO3.3.1: Describe borrowing cost and qualifying assets using examples LO3.3.2: Identify and account for borrowing costs in accordance with IAS 23 LO3.3.3: Disclose borrowing costs in financial statements LO3.3.4: Formulate accounting policies in respect of borrowing cost. D Provisions and contingencies; changes in accounting policies and estimates; errors and events occurring after reporting period; and taxation 1 Provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets (IAS-37) SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO4.1.1: Define liability, provision, contingent liability and contingent asset also describe their accounting treatment. 55 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO4.1.2: Distinguish between provisions, contingent liabilities or contingent assets LO4.1.3: Understand and apply the recognition and de-recognition criteria for provisions LO4.1.4: Calculate/ measure provisions such as warranties/guarantees, restructuring, onerous contracts, environmental and similar provisions, provisions for future repairs or refurbishments LO4.1.5: Account for changes in provisions LO4.1.6: Disclosure requirements for provisions. 2 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates; and errors (IAS-8) 2 LO4.2.1: Define accounting policies, accounting estimates and prior period errors LO4.2.2: Account for the effect of change in accounting estimates and policies in the financial statements LO4.2.3: Understand and analyze using examples, IFRS guidance on accounting policies, change in accounting policies and disclosure LO4.2.4: Understand and analyze using examples, IFRS guidance on accounting estimates, changes in accounting estimates and disclosure LO4.2.5: Understand and analyze using examples, IFRS guidance on errors, correction of errors and disclosure. 3 Events occurring after the reporting period (IAS-10) 2 LO4.3.1: Explain using examples events after the reporting period, adjusting events, and non-adjusting events LO4.3.2: Understand and analyze using examples IFRS guidance on the recognition, measurement and disclosure of adjusting events and non-adjusting events LO4.3.3: Understand and analyze using examples, going concern issues arising after the end of the reporting period. 4 Taxation: Current year, prior years and deferred (IAS-12) Note that the deferred consequences of the following transactions are not examinable: SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO4.4.1: Define temporary differences and identify temporary differences that cause deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets 56 Syllabus Ref Contents • • • • • • • E Level Learning Outcome LO4.4.2: Determine amounts to be recognised in respect of temporary differences Business combination (including goodwill Assets carried at fair value Un-used tax losses and credits Re-assessment of un-recognized deferred tax assets Investments in subsidiaries, branches, associates and interest in joint venture Items recognized outside profit and loss account Share based payment LO4.4.3: Prepare and present deferred tax calculations using the balance sheet approach LO4.4.4: Account for the major components of tax expense/income and its relationship with accounting profit LO4.4.5: Formulate accounting policies in respect of deferred tax LO4.4.6: Apply disclosure requirements of IAS12 to scenarios of a moderate level of complexity. Ethics 1 Fundamental principles (sections 100 to 150 of the Code of Ethics for Chartered Accountants) 2 LO5.1.1: Describe with simple examples the fundamental principles of professional ethics of integrity, objectivity, professional competence and due care, confidentiality and professional behaviour LO5.1.2: Apply the conceptual framework to identify, evaluate and address threats to compliance with fundamental principles. 2 F An understanding of ethics relating to preparation and reporting of financial information (Section 320 of Code of Ethics for Chartered Accountants) 2 LO5.2.1: Explain using simple examples the ethical responsibilities of a Chartered Accountant in preparation and reporting of financial information. 3 LO6.1.1: Following ratios: • Current ratio Financial analysis 1 Compute and interpret various ratios from data and information provided. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 • Acid-test ratio/quick ratio • Gross profit • Return on equity • Return on assets • Return on capital employed • Debt-equity ratio • Inventory turnover • Debtor turnover • Creditor turnover 57 CAF-8 CERTIFICATE IN ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Objective To equip candidates with techniques of cost accounting to provide a knowledge base for decision making skills.. Learning Outcome On the successful completion of this paper candidates will be able to: 1 establish the costs associated with the production of products and provision of services 2 demonstrate an understanding of different costing systems 3 prepare various types of forecasts and budgets 4 apply the concepts of costing in the decision making process 5 demonstrate a functional knowledge of financial instruments 6 apply concept of time value of money 7 understand the concepts of sustainability reporting. Grid Weighting Costs associated with the production 15-20 Costing system 20-30 Budget and budgetary controls 10-15 Decision making 20-25 Financial instruments 5-10 Time value of money 5-10 Sustainability reporting 5-10 Total Syllabus Ref Contents A Costs associated with production 1 Basis of valuation - FIFO, weighted average, lower of cost and net realizable value Level 2 100 Learning Outcome LO1.1.1: Apply inventory valuation methods ( namely, FIFO, weighted average, lower of cost and net realizable value) in simple scenarios LO1.1.2: Comment on the suitability of inventory valuation under FIFO, weighted average, lower of cost and net realizable value LO1.1.3: Compare inventory valuation under FIFO, weighted average, lower of cost and net realizable value LO1.1.4: Calculate NRVs of inventories in a given scenario. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 58 Syllabus Ref 2 Contents Economic Order Quantity Level 2 Learning Outcome LO1.2.1: Describe the economic order quantity (EOQ) and apply the concept in given scenarios LO1.2.2: Calculate the EOQ from data provided. 3 Safety stock 2 LO1.3.1: Describe safety stocks for inventories LO1.3.2: Explain the reasons for maintaining safety stock LO1.3.3: Calculate the safety stock from data provided. 4 Re-order level 2 LO1.4.1: Explain the re-order levels and the objectives of setting re-order levels LO1.4.2: Calculate re-order levels by using data provided. 5 Manufacturing expenses - actual and applied 2 LO1.5.1: Describe manufacturing overheads using examples LO1.5.2: Compare manufacturing, administrative and selling costs LO1.5.3: Identify manufacturing overheads from data provided LO1.5.4: Describe and distinguish between actual overhead and applied overhead LO1.5.5: Calculate applied overheads using data provided. 6 Over or under absorbed overhead 2 LO1.6.1: Compare actual and absorbed overheads from data provided LO1.6.2: Analyze over or under absorption in terms of expenditure and volume variances LO1.6.3: Account for over or underabsorbed overheads. 7 Production and service departments 2 LO1.7.1: Identify production and service departments in a manufacturing facility and analyze their related costs LO1.7.2:Explian the basis of allocation of cost of service department to production department. 8 Apportionment, allocation and absorption of service departments› overheads to production 2 LO1.8.1: Allocate costs to production and service departments using information provided LO1.8.2: Allocate costs of service departments to production department using data and information provided. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 59 Syllabus Ref Contents B Costing systems 1 Marginal costing Level 2 Learning Outcome LO2.1.1: Explain the concept of marginal costing and apply on given data LO2.1.2: Explain how marginal costing helps managerial decisions using examples. 2 Absorption costing 2 LO2.2.1: Describe and apply absorption costing approach in given scenarios LO2.2.2: Compare marginal costing and absorption costing. 3 Manufacturing cost accounting cycle 2 LO2.3.1: Explain the flow of cost in the production process using examples LO2.3.2: Prepare accounting entries for the flow of cost. 4 Job order costing 2 LO2.4.1: Describe job order costing LO2.4.2: Calculate the cost of a job and inventories by application of job order costing LO2.4.3: Prepare accounting entries under the job order costing system. 5 Process costing 2 LO2.5.1: Describe the process costing including the treatment of normal / abnormal loss / gain LO2.5.2: Calculate cost of product and inventories by application of process costing LO2.5.3: Prepare accounting entries under the process costing system. 6 Treatment of Joint and By-Products 2 LO2.6.1: Describe joint and by products using examples LO2.6.2: Allocate joint production costs using sales value, physical units, average units and weighted average methods LO2.6.3: Account for by-products using recognition of gross revenue, recognition of net revenue and replacement cost approaches. 7 Cost of services rendered 2 LO2.7.1: Explain how departmentalization in a service organization helps in cost planning and control LO2.7.2: Calculate cost of services rendered by a service organization. 8 Standard costing 2 LO2.8.1: Explain standard costing using examples LO2.8.2: Perform standard setting for material, labour and factory overhead. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 60 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome 9 Variance analysis-material, labour and overhead 2 LO2.9.1: Calculate, analyze and interpret various variances relating to material, labour and factory overhead. 10 Target costing 2 LO2.10.1: Describe target costing and how target cost is determined LO2.10.2: Apply the target costing tools to given scenarios. C Budget and budgetary controls 1 Planning, forecasting and budgeting of sales, cost and profit 2 LO3.1.1: Explain how budgeting process works and how it fits into overall planning and control LO3.1.2: Prepare forecasts on given data and assumptions LO3.1.3: Identify and describe different purposes of budgeting LO3.1.4: Identify and describe the various stages in the budgeting process LO3.1.5: Prepare following types of budgets: • fixed and flexible budgets; • performance budgeting; • sales budget; • production budget; • direct materials budget; • direct labour budget; • manufacturing overhead budget; • inventory budget; • cost of goods sold budget; • selling and administrative expenses budget with inflation aspects; • Master/cash budget; • zero based budgets, and • capital expenditure budgets; LO3.1.6: Describe the human & motivational aspects of budgets LO3.1.7: Describe budgeting and planning in a non-profit organisation LO3.1.8: Prepare forecasts and budgets for a non-profit organisation. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 61 Syllabus Ref Contents D Decision making Level Learning Outcome 1 Opportunity cost 2 LO4.1.1: Describe opportunity cost using examples. 2 Relevant cost 2 LO4.2.1: Describe relevant costs using examples LO4.2.2: Identify the costs that are relevant to a particular decision in given data. 3 Breakeven analysis 2 LO4.3.1: Explain the break-even point using examples and margin of safety LO4.3.2: Calculate the breakeven point in quantity and amount from information provided LO4.3.3: Apply cost volume profit (CVP) analysis and explain its usefulness for management. 4 Make or buy decisions 2 LO4.4.1: Apply marginal and relevant costing concepts to analyze make or buy options LO4.4.2: Analyze make or buy options in case of capacity constraints LO4.4.3: Discuss using examples the importance of qualitative considerations in make or buy decisions. 5 Pricing for special orders 2 LO4.5.1: Perform incremental cost benefit analysis for a special order. 6 Further processing decisions 2 LO4.6.1: Perform incremental cost benefit analysis for further processing costs. 7 Utilization of spare capacity 2 LO4.7.1: Analyze the impact of spare capacity on management decisions regarding make or buy, special order and further processing. 1 LO5.1.1: Describe direct and indirect investment using examples E Financial instruments (basic functions) 1 Shares, debentures, bonds, futures, options, cap, floor, collar, swaps, forward LO5.1.2: Describe using examples shares, debentures, bonds, futures, options LO5.1.3: Describe using simple examples the following characteristics of indirect investments and compare them with direct investments: SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 • Divisibility • Liquidity • Holding period 62 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO5.1.4: Differentiate between investment and speculation using simple examples LO5.1.5: Describe using simple examples cap, floor, collar, swaps, forwards. F Time value of money 1 G Computation of net present value and internal rate of return 1 LO6.1.1: Explain the time value of money LO6.1.2: Calculate net present value and internal rate of return of given cash flows. Sustainability reporting 1 An introduction to sustainability reporting 1 LO7.1.1: Apply the concept of sustainability reporting LO7.1.2: Describe the concept of integrated reporting LO7.1.3: Identify and explain the users of sustainability report LO7.1.4: Explain benefits of sustainability reporting and apply this in given scenarios LO7.1.5: Explain the IFAC Framework of sustainability reporting. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 63 CAF-9 CERTIFICATE IN ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE AUDIT AND ASSURANCE Objective To acquire knowledge of theory, skills, techniques of auditing and to enable the students to understand International Standards on Auditing, Assurance and Ethics. Learning Outcome On the successful completion of this paper candidates will be able to: 1 demonstrate knowledge of general concepts governing an audit 2 demonstrate working knowledge in respect of performance of simple audit procedures and understand the audit report requirement under the companies ordinance, 1984 3 understand the requirement and application guidelines relating to some of the specific areas of audit procedures including external confirmation, review of subsequent events etc. 4 comprehend nature of engagements of review of interim financial statements 5 demonstrate familiarity with computer programming and IT controls relevant to financial reporting 6 respond on audit matters in the light of fundamental principles given in the code of ethics. Grid Weighting General concepts and principles of audit 15-20 Performance of audit and reporting 25-35 Specific areas 20-25 Computer programming and IT controls 10-15 Professional Ethics 10-15 Total Syllabus Ref A Contents Level 100 Learning Outcome General concepts and principles of audit 1 Introduction to International Federation of Accountants 1 LO1.1.1: Briefly describe the organizational overview encompassing • History; • Vision and mission 2 Introduction to international auditing and assurance standard setting body 1 LO1.2.1: Briefly describe the objectives and functions of IAASB. 3 Objective and general principles governing an audit (ISA 200) 2 LO1.3.1: Describe the objectives of audit including concepts of accountability, stewardship, agency, independence and fair presentation LO1.3.2: Describe the overall objectives of the independent auditor. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 64 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO1.3.3: Describe the concepts of assurance and levels of assurance i.e. absolute, reasonable and limited assurance including elements of an assurance engagement, assurances provided by audit and review engagement LO1.3.4: Explain the requirements of an external audit, eligibility and ineligibility of auditor LO1.3.5: Describe the rights and duties of auditors LO1.3.6: Explain the nature and scope of an audit designed to enable the independent auditor to meet those objectives LO1.3.7: Outline the requirements establishing the general responsibilities of the independent auditor applicable in all audits including consideration of inherent limitations of an audit LO1.3.8 Discuss the concept of professional scepticism. 4 Responsibility for the financial statements 2 LO1.4.1: Understand the responsibility of management and those charged with governance for financial reporting and related internal control on financial reporting. 5 Auditor’s responsibility to consider fraud (ISA 240) 2 LO1.5.1: Distinguish between the terms ‘error’, ‘fraud’ and ‘misstatement’ LO1.5.2: Compare the respective responsibilities of management and auditors for fraud LO1.5.3: Describe the matters to be considered and procedures to be carried out to assist the auditor in identifying, assessing and detecting the risks of material misstatement due to fraud LO1.5.4: Identify the fraud risk factors in the simple scenario as given in the appendix 1 of ISA 240 LO1.5.5: Identify the circumstances that indicate the possibility of fraud in the simple scenario as given in the appendix 3 of ISA 240. 6 Legal considerations relating to appointment and removal of auditors (sections 252 to 260 of the Companies Ordinance 1984) SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 2 LO1.6.1: Explain how the first and subsequent auditors are appointed LO1.6.2: Explain how the first and subsequent auditors are removed 65 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO1.6.3: Explain the procedure of resignation of auditors LO1.6.4: Describe qualification and disqualification of the auditor LO1.6.5: Describe the powers and duties of auditors LO1.6.6:Decribe the concept of audit of cost accounts LO1.6.7: Discuss the additional matters to be included in the auditor’s report LO1.6.8: Discuss the auditor’s responsibilities with respect to attendance at general meeting and access to books and records. 7 Terms of Audit engagements (ISA 210) 2 LO1.7.1: Describe the preconditions for an audit and upon which it is necessary for the auditor and the entity’s management to agree LO1.7.2: Respond if preconditions are not present or limit is imposed on scope of audit in well explained simple situations LO1.7.3: State the contents of an audit engagement letter LO1.7.4: Discuss the requirement of issuance of engagement letter and factors that necessitate the issuance of engagement letter in case of recurring audit LO1.7.5: Discuss the circumstances of acceptances of changes in terms of engagement by the auditor. B Performance of audit and reporting 1 Planning an audit (ISA 300) 2 LO2.1.1: Discuss the need for planning an audit including contents of an audit plan and its relation with risk assessment LO2.1.2: Discuss the contents of overall audit strategy and audit plan LO2.1.3: State who should be involved in planning and what preliminary engagement activities are necessary LO2.1.4: Discuss overall planning and the audit plan for a recurring audit LO2.1.5: Outline the additional considerations that should be identified while planning the initial audit. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 66 Syllabus Ref 2 Contents Assessment of audit risks (ISA 315 and 330) Level 2 Learning Outcome LO2.2.1: Discuss the risk based approach to auditing including audit risk model LO2.2.2: Identify the inherent risk, control risk and detection risk in simple scenario LO2.2.3: Explain relationship between audit risk and its components i.e. inherent risk, control risk and detection risk LO2.4.: Discuss the identification and assessment of the risks of material misstatement at both the financial statement level and assertion level, including understanding of entity, its environment, accounting and internal control systems LO2.2.5: Explain the elements of internal control LO2.2.6: Discuss the evaluation of controls and control environment and communication of deficiencies to the management LO2.2.7: Explain the categories of control activities (internal controls) by using simple examples including Application and General IT Controls LO2.2.8: Differentiate between control activities relevant and irrelevant to audit in a well explained scenario LO2.2.9: Explain and identify the control weaknesses in the given scenario and suggest appropriate recommendations to remove these weaknesses LO2.2.10: Discuss and explain the limitations of internal control system LO2.2.11: Discuss and explain the risks in specialized IT systems LO2.2.12: Explain the different methods of recording internal control systems. 3 Audit materiality (ISA 320) 2 LO2.3.1: Explain the concepts of materiality and performance materiality using simple examples. 4 Audit evidence (ISA 500) 2 LO2.4.1: Explain, using examples, sufficient appropriate audit evidence LO2.4.2: Discuss the general principles assisting the auditor in assessing the relevance and reliability of audit evidence SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 67 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO2.4.3: Discuss audit procedures to obtain audit evidence including types of audit procedures LO2.4.4: Discuss the course of action available to auditor in case sufficient appropriate audit evidence is not obtained LO2.4.5: Explain the financial statement assertions including Assertions about class of transactions, account balances and presentation and disclosure LO2.4.6: Explain what information can be used as audit evidence. 5 Audit sampling (ISA 530) 2 LO2.5.1: Explain audit sampling, statistical sampling and sampling and non-sampling risk using simple examples LO2.5.2: Discuss the relationship between sampling and audit risk model LO2.5.3: Explain what matters are considered by auditors in respect of sample design, size and selection of items for testing using simple examples including sample selection method LO2.5.4: Discuss the concept of misstatement and rate of deviation including expected and tolerated LO2.5.5: State the audit procedures to be performed on selected sample LO2.5.6: Discuss the concept of Projecting misstatement and evaluating the results of audit sampling. 6 Substantive procedures (ISA 330) 2 LO2.6.1: Understand the financial statement assertions LO2.6.2: Identify the financial statement assertions in simple scenarios LO2.6.3: Discuss the use of computer software in substantive testing, auditing around the computer and directional testing LO2.6.4: Discuss the methods of obtaining audit evidence for substantive testing LO2.6.5: Explain the nature, extent and timing of substantive procedures for different items of financial statements. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 68 Syllabus Ref 7 Contents Tests of controls (ISA 330) Level 2 Learning Outcome LO2.7.1: Explain the nature, extent and timing of test of controls using simple examples LO2.7.2: Explain the concept of Computer Assisted Audit Techniques LO2.7.3: Explain how auditors evaluate the operating effectiveness of controls using simple examples LO2.7.4: Explain the controls over major transaction cycles including related risks, weaknesses control objectives and designing appropriate tests of controls. 8 Analytical procedures (ISA 520) 2 LO2.8.1: Explain the nature and purpose of substantive analytical procedures using simple examples LO2.8.2: State the purpose of analytical procedures performed near the end of the audit LO2.8.3: Applying analytical procedures through calculations of different ratios for different items of financial statements. 9 Documentation (ISA 230) 2 LO2.9.1: Explain the nature and purpose of audit documentation LO2.9.2: Describe the form, content and extent of audit documentation using simple examples LO2.9.3: Discuss the use of computer based audit working papers LO2.9.4: Discuss the ownership, custody and confidentiality of audit working papers LO2.9.5: Understand the nature of assembly of the final audit file. 10 Audit opinion and form of audit report under International Standards on Auditing and under the Companies Ordinance 1984 2 LO2.10.1: Understand modified and unmodified audit opinion LO2.10.2: Explain qualified opinion, disclaimer of opinion and adverse opinion LO2.10.3: Explain emphasis of matter and other matter in the auditor’s report LO2.10.4: Discuss the modification of audit opinion and audit report in different situations LO2.10.5: Briefly state the contents of the auditor’s report under International Standards on Auditing and under the Companies Ordinance 1984 SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 69 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO2.1.0.6: Explain the differences between auditor’s report under International Standards on Auditing and under the Companies Ordinance 1984 LO2.10.7: State the penalty for noncompliance with provisions related to the audit report. C Specific areas 1 External confirmations (ISA 505) 2 LO3.1.1: Describe the significance of using external confirmation procedures for obtaining relevant and reliable audit evidence LO3.1.2: Describe the steps involved in external confirmation procedures LO3.1.3: Differentiate between the positive confirmation request and negative confirmation request, including their appropriateness in different situations LO3.1.4: Discuss the conditions of sending negative confirmations LO3.1.5: Discuss the auditor’s course of action if management refuses to allow auditor to send confirmation. 2 Subsequent events (ISA 560) 2 LO3.2.1: Explain subsequent events and its relevance with the following critical dates • Date of the financial statements • Date of approval of the financial statements • Date of the auditor’s report • Date the financial statements are issued LO3.2.2: Explain the subsequent events review procedure LO3.2.3: Discuss the classification of subsequent events into adjusting and non adjusting events LO3.2.4: Describe the auditor’s responsibility in respect of following situations • SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 Events occurring between the date of the financial statements and the date of the auditor’s report 70 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome • Facts which become known to the auditor after the date of the auditor’s report but before the date the financial statements are issued • Facts which become known to the auditor after the financial statements have been issued LO3.2.5: Identify the subsequent events and explain the auditor’s responses. 3 Written representation (ISA 580) 2 LO3.3.1: Discuss the nature of written representations as audit evidence LO3.3.2: Discuss the circumstances where written representations are necessary and the matters on which representations are commonly obtained LO3.3.3: Discuss the form and content of written representations LO3.3.4: Discuss the auditor’s course of action if management refuses to provide requested written representation. 4 Consideration of related parties (ISA 550) 2 LO3.4.1: Describe the term related party using simple examples LO3.4.2: Discuss how related party transactions can give rise to the risk of material misstatement using simple examples LO3.4.3: describe the audit procedures including risk assessment procedures and related activities to obtain information relevant to identifying the related party relationships and transactions including responses to the assessed risk of material misstatement. 5 Using the work of component auditors, internal audits and auditor’s experts (ISA 600, ISA 610 and ISA 620) 2 LO3.5.1: Explain the responsibility of the group engagement partner in respect of acceptance and continuance, overall audit strategy, understanding the group, its components and their environment, their auditor and materiality LO3.5.2: Discuss the planning and controlling of a group audit, working and communication with the component auditor and involvement of the group auditor in the work performed by component auditor LO3.5.3: Explain the relationship between the external auditor with internal auditors and auditor’s experts SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 71 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO3.5.4: Explain the internal audit function including internal audit activities LO3.5.5: Discuss the factors determining the independence of internal auditors and weaknesses and limitations of internal audit LO3.5.6: Discuss how external auditors determine whether and to what extent they use the work of internal audit LO3.5.7: Discuss using examples how external auditors uses the specific work of internal audit LO3.5.8: Discuss how the auditor assesses the work of an expert LO3.5.9: Discuss how the external auditor uses the work of an auditor’s expert when that work is used to assist in obtaining sufficient appropriate audit evidence. 6 Engagement to review financial statements 2400 2 LO3.6.1: Explain the objective of a review engagement of financial statements and how it differs from an audit LO3.6.2: State the terms of engagement which may be included in the engagement letter LO3.6.3: Describe the procedures generally adopted by the practitioner to obtain evidence in review engagements LO3.6.3: Discuss and explain the report issued under engagement to review financial statements. D Computer programming and IT controls 1 Benefits and limitations of flowcharts 1 LO4.1.1: State the benefits and limitations of flowcharts using simple examples. 2 Types of flowcharts 1 LO4.2.1: Classify and distinguish between types of flowcharts, namely, linear, deployment and opportunity flowcharts LO4.2.2: Describe the macro, mini and micro level details of flowcharts. 3 Drawing flowcharts for specific situations/ programs 2 LO4.3.1: Draw different types of flowcharts for given situations. 4 Control design 2 LO4.4.1: Describe appropriate controls while designing the system using simple examples. SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 72 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome 5 General controls 2 LO4.5.1: Describe general controls and classify them into environment, development, maintenance and operational controls using simple examples. 6 Preventative, detective and corrective controls 2 LO4.6.1: Describe preventative, detective and corrective controls using simple examples. 7 Audit trails 2 LO4.7.1: Describe the concept of an audit trail in a computerized environment using simple examples. 8 Logical access controls 2 LO4.8.1: Describe logical access controls for a given situation/system. 9 Physical access controls 2 LO4.9.1: Describe physical access controls for a given situation/system. 10 Program security techniques 2 LO4.10.1: Describe checks/controls into the software system to protect data from corruption and unauthorized access. 11 Data security and public networks 2 LO4.11.1: State controls over data transmission LO4.11.2: Describe data encryption techniques for transmission of data over public networks LO4.11.3: Describe communications protocol LO4.11.4: Understand the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. 12 E Monitoring and surveillance techniques 2 LO4.12.1: Describe the usefulness of system logs for analyzing a system’s performance. 2 LO5.1.1: Describe with simple examples the fundamental principles of professional ethics of integrity, objectivity, professional competence and due care, confidentiality and professional behavior Professional Ethics 1 Fundamental principles (sections 100 to 150 of the Code of Ethics for Chartered Accountants) LO5.1.2: Apply the conceptual framework to identify, evaluate and address threats to compliance with fundamental principles LO5.1.3: Understand the threats and circumstances that cause threats of selfinterest, self-review, advocacy, familiarity, and intimidation SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 73 Syllabus Ref Contents Level Learning Outcome LO5.1.4: Discuss the safeguards to offset the threats to compliance with the fundamental principles LO5.1.5: Discuss the concept of ethical conflict resolution. 2 Client and engagement acceptance (section 210 of the Code of Ethics for Chartered Accountants) 2 LO5.2.1: Explain the advertisement and publicity guidelines of ICAP’s Code of Ethics for obtaining the audit work LO5.2.2: Apply the conceptual framework to identify, evaluate and address threats in case of Fees, Referral Fees and Tendering for audit work. LO5.2.3: Explain using simple examples the matters to be considered and the procedures that an audit firm/ professional accountant should carry out in the following circumstances: • Client acceptance • Engagement acceptance • Changes in a professional appointment (including Additional work, Mid-Term Removal and Non reappointment) SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 74 PCSC – 01 PRESENTATION AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS COURSE - I 50 Hours Course to be completed in any RAET or recognized institutes Learning outcomes of the Course S. No. 1 Skills Weighting Intellectual Demonstrate openness and objectivity in giving and receiving feedback. 2 3 10 Interpersonal and Communication Present information in written and numeric form clearly. Depict awareness of clear communication. 60 Demonstrate listening skills and understands given instructions. 10 Professional skepticism and professional judgment Probe and questions the relevant facts. 20 Total 100 Methodology Method Numbers Hours Classroom lectures and practice 5 10 Formal presentations before a group: • Attended • Presented • Facilitator’s feedback on presentations 12 6 2 24 3 5 Group Discussion on pre-seen and well prepared topics 4 8 50 SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 75 PCSC-02 PRESENTATION AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS COURSE - II 50 Hours Course to be completed in any RAET or recognized university Learning outcomes of the Course S. No. 1 2 3 4 Skills Weighting Intellectual Demonstrate openness and objectivity in giving and receiving feedback. 5 Apply reasoning, criticalanalysis and innovative thinking and recommend solutions to problems. 5 Interpersonal and Communication Present information in written and numeric form clearly. Depicts awareness of clear communication. 50 Demonstrate listening skills and understands given instructions. 10 Apply consultative skills to minimize or resolve conflict and solve problems. 5 Present ideas and influence others to provide support and commitment. 5 Professional skepticism and professional judgment Probe and questions the relevant facts. 5 Identify and evaluate reasonable alternatives to reach well-reasoned conclusions based on all relevant facts and circumstances. 5 Ethical principles Apply the fundamental ethical principles, namely, integrity, objectivity, professional competence and due care, confidentiality and professional behavior to respond to ethical dilemmas. 10 Total 100 Methodology Minimum Numbers Minimum Hours Classroom lectures and practice 6 12 Formal presentations before a group: • Attended • Presented • Facilitator’s feedback on presentations 12 8 2 24 4 5 Group Discussion on pre-seen and well prepared topics 2 5 Method 50 SYLLABUS AUTUMN - 2015 76