Case Study 1 - Sudden Pressure Release
advertisement
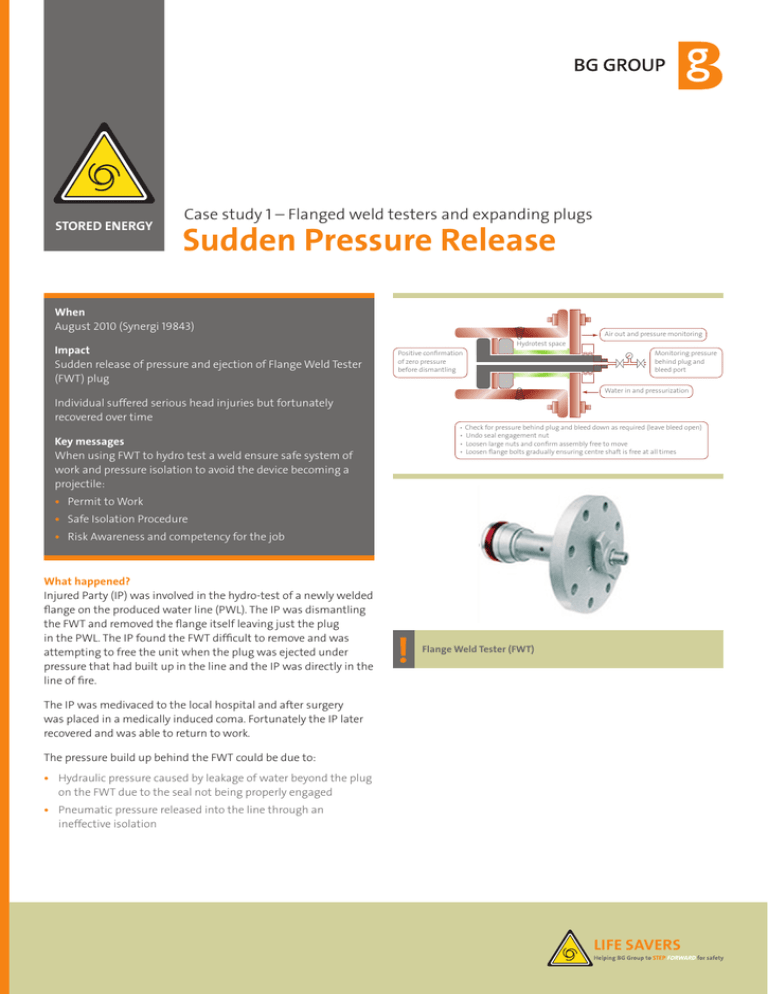
STORED ENERGY Case study 1 – Flanged weld testers and expanding plugs Sudden Pressure Release When August 2010 (Synergi 19843) Impact Sudden release of pressure and ejection of Flange Weld Tester (FWT) plug Air out and pressure monitoring Hydrotest space Positive confirmation of zero pressure before dismantling Monitoring pressure behind plug and bleed port Water in and pressurization Individual suffered serious head injuries but fortunately recovered over time • Check for pressure behind plug and bleed down as required (leave bleed open) • Undo seal engagement nut • Loosen large nuts and confirm assembly free to move • Loosen flange bolts gradually ensuring centre shaft is free at all times Key messages When using FWT to hydro test a weld ensure safe system of work and pressure isolation to avoid the device becoming a projectile: • Permit to Work • Safe Isolation Procedure • Risk Awareness and competency for the job What happened? Injured Party (IP) was involved in the hydro-test of a newly welded flange on the produced water line (PWL). The IP was dismantling the FWT and removed the flange itself leaving just the plug in the PWL. The IP found the FWT difficult to remove and was attempting to free the unit when the plug was ejected under pressure that had built up in the line and the IP was directly in the line of fire. ! Flange Weld Tester (FWT) The IP was medivaced to the local hospital and after surgery was placed in a medically induced coma. Fortunately the IP later recovered and was able to return to work. The pressure build up behind the FWT could be due to: • Hydraulic pressure caused by leakage of water beyond the plug on the FWT due to the seal not being properly engaged • Pneumatic pressure released into the line through an ineffective isolation LIFE SAVERS STORED ENERGY Case study 1 – Flanged weld testers and expanding plugs Sudden Pressure Release Problems The following issues were identified as root causes of the incident: As a result of this incident the following items were highlighted: • No Permit to Work • Use competent people familiar with the risk • Lack of awareness that pressure could build up behind the plug • Risk assessment with toolbox talk • No means to monitor the pressure behind the plug seal • Follow operating procedures • Risk Assessment and Standard Operating procedures not followed • A means to monitor the pressure behind the FWT is required • Permit to Work must be adhered to with procedures for Safe Isolation and Reinstatement Learning points Flanged weld testers and expanding plugs are used for hydrotesting of new welds or for creating temporary isolation while welding takes place. These devices can become a projectile and cause serious injury with only limited pressure due to: • Pressure from the test area passing the seal • Passing isolations upstream of the tester • Change in isolation status during the use of the flange tester • Head of liquid from hydro-test fluid, passing isolations on liquid systems or gradual draining of liquids within the line • Thermal expansion, especially when liquids are in the line For more information on Stored Energy safety: • Group Subject Matter Expert on Stored Energy – Paul Dows (Paul.dows@bg-group.com) ! • BG Life Savers Portal pages and Step Forward website • BG Group Standard BGA-OPS-OS-0019 Application of Process Isolations • BG Group Standard BG-ST-OPS-OPS-022 Permit to Work System Requirements • BG Group Standard BG-ST-ENG-PROC-002 Safe Plant and Equipment Isolation • Safety Moments on Jive LIFE SAVERS