Exponential Graphs
advertisement

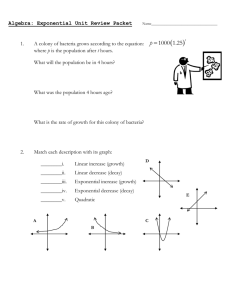
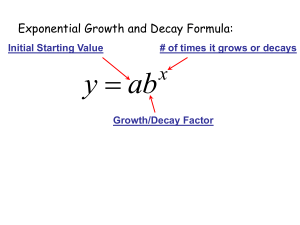
Overview Exponential Graphs This presentation will include: I Exponential equations; I The Learning Centre 1 Exponential equations Exponential equations: Growth Your graph should look something like the one below. Let us look at the number of ancestors a person has. Grandparent Grandparent 6 2 y Grandparent 6 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 Grandparent 6 6 ? ? Parent Parent 6 6 y = 2x ? x You 1 We could continue this indefinitely, but let us instead look at this information in a table. Generations back (x) Number of ancestors (y) 0 1 1 2 2 4 3 8 4 16 5 32 6 64 7 128 8 256 3 2 3 4 I The equation to this curve is y = 2x . We call this type of graph an exponential growth curve and often use it in population growth studies. I The name refers to the position of the x in the exponent of the equation. I As the number of generations back (x) increases, the number of ancestors (y) becomes greater and greater. The curve grows steeper and steeper. 4 Exponential growth graph: Another example Exponential equations: Decay y 25 y = ex 20 I Consider the equation to the curve y = 2−x I We call this type of graph an exponential decay curve. I This time as x takes on more positive values, the curve comes closer and closer to the x-axis but never touches it. I Exponential decay curves occur in such areas as science when we talk about radio active decay and in business when we talk about depreciation. 15 10 5 y-intercept (0, 1) x −3 −2 −1 1 2 3 4 5 Exponential decay Graph y 10 8 6 4 y-intercept (0, 1) 2 y = 2−x x −3 −2 −1 1 2 3 4 7 6