Q.1 (A) Draw neat line diagram of a high pressure boiler in which
advertisement

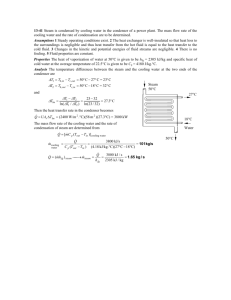
Enrollment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Dr. JIVRAJ MEHTA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MOJAR, ANAND. B.E. 5th Semester Mechanical Engineering MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION Date/Day : 05/09/2012, Wednesday Sub Code : 151904 Time : 10:30am to 12:00noon Instructions: 1) All questions are compulsory. Branch : Mechanical Engineering Subject Name : POWER PLANT ENGINEERING Max. Marks : 30 2) Figures to the right indicate full marks. 3) Use of steam table is permissible. 4) Indicate clearly, the options you attempt along with its respective question number. Q.1 (A) (B) Q.2 (A) (B) Q.3 (A) (B) Draw neat line diagram of a high pressure boiler in which stem is generated by mixing the superheated steam with feed water. Discuss relative merits & demerits. Convection & radiant superheaters have opposite characteristics of temperature v/s load – Explain. 05 Draw a neat named general layout of modern thermal power plant. Explain four main circuits. Name factors to be considered for selection of site for thermal power station. A boiler uses 1000 kg of coal/ h. The temperature of hot gases inside the chimney is 650 K and the outside air temperature is 300 K. The draught produced by the chimney of 25 m height is 15 mm of water. Determine the air supplied per kg of fuel burnt , draught in terms of hot gases, mass flow rate of hot gases and area of the chimney required if the co-efficient of velocity is 0.4 OR A 40 m high chimney is discharging flue gases at 350 °C, when the ambient temperature is 30 °C. The quantity of air supplied is 18Kg/Kg of fuel burnt. Determine: (i) Draught produced in mm of water (ii) Equivalent draught in m of hot-gas column (iii) Efficiency of chimney if minimum temperature of artifical draught is 150 °C mean specific heat of flue gases is 1.005K J/Kg K, (iv) Percentage of heat spent in natural draught system if Calorific value of fuel supplied is 30600K J/Kg (v) Temperature of chimney gases for maximum discharge in given time and what will be corresponding draught in mm of water produced. 05 1) Why is draught necessary in a boiler? Compare the natural draught and artificial draught. 2) Derive an expression for chimney height in order to obtain a draught of ‘h’ mm of water column if the boiler used ‘m’ kg of air / kg of fuel. Assume, surrounding air temperature as ‘T1’ and flue gas temperature as ‘T2’ in degree absolute. A steam turbine of 20 MW capacity requires 5 kg of steam per hour per kW. The quantity of air leakage into the condenser is 1 kg per 1000 kg of steam used by turbine. The vacuum in the condenser is 70 cm of Hg when the barometer reads 76 cm of Hg. The temperature at the suction of the air pump is 300C. The surface condenser used is fitted with a separate condensate pump and air pump. Find: (a) The capacity of the air pump requires per minute. (b) Vacuum efficiency (c) Condenser efficiency (d) The mass of water vapor carried by air in kg/hr. (e) The quantity of cooling water required per minute in tons if the rise in temperature of water is limited to 80C. The quantity of steam entering the condenser is 0.9 dry and there is no under cooling in the condenser. Assume inlet temperature of water as 20°C. Properties of steam at 300C : Absolute Pressure = 0.04325 bar, Enthalpy of liquid hf = 125.8 kJ/kg, Enthalpy of evaporation hfg = 2438.1 kJ/kg, Specific volume = 32.8 m3/kg 05 05 05 05 OR Q.3 (A) (B) 1) Why cooling towers used in a thermal power plant? Discuss the working of a natural cooling tower. 2) Explain following terms pertaining to cooling tower: Drift, Fill, Approach and Range of cooling tower The air leakage into a surface condenser operating with a steam turbine is estimated 84kg/hr. the vacuum near the inlet of air pump is 70mm of Hg when barometer reads 76mm of Hg. The temperature at the inlet of vacuum pump is 20 °C Calculate: (i) Minimum capacity of pump in cu-meters per hour (ii) Dimensions of reciprocating air pump to remove air if it runs at 200rpm (iii) L:D=3:2 and volumetric efficiency=80% (iv) Mass of vapour extracted per minute with air 05 05 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Dr. JIVRAJ MEHTA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MOJAR, ANAND. B.E. 5th Semester Mechanical Engineering RESPONSE OF MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION Date/Day : 05/09/2012, Wednesday Sub Code : 151904 Time : 10:30am to 12:00noon Q.1 (A) (B) Q.2 (A) (B) Branch : Mechanical Engineering Subject Name : POWER PLANT ENGINEERING Max. Marks : 30 Draw neat line diagram of a high pressure boiler in which stem is generated by mixing the superheated steam with feed water. Discuss relative merits & demerits. Convection & radiant superheaters have opposite characteristics of temperature v/s load – Explain. 05 Draw a neat named general layout of modern thermal power plant. Explain four main circuits. Name factors to be considered for selection of site for thermal power station. A boiler uses 1000 kg of coal/ h. The temperature of hot gases inside the chimney is 650 K and the outside air temperature is 300 K. The draught produced by the chimney of 25 m height is 15 mm of water. Determine the air supplied per kg of fuel burnt , draught in terms of hot gases, mass flow rate of hot gases and area of the chimney required if the co-efficient of velocity is 0.4 05 05 05 OR A 40 m high chimney is discharging flue gases at 350 °C, when the ambient temperature is 30 °C. The quantity of air supplied is 18Kg/Kg of fuel burnt. Determine: (i) Draught produced in mm of water (ii) Equivalent draught in m of hot-gas column (iii) Efficiency of chimney if minimum temperature of artifical draught is 150 °C mean specific heat of flue gases is 1.005K J/Kg K, (iv) Percentage of heat spent in natural draught system if Calorific value of fuel supplied is 30600K J/Kg (v) Temperature of chimney gases for maximum discharge in given time and what will be corresponding draught in mm of water produced. hw = 23.30 mm of water Q.3 (A) (B) 3) Why is draught necessary in a boiler? Compare the natural draught and artificial draught. 4) Derive an expression for chimney height in order to obtain a draught of ‘h’ mm of water column if the boiler used ‘m’ kg of air / kg of fuel. Assume, surrounding air temperature as ‘T1’ and flue gas temperature as ‘T2’ in degree absolute. A steam turbine of 20 MW capacity requires 5 kg of steam per hour per kW. The quantity of air leakage into the condenser is 1 kg per 1000 kg of steam used by turbine. The vacuum in the condenser is 70 cm of Hg when the barometer reads 76 cm of Hg. The temperature at the suction of the air pump is 300C. The surface condenser used is fitted with a separate condensate pump and air pump. Find: (a) The capacity of the air pump requires per minute. (b) Vacuum efficiency (c) Condenser efficiency (d) The mass of water vapor carried by air in kg/hr. (e) The quantity of cooling water required per minute in tons if the rise in temperature of water is limited to 80C. The quantity of steam entering the condenser is 0.9 dry and there is no under cooling in the condenser. Assume inlet temperature of water as 20°C. Properties of steam at 300C : Absolute Pressure = 0.04325 bar, Enthalpy of liquid hf = 125.8 kJ/kg, Enthalpy of evaporation hfg = 2438.1 kJ/kg, Specific volume = 32.8 m3/kg 05 05 OR Q.3 (A) (B) 3) Why cooling towers used in a thermal power plant? Discuss the working of a natural cooling tower. 4) Explain following terms pertaining to cooling tower: Drift, Fill, Approach and Range of cooling tower The air leakage into a surface condenser operating with a steam turbine is estimated 84kg/hr. the vacuum near the inlet of air pump is 70mm of Hg when barometer reads 76mm of Hg. The temperature at the inlet of vacuum pump is 20 °C Calculate: (i) Minimum capacity of pump in cu-meters per hour (ii) Dimensions of reciprocating air pump to remove air if it runs at 200rpm (iii) L:D=3:2 and volumetric efficiency=80% (iv) Mass of vapour extracted per minute with air 05 05 mw = 21.59 kg/hr = 0.359 kg/min