FusionCompute
V100R003C10
Quick User Guide
Issue: 02
Date: 2014-06-30
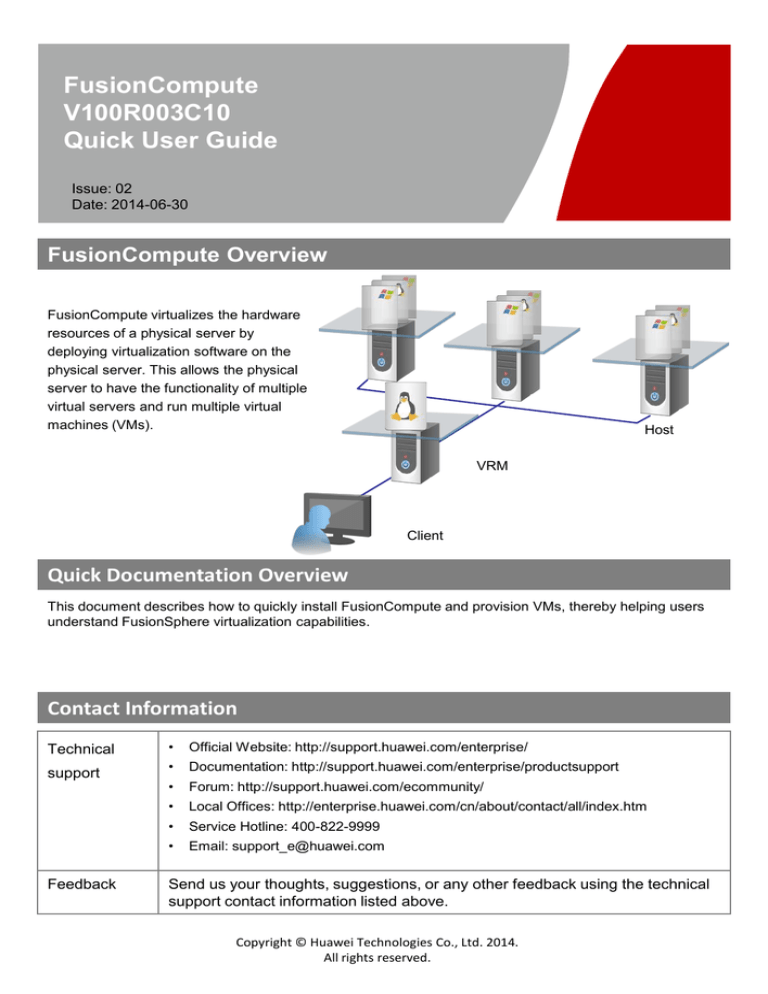
FusionCompute Overview
FusionCompute virtualizes the hardware
resources of a physical server by
deploying virtualization software on the
physical server. This allows the physical
server to have the functionality of multiple
virtual servers and run multiple virtual
machines (VMs).
Host
VRM
Client
Quick Documentation Overview
This document describes how to quickly install FusionCompute and provision VMs, thereby helping users
understand FusionSphere virtualization capabilities.
Contact Information
Technical
support
Feedback
•
Official Website: http://support.huawei.com/enterprise/
•
Documentation: http://support.huawei.com/enterprise/productsupport
•
Forum: http://support.huawei.com/ecommunity/
•
Local Offices: http://enterprise.huawei.com/cn/about/contact/all/index.htm
•
Service Hotline: 400-822-9999
•
Email: support_e@huawei.com
Send us your thoughts, suggestions, or any other feedback using the technical
support contact information listed above.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2014.
All rights reserved.
1 Introduction
Component
Description
Server
A physical server. After the virtualization software is installed on a server, the server
functions as a host in the FusionCompute system, providing virtualized computing
resources, including virtual CPUs (VCPUs), memory, and network ports.
Storage device
Connects to a host through network devices, provides virtual storage resources to VMs.
Local disks on servers function as storage devices only in the FusionCompute
Foundation Edition.
FusionCompute
A component of the virtualization software. FusionCompute consists of two hosts and the
virtualization resource management module, that is, active and standby virtualization
resource management (VRM) VMs. FusionCompute virtualizes physical resources and
creates and manages VMs.
2 FusionCompute Installation Preparations
Check installation conditions
Obtain software
Obtain data
Learn
installation process
Learn
installation
process
Prerequisites
You have obtained the integration design plan.
All hardware has been installed and is working properly.
You have configured network and storage devices based on the design plan.
Servers used in the FusionCompute system must meet the following requirements.
Item
Requirement
Hardware
Intel or AMD 64-bit CPU with virtualization function enabled
Memory ≥ 8 GB
Single disk space ≥ 360 GB
RAID
Use RAID 1 that consists of hard disks 1 and 2 to install an OS and software on the host,
thereby enhancing host reliability.
Boot device
The first boot device for the host is set to Hard disk.
The local PC used for FusionCompute installation must meet the following requirements.
Item
Requirement
Hardware
CPU: 32-bit; memory ≥ 2 GB
System disk free space ≥ 1 GB; User disk free space ≥ 30 GB
Operating system
(OS)
Network
Windows XP or Windows 7
The Windows firewall is disabled.
Communication between the local PC and the management and host BMC planes
is normal.
2
Check installation conditions
Obtain data
Obtain software
Obtain the following software files for FusionCompute installation.
Item
Software Package
FusionCompute host OS
installation
process
How to Obtain
FusionCompute
Visit http://support.huawei.com
V100R003C10SPC600_CNA.iso
and choose Enterprise > Software
FusionCompute installation
FusionCompute
wizard
V100R003C10SPC600_Tools.zip
VRM VM template file
Learn
Learn
installation process
> IT > FusionCloud >
FusionSphere > FusionCompute >
FusionCompute
V100R003C10SPC600
V100R003C10SPC600_VRM.zip
Remote access tool
PuTTY
Check installation conditions
Obtain software
Visit http://www.putty.org.
Obtain data
Learn installation process
Learn
Before installation, finish the integration design plan and obtain all the data required for
installing
installation
FusionCompute. The following figures show a sample networking plan. The table on the next page lists
process
sample data for this plan.
NOTE: If a parameter SN (such as A4) is mentioned in a procedure below, use the planned value for this parameter.
Type
Parameter
Example and Planned Value
(A1) IP address of the host BMC
Used to access the host BMC.
188.100.200.71
Planned value: _________________
(A2) Host BMC username and password
Used to log in to the host BMC.
Username: root Planned value: ____
Password: root
____
(A3) Host management plane ports
During host OS installation, set a management plane port for the eth0 and eth1
host. If multiple ports are deployed, bind a second port to the
Planned value: _________________
first port in the configuration phase.
A. Host
(A3) Host management plane port parameters
The parameters are required during host OS installation.
IP address: 188.100.200.21
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 188.100.200.1
Planned value: __________________
__________________
__________________
(A5) Host name
Used to identify the host.
Host01
Planned value: _________________
(A6) Password of user root
Used to log in to the host.
huawei_123
Planned value: _________________
(B1) IP address
Used to communicate with the host.
188.100.4.241
Planned value: _________________
information
(B2) User information
PC OS user account, which is required when you obtain the VRM
VM template file from the PC.
Username: administrator
Password: 123456
Planned value: _________________
_________________
C. VRM node
(C1) Management IP addresses
Management IP addresses of the active and standby VRMs.
Required during the VRM installation phase.
188.100.200.31 (active)/ 188.100.200.32
(standby)
Planned value:
_______________ / ______________
information
B. Local PC
information
3
Check installation conditions
Obtain software
Obtain data
Procedure
FusionCompute installation includes the installation of Host and VRM.
Learn
installation process
Learn
installation
process
In the following table, the left column describes the operation guidelines and the right column provides the
operation background, principles, and other descriptions. The configuration process includes the icons
pictured below. It is recommended to familiarize yourself with the meanings of the icons before proceeding.
Icon
Description
Example:
1
1
2
3
Operation sequence
2
Transition between different
sections of the interface
Skip to step
Step 1: Click VDC Management.
Step 2: Click Network Management.
4
Host Installation — ISO
Note: The screenshots in the steps below include sample parameter values, which may vary from the actual
parameter values onsite.
3 Install FusionCompute
3.1
Install
an OS on the Host
Host
Installation
—
ISO
Step 1: Mount an ISO File to the VM
1. Enable communication between the local PC and the host where FusionCompute is to be
installed.
Connect the PC and the host to
the same switch.
2. Open the web browser on the PC, then enter the BMC IP address into the address bar to
access the host BMC.
Huawei RH2285 is used as an
example host.
3. Log in to the BMC as an administrator.
The administrator account is
root.
4. Open the Remote Control window.
You may need to click Remote
Virtual Console (requiring JRE)
on the Remote Control page of
some Huawei server BMCs.
5. Mount an ISO image to the VM to install an OS on the VM.
3 Select FusionCompute
V100R003C10SPC600_CNA.iso.
1
When the ISO file is mounted
4
successfully,
Connect turns to
Disconnect.
4
2
3
Step 2: Load a Host OS Installation File
1. Restart the host after the ISO file is mounted.
When the host begins to
restart, press F11
3 repeatedly until the screen
for selecting boot device is
displayed.
NOTE
The host BIOS password
may be required during the
restart. Obtain the password
in advance.
1
2
5
Step 2: Load a Host OS Installation File
2. Set DVD-ROM as the boot device.
NOTE
The DVD-ROM name and the
configuration screen may vary
depending on the server used.
1
3. Select Install.
The host loading begins,
which takes about 2 minutes.
1
Step 3: Configure Host Information
1. Select Network, then select a management plane port, for example, eth0.
1
2
2. Configure the IP address and subnet mask for eth0 (A4).
TIP
When configuring host data on
the configuration screen:
Press Tab or the up and down
arrow keys to move the cursor.
Press Enter to expand or
execute the highlighted item.
Press the space bar to toggle
between options.
-
1
2
3
Use the
number pad
on the
keyboard to
enter numbers.
3. Configure the gateway for eth0 (A4) on the Network Configuration page.
1
2
6
-
Step 3: Configure Host Information
4. Select Hostname, then set the host name.
-
2
1
3
5. Select Timezone, then set the local time zone and time.
-
2
1
3
4
6. Select Password, then set the password for user root (A6).
Enter the password carefully.
2
1
3
NOTE
The password must contain at
least:
• Eight characters
• One space or one of the
following special characters: `
~!@#$%^&*()-_=+\|
[{}];:'",<.>/?
• At least two of the following:
lowercase letters, uppercase
letters, and numbers.
Step 4: Install an OS on the Host
1. Select OK in the bottom right corner of the screen, then select Yes in the displayed dialog
box to install the OS on the host.
1
2
2 Ensure that the OS is
installed on the default disk
partition.
3 Confirm the configuration,
then select Yes to install the OS.
The installation takes about 10
minutes.
After the installation is
complete, the host restarts.
3
7
3.2 Install the VRM
Step 1: Decompress the Software Packages
1. Decompress FusionCompute V100R003C10SPC600_Tools.zip onto the PC to obtain the
Installer, ModCNABFileTool, PlugIn, and ToDPS folders.
-
2. Decompress FusionCompute V100R003C10SPC600_VRM.zip into a new folder to obtain
two VRM VM template files whose file name extensions are .xml and .vhd, respectively.
Share the folder to the current PC user.
The path of this folder cannot
contain Chinese characters.
After sharing the folder, the
host can access to the VRM VM
template files.
Step 2: Check the System Environment
1. Run FusionCompute_EnvCheck.bat in the PlugIn folder to check whether the
PC has .Net 4.0 and JRE installed and whether the file sharing service is enabled. If
not, the system will install the plugins and configure the service. Check the output
information to confirm.
If "Press any key to continue..." is displayed, the check is complete and the PC
meets the requirements.
-
Step 3: Initialize the Installation Wizard
1. Run FusionComputeInstaller.exe in the Installer folder.
The installation wizard is
opened.
2. Select a language.
-
3. Select an installation mode.
The system begins to install
components, which takes about
30 seconds.
1
2
4. Click Next after the components are installed.
The Configure Host page is
displayed.
Step 4: Configure the Host
1. Configure the host where the active VRM VM is deployed, then click Next.
1 Enter the management IP
address you set during host
installation (A4).
2 Enter the password you set
during host installation (A6).
1
NOTE
If the message "The host is
unreachable" is displayed,
ensure that the IP address set in
is correct and can be pinged
1
from the local PC.
2
3
8
Step 5: Configure a Data Store
1.
Select Local disk/FC SAN, then click Next.
The storage devices are automatically refreshed, and the system adds the storage device
You are advised to use local
disks to install VRMs.
A VRM node requires 80 GB
space on the local disk.
in the first row as the data store by default.
If local disks are used, the active
and standby VRM nodes use
different disks, which provide
higher reliability.
You are advised to select disks
configured in RAID 1 mode to
enhance reliability.
The length of disks configured in
RAID 1 mode is twice as that of
common disks.
For details about VM storage
working principles, see Appendix
2.
You can click Add to add other data stores.
Step 6: Configure VRM VM Information
Select
1. Configure VRM VM template information.
1
FusionCompute_V100R003C10S
PC600_VRM.xml in the shared
folder.
Enter information about the
1
2
current
PC user (C2).
2
2. Set the management IP address of the VRM (D1).
-
3. Set VRM VM specifications.
You can set the specifications
based on the deployment
scale or customize the
specifications.
VM to the right of By
deployment scale refer to the
VM to be created; PM refers
to the host deployed.
4. Click Verify Configuration and click Next after the verification succeeds.
9
The configuration page for the
standby VRM is displayed.
Step 7: Configure the Rights Management Mode
-
1. Select a rights management mode as instructed.
Step 8: Install the VRMs
1. Click Next to start installation.
The installation takes about
50 minutes.
During VRM installation, you
can install OSs on other
hosts.
2. Click the link on the displayed page and log in to FusionCompute.
1
Common mode
FusionCompute Login:
Enter the VRM floating IP
address in the browser.
The default username and
passwords are shown in the
figure on the left.
2 Log in to FusionCompute as prompted.
3. Click Finish to finish the installation.
10
4. Using FusionCompute
4.1 FusionCompute Web Client Login
Internet Explorer (IE):
Go to Step 1: Configure IE
Firefox:
Go to Step 2: Configure Firefox
Step 1: Configure IE
1. In the address bar of the IE browser, enter http://Floating IP address of the VRM
-
node, press Enter, select Continue to this website (not recommended), and log in
to the FusionCompute Web Client.
For example, http://188.100.4.30/
2. Click Google Chrome Frame and follow the instructions to install the Google
Chrome Frame plugin.
Installing the Google Chrome
Frame plugin improves the
web page response speed.
3. Click Certificate Error in the top right corner of the browser, then click View
certificate.
After installing the certificate,
FusionCompute is
considered to be a safe site
and you can directly access
the login page.
1
2
4. Click Install Certificate. In the displayed dialog box, click Next.
-
5. Import the certificate as follows:
-
1
2
3
5
4
11
Step 1: Configure IE
6. Click Finish, then click Yes in the popup dialog box. A message is displayed
-
indicating that the import is complete.
7. Click OK to close the certificate dialog box.
-
8. Press Shift+Ctrl+Delete.
After deleting the browsing
history, restart the browser
for the configuration to take
effect.
9. Check the box to the left of the following items, then click Delete to delete the
browsing history:
• Preserve Favorites website data
• Temporary Internet files
• Cookies
• History
10. Close the browser, then reopen it.
11. Skip to Step 3: FusionCompute Web Client Login.
-
Step 2: Configure Firefox
1. In the address bar of the Firefox browser, enter http://Floating IP address of the
VRM node, press Enter, select Continue to this website (not recommended), and
log in to the FusionCompute Web Client.
After configuration, you can
directly access the
FusionCompute Web Client
login page.
For example, enter http://188.100.4.30/
2. Under I Understand the Risks, click Add Exception.
3. In the popup dialog box, check the box next to Permanently store this exception,
then click Confirm Security Exception.
Step 3: FusionCompute Web Client Login
1. Enter http://Floating IP address of the VRM node, then press Enter.
-
2. Log in as user admin.
-
12
4.2 Create a Bare VM
Step 1: Select a VM Location
-
1. Go to the Create VM page.
1
2
3
4
Right
-click
2. Select the location at which to create the VM.
A cluster is a group of hosts.
1
• If there are no specific requirements
for the location of a VM host, select
Cluster. The system will select a
suitable host in the cluster to create
the VM on.
2
After the VM is bound to a
host, the VM can only run on
this host and cannot be
migrated to another host.
• To deploy the VM on a specified host,
select Host. You can also check the
box next to Bind to Host to bind the
VM to the host.
3
Step 2: Configure the VM Attributes
1. Configure the VM attributes in the figure below based on the planned data. All
-
other VM attributes use the default configuration.
1
2
2. Click Next to go to the Set VM page.
-
13
Step 3: Configure VM Network Attributes
1. Select a VM NIC port group according to the VM network configuration
requirements of the customer.
1
A DVS is similar to a switch
used for communications on
the layer 2 network. The DVS
allows the VM to
communicate with the
physical network.
A port group is a logical port
of the VM. The port group is
used to define the mode the
VM NIC uses to connect to
the network.
2
For details, see Principles of
VM Network Access.
3
4
2. Repeat the above procedure to configure the port groups for other VM NICs.
Step 4: Configure VM Disk Attributes
1. Configure the VM attributes in the figure below based on the planned data.
1
4
5
6
7
2
2 The storage resource
pool associated with the host
is used as the data store.
The data store is used to
create VM disks.
For details, see Principles of
VM Storage Access.
4 For virtualized data
stores, VM disks can use the
following configuration
modes:
• Common: Distributes disk
space according to
capacity. Immediate disk
formatting.
• Thick provisioning lazy
zeroed: Distributes disk
space according to
capacity. Delayed
formatting. Above average
disk creation speed.
• Thin provisioning:
Distributes disk space
according to actual usage.
3
2. Repeat the above procedure to configure the attributes of other VM disks.
3. After configuring all disks, click Next. Confirm the configuration information, then
click Finish.
14
-
Step 5: Confirm VM Creation
1. Click Query Task. Enter the task center and check the progress of VM creation.
-
The creation time of a bare VM depends on the VM disk size and disk storage type.
The formatting process for thin provisioning disks is relatively slow, please wait a
moment.
4.3 Install an OS on the VM (Using a Windows VM as an Example)
Step 1: Log In to the VM Using VNC
1. Use Virtual Network Computing (VNC) to log in to the VM, as shown in the
following figure.
1
3
2
VNC login refers to the
process of using VNC
protocol to remotely access a
VM. VNC login allows you to
log in to the VM and locate
faults through the
management plane when the
VM network is unavailable.
4
5
2. Accept the operation risks in the prompt, then open the VNC window.
-
Click here for help with VNC login
Step 2: Install an OS on the VM
1. Mount the OS image from the CD/DVD-ROM drive to the VM.
If only the OS installation disc
is available, insert the disc
into the CD/DVD-ROM drive,
select CD/DVD-ROM, and
then specify the drive name.
1
2
3
4
5
6
2. Restart the VM, then follow the instructions below to install the OS on the VM.
CAUTION
-
Do not close the VNC window before the OS installation completes.
Otherwise, the CD/DVD-ROM drive is automatically unmounted from
the VM, which causes the installation to fail.
3. After the OS is installed, click
on the top of the VNC window, then select
Unmount CD/DVD-ROM Drive.
15
Do not close the VNC
window, as it is needed for
subsequent operations.
Step 3: Install Tools on the VM
1. On the VM Summary page, click Install Tools, then follow the procedure to
complete installation.
1
Tools contains the
paravirtualized (PV) driver for
the VM.
The PV driver improves I/O
processing, hardware
monitoring, and other highlevel functions on the VM.
Mounting Tools mounts a PV
driver to the VM.
2. Open the CD-ROM drive on the VM. Right-click Setup, select Run as
Administrator, and follow the procedure to complete installation.
-
3. Restart the VM according to the procedure for Tools to take effect.
VMs running Windows Server 2008 must be restarted twice.
-
Step 4: Initialize the User Disk
1. On the OS interface on the VM, click Start, right-click Computer, and click
Manage.
The user disk refers to a disk
drive other than the C drive.
If the VM does not have any
user disks, skip this step.
2. Initialize the user disk. (Windows 7 is used as an example below.)
3 Select the layout of disk
partitions according to the
user requirements.
1
2
3
4
3. Right-click the disk space that has not been distributed, select New Simple
Volume, and follow the procedure to complete volume creation.
16
-
Step 5: Install Applications
1. If the VM uses VLAN to access the network, configure an IP address for the VM.
This allows the VM to intercommunicate with external networks.
-
2. Install applications on the VM.
• If the application is an ISO file or on a disc, you must use the CD/DVD-ROM
mounting method to install the application.
• All other types of installation files must be copied onto the VM before
proceeding with installation.
Applications are installed on
the VM.
4.4 Create a VM Using a Template
Step 1: Convert the VM to a Template
1. On the FusionCompute Web Client, safely stop the VM.
Stop: Stops a VM by
stopping its OS. This mode
automatically saves data and
is highly secure. However, it
takes a long time for the VM
to stop in this mode.
Therefore, select this mode
when the VM is running
properly.
1
Forcibly stop: Only use this
mode when the VM is not
running properly.
2. After the VM stops, click Convert to Template, and follow the procedure to
-
complete template creation.
Step 2: Create a VM Using a Template
1. On the VM Summary page, click Deploy VM Using Template.
This starts the process of
creating a VM using a
template.
1
2. Select the location at which to create the VM.
A cluster is a group of hosts. Under
normal conditions:
1
• If there are no specific requirements for
the location of a VM host, select
Cluster. The system will select a
suitable host in the cluster to create the
VM on.
2
3
• If there are specific requirements for VM
deployment, select Host and check the
box next to Bind to Host to bind the
VM to the host.
17
After the VM is bound to a
host, the VM can only run on
this host and cannot be
migrated to another host.
Step 2: Create a VM Using a Template
3. Configure the VM name and hardware specifications based on the planned data,
then click Next.
1
Use the default values for all
other property configurations.
You cannot set the number of
disks or NICs when creating
a VM using a template. After
the VM is created, you can
add disks and NICs to it.
2
Step 3: Configure VM Network Attributes
1. Select a VM NIC port group according to the VM network configuration
requirements of the customer.
1
A DVS is similar to a switch
used for communications on
the layer 2 network. The DVS
allows the VM to
communicate with the
physical network.
A port group is a logical port
of the VM. The port group is
used to define the mode the
VM NIC uses to connect to
the network.
2
For details, see Principles of
VM Network Access.
3
4
2. Repeat the above procedure to configure the attributes of other VM NIC port
groups.
18
Step 4: Configure VM Disk Attributes
1. Configure the VM disk attributes in the figure below based on the planned data.
1
4
2 The storage resource
pool associated with the host
is used as the data store.
The data store is used to
create VM disks.
For details, see Principles of
VM Storage Access.
5
6
7
2
3
2. Repeat the above procedure to configure the attributes of other VM disks.
3. After configuring all disks, click Next. Confirm the configuration information, then
click Finish.
-
4. Click Query Task to enter the task center and check the progress of VM creation.
-
19
Appendix 1 Principles of VM Network Access
A virtual NIC of a VM communicates with an external network by connecting to the DVS through the port group,
then by connecting to the physical NIC of a host through the DVS uplink. These connections are shown in the
following figure.
Host 1
Host 2
VM
Port Group
DVS
Virtual
Resources
Uplink
Physical
Resources
Physical Network
Network
Element (NE)
Description
Port group
A port group is a virtual logical port similar to a template with network attributes. A port group is
used to define VM NIC attributes and uses a DVS to connect to the network:
• Subnet: FusionCompute automatically allocates an IP address in the subnet IP address pool
to each NIC on VMs that use the port group.
• VLAN: Users must manually assign IP addresses to VM NICs. VMs connect to the VLAN
defined by the port group.
DVS
A DVS is similar to a switch used for communications on the layer 2 network. A DVS links the
port group to the VM and connects to the physical network through the uplink.
Uplink
An uplink connects the DVS to the physical network. An uplink is used for VM upstream data
transmission.
Appendix 2 Principles of VM Storage Access
A data store is a logical storage unit
on FusionCompute. A data store is
used to universally define all types
of storage resources.
You can create a virtual disk on a
data store for use by a VM.
Host Local
Disk
VM
LUN
Virtual
Disk
IP SAN Storage
Data Store
Host
20
Shared Storage




