METHODOLOGY FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF
advertisement

1
METHODOLOGY FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
SYSTEMS
Ricardo Chalmetaa (Corresponding author), Reyes Grangel a
a
Grupo de Investigación en Integración y Re-Ingeniería de Sistemas (IRIS).
Universitat Jaume I. 12071 Castelló. Spain.
Tel:+ 34 964 728329 Fax: + 34 964 728435
{rchalmet, grangel}@uji.es
2
PHASES
ACTIVITIES
TECHNIQUES
EXPECTED RESULTS
COMPUTER SUPPORT
TOOLS
PHASE I.
Identification
• Identify the conceptual blocks of
knowledge
• Classify into ontological categories
• Define the target knowledge (knowledge
requirements)
• Templates and
questionnaires to identify
blocks of knowledge
• Reference models
concerning the target
knowledge
• Conceptual blocks of
knowledge
• Target knowledge
• Categories
• Office automation tools
• Modelling tools
PHASE II.
Extraction
• Extract knowledge from sources in order
to define the input variables and categorise
it
• Define the extraction and calculation
procedures
• Templates to define the
input variables
• Reference models for
extracting and calculating
target knowledge
• Set of input variables
• Extraction and calculation
procedures
• Office automation tools
• Modelling tools
PHASE III.
Representation
• Establish the relations within the target
knowledge
• Draw up the knowledge map
• Metamodelling (UML)
• Ontologies
• Conceptual maps
• Model of the Knowledge
map
• Modelling tools
• Ontology engineering
tools
PHASE IV.
Processing
• Develop the technological infrastructure
supporting the knowledge map by following
an object-oriented methodology for the
development of computer systems
• BPM techniques
• ETL techniques
•Document/DBMS
• Data warehouse
• OLAP
• Data mining
• Knowledge portal
(Executable knowledge
map)
• BPM tools
• ETL tools
• Document/DBMS
• Data warehouse
• OLAP
• Data mining
PHASE V.
Utilisation
• Establish training and continuous
improvement mechanisms among the
members of the organisation
• Carry out maintenance and the feedback
process on the knowledge management
system
• e-Learning
• Groupware
• TQM
• ISO standard of quality
• Efficient use of knowledge
within the organisation
• Office automation tools
• Modelling tools
• Learning tools
Fig. 1. KM-IRIS Methodology for knowledge management in an organisation.
3
Generate
DATA
Processed
Distributes
INFORMATION
KMS
(ICT)
Supports
Systematises (collects,
codifies, stores)
Create new
KNOWLEDGE
Is used
To carry out
activities
To make
decisions
Fig. 2. KMS relation with information and knowledge.
Transforms
knowledge
into
information
Knowledge Sources
4
Explicit Knowledge Sources
Tacit Knowledge Sources
Input Variables
Explicit Input Variables
Process
Documents
Tacit Input Variables
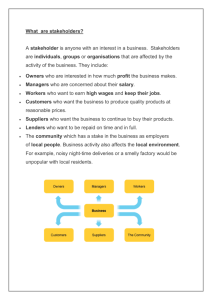
Owners
Employees
input
Extraction and
Calculation
Procedure
Knowledge that
organisations
want to
“manage”
output
TARGET
KNOWLEDGE
Conceptual Block
of Knowledge
‘OWNER’
Fig. 3. Phase II of the KM-IRIS Methodology for knowledge management.
5
Conceptual blocks of knowledge
PHASE I.
Identification
Owners
Suppliers &
customers
Administration
& trade union
Employee
Business
district
Organisation
Product/
Service
Process
Resource
Organisational
Structure
Decisional
Structure Roles
Composition/
Structure
Range of products
Design
Brand
Map of processes
Best practices
Workflow
Materials planning
Availabilities
Employees
Customers
Suppliers ...
Employees
Owners
Customers ...
Target knowledge
Vision
Mission
Strategy
Objectives & Policies
Unification
Values
Skills
Experience
Competencies
Work climate
Contacts
Values
Regulations
Procedures
Sustainability
Indicators RSC
Policy & RSC
Rights
Learning
District Know-How
District Culture
Traditional Skill
Code of Conduct
Sources of knowledge
Owners
Employees
Administrations
Supplier & Customer Employees & Know-How
Employees &
Customer & Supplier
Competitors
Owners & Trade Unions
Administrations
Trade Unions
Web
Competitors
Associations
Employees & Owners
Business District
Owners
Employees
Trade Unions
Employees
Customers
Suppliers ...
Document/databases & DKW/DMN/Business Intelligence/e-Business Information Systems
Tacit
PHASE II.
Extraction
Chance of
collaboration
Degree of
satisfaction
Values
Explicit
Tacit & Explicit Input Variables
Extraction and calculation procedure
PHASE IV.
Processing
PHASE V.
Utilisation
Production of
the Enterprise
KMS
Conceptual Maps
of the Tacit/Explicit
Knowledge
Identified/Captured
Ontologies
Organisation
Structuring
Technological Model & Architecture
of the knowledge management system
(KNOWLEDGE PORTAL)
STRATEGIC
Model of Development
& Implementation
CIM
Model of the knowledge map at the CIM level
PIM
Model of the knowledge map at the PIM level
PSM
CODE
Knowledge portal
(Executable knowledge map)
Management System & Knowledge Portal
Owners & Executives Responsible for Managing the Enterprise, Chief Executive Officers and/or Authorised
Employees & Professionals Collaborating with the Enterprise/ Private
Staff
Collaborations
Authorised Customers & Suppliers/
Administration & Trade Unions, with restricted access rights (increase in business trust)
Management & Strategic Planning
of Training
Fig. 4. Specialised version of the KM-IRIS Methodology for knowledge management in an enterprise.
Cont. Improvement
Property Rights
& Involvement
KMS Maintenance
Bridges
Close Management
Cycle
PHASE III.
Representation
MDA Approach
TARGET
KNOWLEDGE
6
ENTERPRISE
ONTOLOGY
According to the conceptual
blocks of knowledge and
the target knowledge that
are identified
Business
view
Organisational
view
Representation of the
enterprise concepts
at a high level
Generation of
views
Product
view
Process
view
According to the
enterprise ontology that
is defined
Resource
view
...
Knowledge
Facts
Rules
Attitudes
Graphic
model
Modelling of
enterprise
knowledge
Fig. 5. Conceptual diagram for obtaining the map of enterprise knowledge at the CIM level.
7
Fig. 6. Technological infrastructure proposed to support a knowledge portal.